Therapeutic treatment for lung conditions
A technology of pulmonary hypertension and its precursors, which can be applied to respiratory diseases, cardiovascular diseases, medical preparations containing active ingredients, etc., and can solve problems such as death and right-sided heart failure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1-4
[0056] The following example evaluates whether oral supplementation with L-citrulline prevents the development of pulmonary hypertension and the consequent decrease in NO production during exposure of neonatal piglets to chronic hypoxia for 10 days.
[0057] The method used in Examples 1-4
[0058] animal care
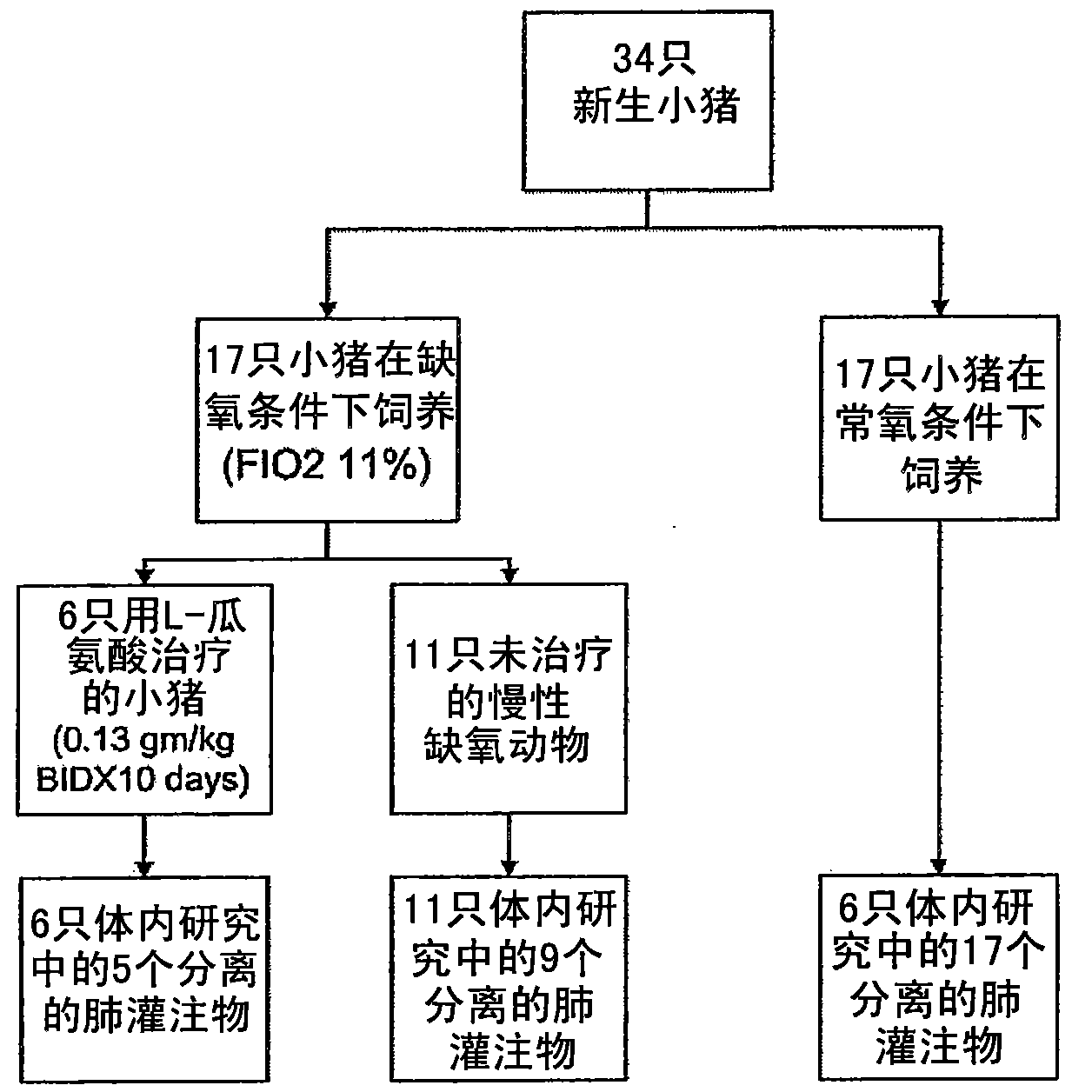
[0059] A total of 17 hypoxic and 17 control piglets were studied. see figure 2 . Twelve-day-old control animals were studied on the day of arrival from the farm. Hypoxic pigs (2 days old) were placed in a hypoxic chamber at atmospheric pressure for 10-11 days. Atmospheric hypoxia was provided using compressed air and nitrogen to produce 8-11% inspired oxygen (PO 2 60-72Torr), and the CO is absorbed by soda lime 2 Keep it at 3-6Torr. Animals' daily body weight was monitored and physical examination was performed twice daily. They were bred ad libitum with pig milk substitute in a cage feeding facility.
[0060] L-Citrulline Supplement
[0061] Oral supplemen...
Embodiment 1
[0080] In vivo hemodynamic measurements
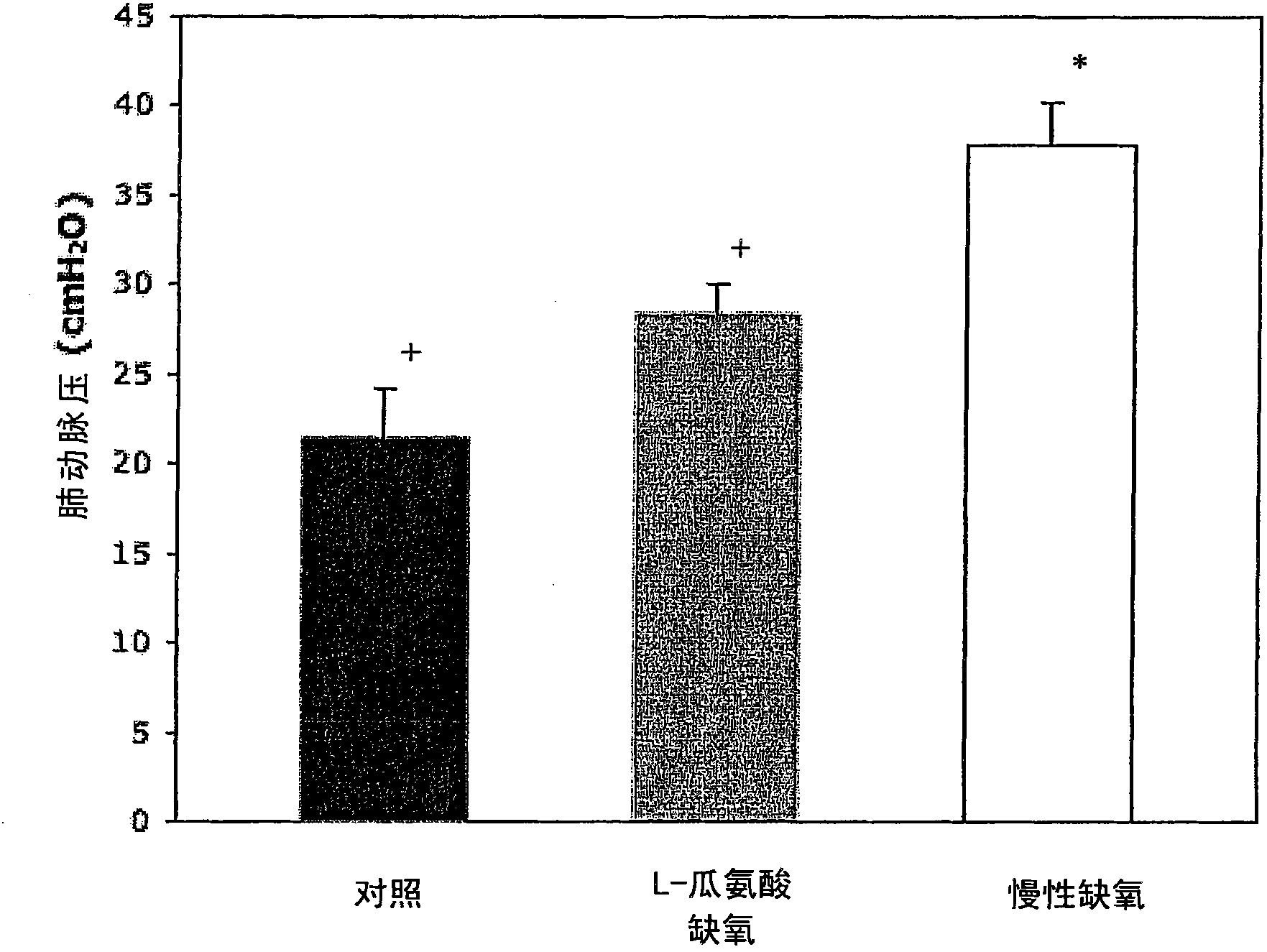
[0081] On the study day in 12-13 day old animals, both L-citrulline-treated and untreated hypoxic animals had lower cardiac output and weight compared to age-matched control piglets and higher LVEDP measurements (Table 1). Measurements of aortic pressure and blood gas indices were similar in the cohort (paO in control piglets 2 74 ± 5 Torr, paO in untreated hypoxic piglets 2 74±8 Torr, paO in hypoxic piglets treated with L-citrulline 2 78±7 Torr; paCO2 in control piglets was 39±2, paCO2 in untreated hypoxic piglets was 41±4, and paCO2 in hypoxic piglets treated with L-citrulline was 30±1.0 ). obviously, as image 3 As shown, hypoxic animals treated with L-citrulline had significantly lower pulmonary arterial pressure compared to untreated hypoxic animals (p-value 0.01). Pulmonary arterial pressure did not differ between normoxic control animals and hypoxic animals treated with L-citrulline (p=0.08).
[0082] Additionally, if ...
Embodiment 2
[0084] exhaled NO output and perfusate NO x -
[0085] Such as Figure 5 As shown, exhaled NO output was higher in control animals and hypoxic animals treated with L-citrulline than in untreated hypoxic animals (p-values 0.001 and 0.032, respectively). However, there was no difference in exhaled NO output between control animals and hypoxic animals treated with L-citrulline (p=0.124).
[0086] Such as Image 6 As shown, lungs of control animals (p=0.02) and L-citrulline-treated hypoxic animals (p=0.04) had significantly higher NOx compared to lungs of untreated hypoxic animals - accumulation rate. Moreover, NOx in the lungs of hypoxic animals treated with L-citrulline compared - There was no difference in the rate of accumulation.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com