Steel rail used for high-speed and quasi-high speed railways and manufacturing method thereof
A quasi-high-speed, rail technology, applied in the field of rail materials, can solve the problems of high cost of grinding trains, high traffic density, and restrictions on mass promotion and use, so as to improve service life and transportation safety, improve toughness, plasticity and yield strength, improve Effect of rolling contact fatigue performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
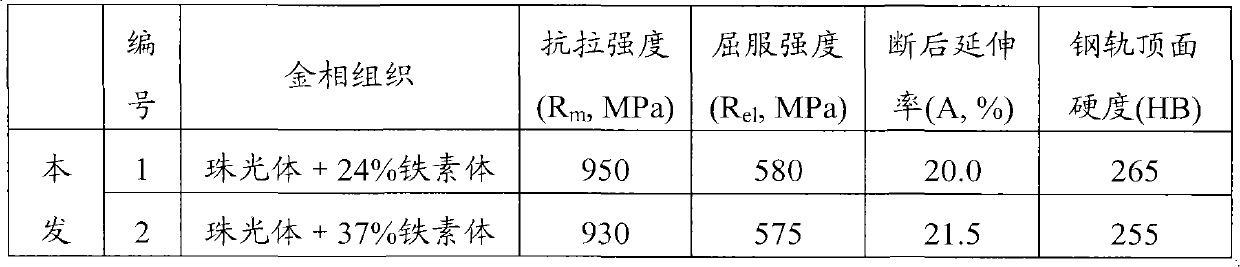
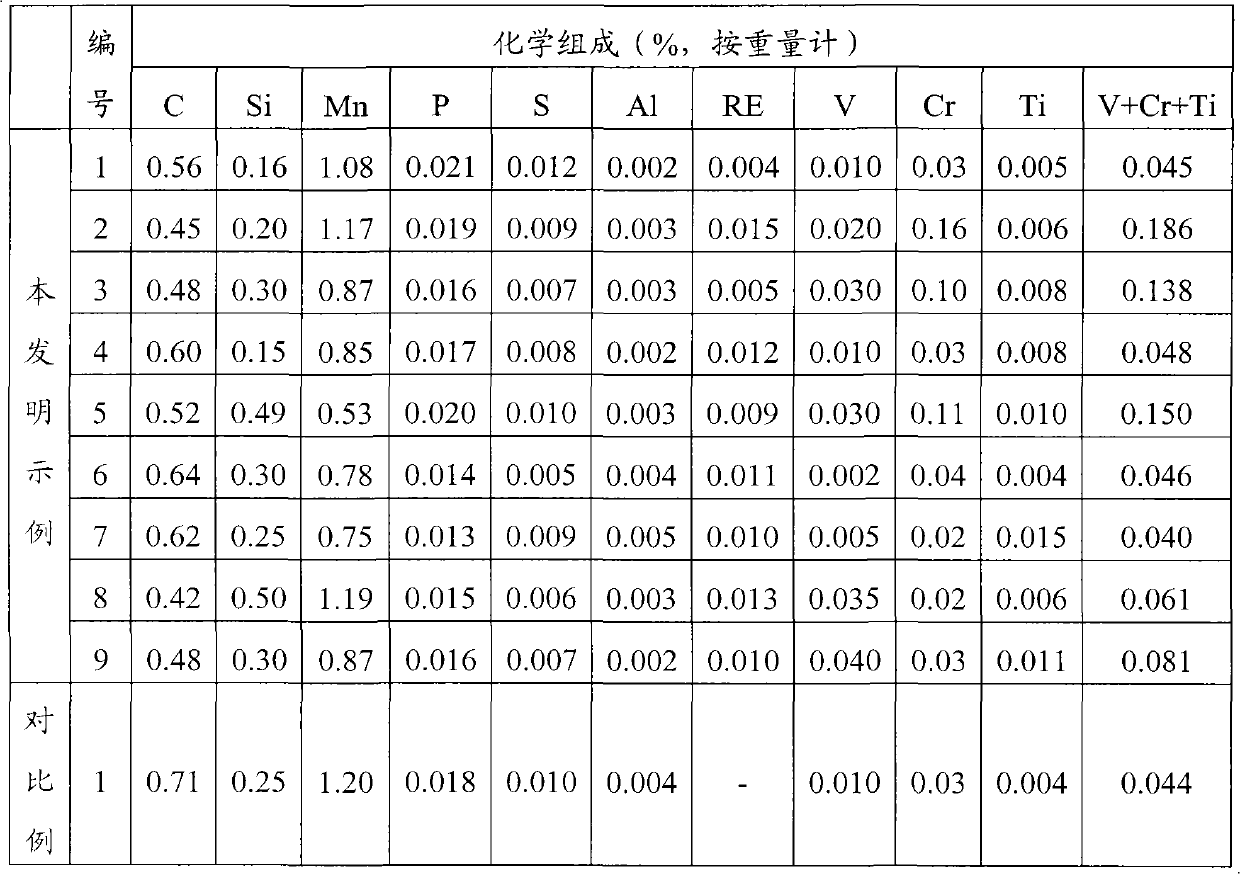
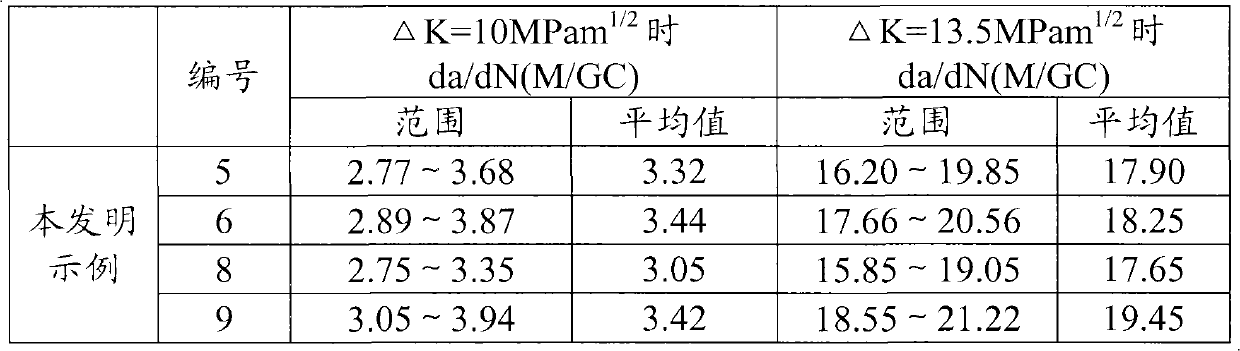
[0056] Converter is used to smelt the steel whose composition is listed in Table 2 below, and then LF furnace refining, vacuum degassing, billet continuous casting, billet heating furnace heating, rail rolling, the final rolling temperature is 903 °C, and after standing for 40s, When the temperature on the top surface of the rail head drops to 800°C, start to spray compressed air, and evenly cool the rail head at a cooling rate of 3.1°C / s. After the injection is completed, the temperature on the top surface of the rail head is 520°C, and the temperature of the rail waist and rail bottom is greater than 600°C , and then the rail was naturally cooled to room temperature in the air to obtain sample 1.
example 2
[0058] Steel rails were manufactured in the same manner as in Example 1 except for the step of controlled cooling after rolling. Specifically, in this example, the final rolling temperature is 910°C. After standing for 45s, the temperature of the top surface of the rail head drops to 780°C and starts to spray compressed air and oil-air mixture to uniformly cool the rail head at a cooling rate of 2.9°C / s. After the injection, the temperature of the top surface of the rail head is 514°C, and the temperature of the rail waist and rail bottom is greater than 600°C. Then the rail is placed in the air and naturally cooled to room temperature to obtain sample 2.
example 3
[0060] Steel rails were manufactured in the same manner as in Example 1 except for the step of controlled cooling after rolling. Specifically, in this example, the final rolling temperature is 900°C. After standing for 42s, the temperature on the top surface of the rail head drops to 770°C and begins to spray the oil-air mixture. The rail head is uniformly cooled at a cooling rate of 2.7°C / s. After the completion, the temperature of the top surface of the rail head was 530°C, and the temperature of the rail waist and rail bottom was greater than 600°C. Then the rail was placed in the air and naturally cooled to room temperature to obtain sample 3.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com