Method of pooling samples for performing a bi0l0gical assay
A sample, in-sample technique, applied in the field of measurement with classification results, to achieve the effect of reducing the cost of analysis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0096] Example of genotyping a sample of diploid individuals for the presence of a SNP using a normalized pool of 50 individuals
[0097] Step 1) Test 50 individuals individually
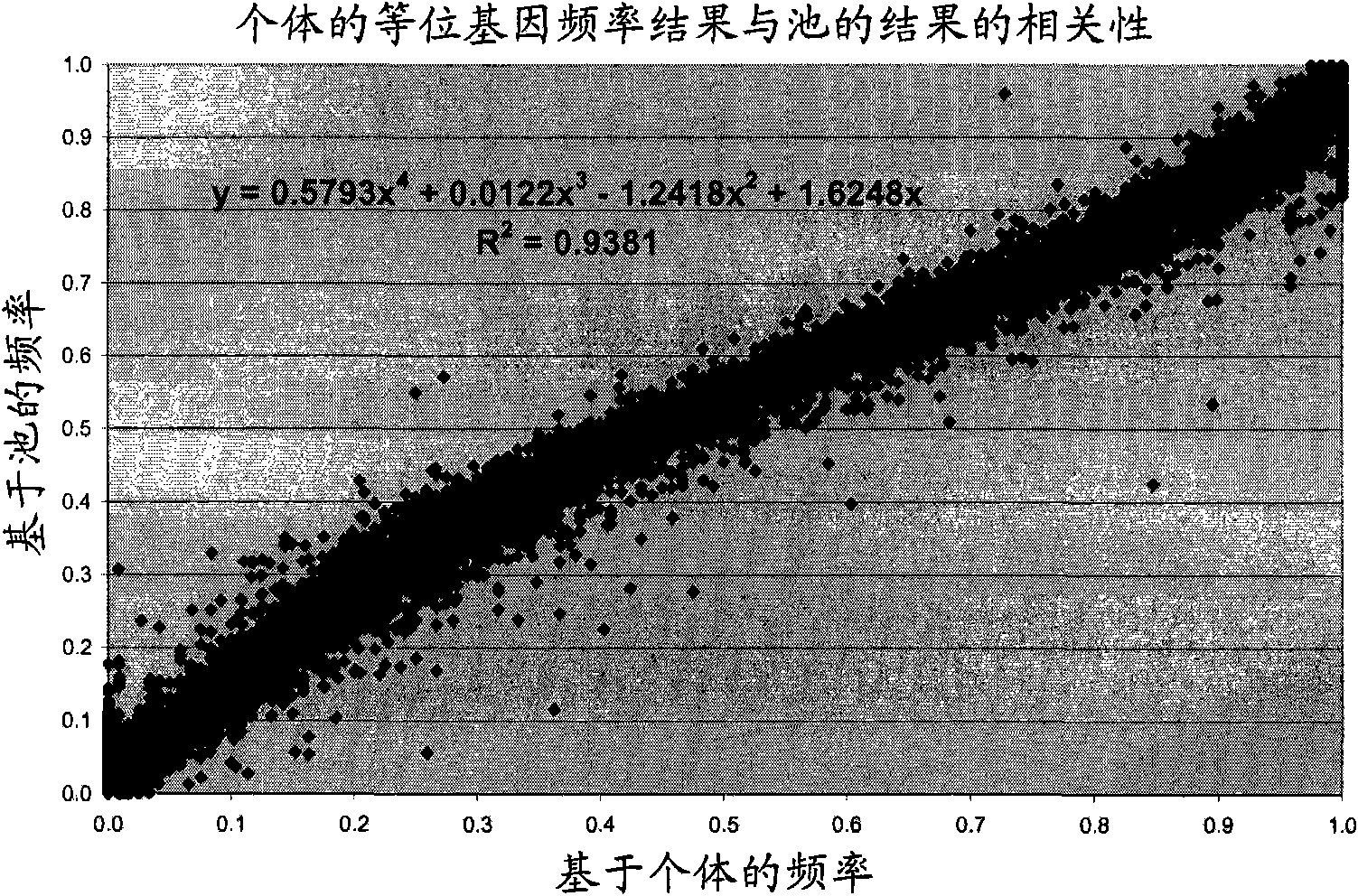
[0098] For each SNP and each individual, we obtained the intensities of red fluorescence (allele present) and green fluorescence (allele absent) in microarray format using two different fluorescent dyes. The ratio between red and green intensities is not always 1 (or 0) for animals that are homozygous or 0.5 for animals that are heterozygous.
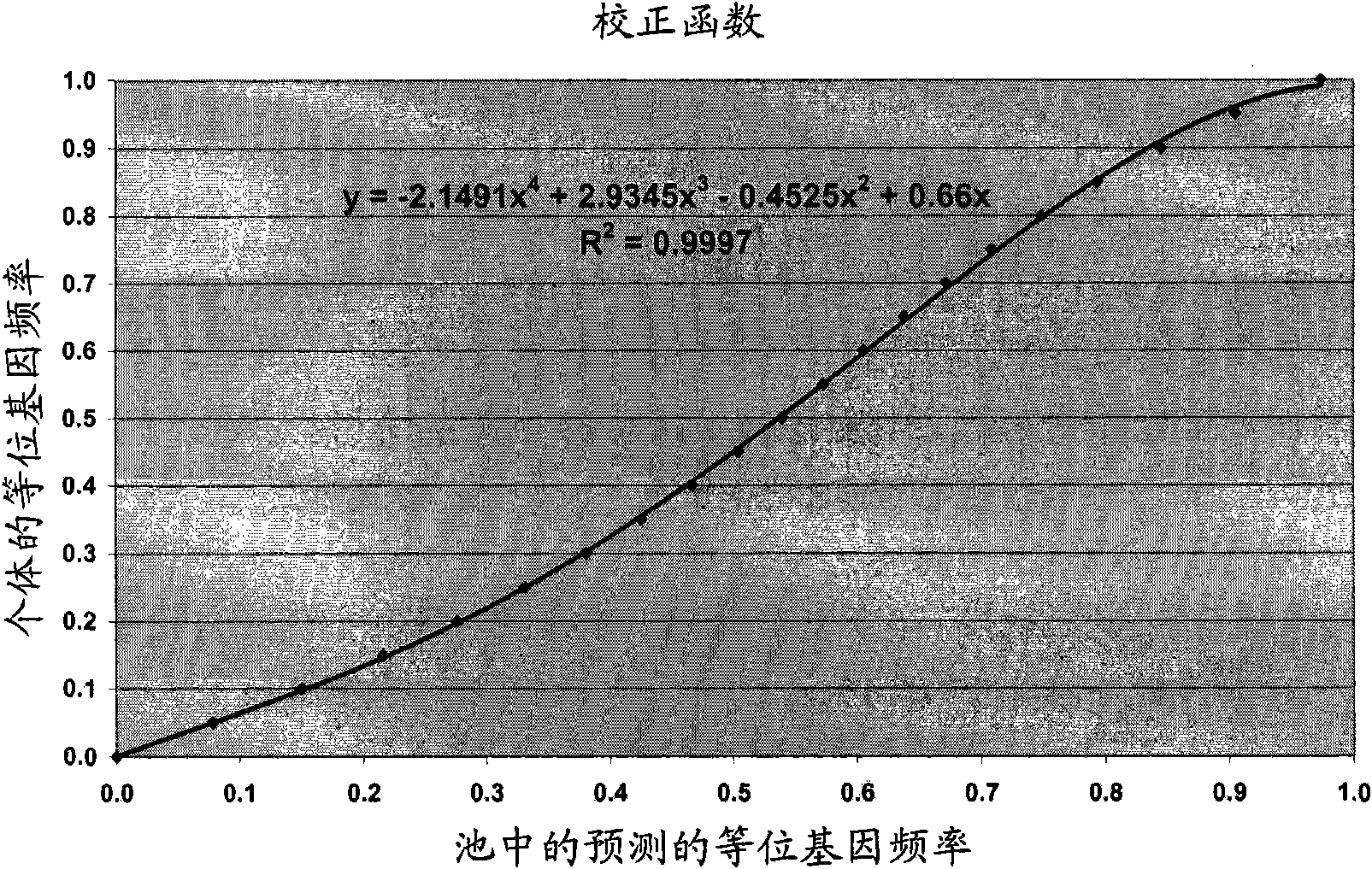
[0099] Individual genotyped data were used to calculate correction factors for the signal intensities of all genotyped SNPs.
[0100] To obtain the most important correction factor (K), which is usually used to correct data representing arbitrary unequal efficiencies among alleles, we use the signal from the heterozygous genotype. If no heterozygous genotypes are present, we assume that the SNP under study does not segregate in the population under study, a...
Embodiment 2
[0141] Example of Genotyping Diploid Individual Samples Using a Pool of 25 Normalized 2 Individuals
[0142] Step 1) As in Step 1 of Example 1, 50 individuals were individually tested.
[0143] Step 2) Construct 25 pools at a ratio of 1:3, with 2 samples in each pool, which include all 50 individuals from step 1) above. In these pools, the allele frequencies are estimated uncorrected or based on the correction factors obtained in the first step.
[0144] Step 3) Compare the sum of the typed allele frequencies of the 2 individuals to the estimated frequency in the pool with a sample of 2 individuals. Compute the regression line from these 25 points. The regression coefficients and intercepts can then be used to correct the estimated frequencies for the other pools.
[0145] Step 4) Then at 1:3, 1:3:9 or 1:3 1 : 3 2 : 3 (n-1) Construct DNA pools of 2, 3 or n samples at a ratio of .
[0146] Step 5) With the correction factors obtained in steps 1 and 3, calculate the allel...
Embodiment 3
[0149] Example of genotyping samples from haploid individuals
[0150] When pooling two haploid samples and measuring the presence of allele A at certain locations in the genome, the ratios in the expected measurements (peak height, surface area, intensity) are;
[0151] Table 4. Results points for allele frequencies of pooled samples and deduced genotypes for two individuals in the pool of SNPs with A and C alleles
[0152] Allelic of pooled samples
frequency of gene A
Deduced genotype of individual 1
(takes 1 share in the pool)
Deduced genotype of individual 2
(takes 3 shares in the pool)
0.00
C
C
0.33
A
C
0.67
C
A
[0153] 1.00
A
A
[0154] If only two-sample pools are used, no correction factor may be required. Correction factors may be required when more samples are pooled. It can then be calculated by simulating a pool of 2 samples of heterozygous and hom...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com