Adjustable gain low noise amplifier
A low-gain technology for amplifiers, applied in the direction of high-frequency amplifiers, amplification control, and control of components of amplification devices, can solve problems such as the inability to directly realize the logarithmic linear relationship between gain and gain control voltage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0044] The content of the present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
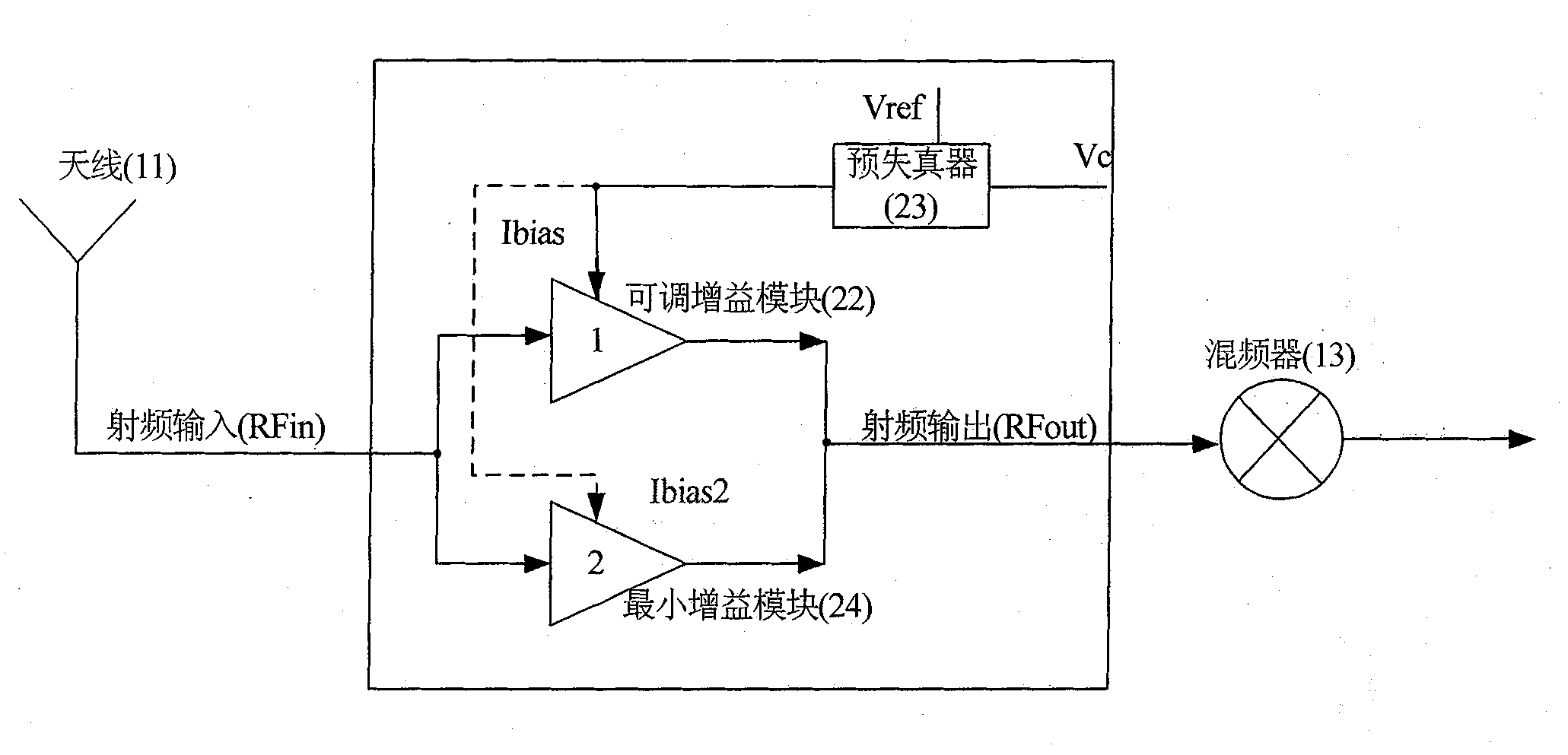
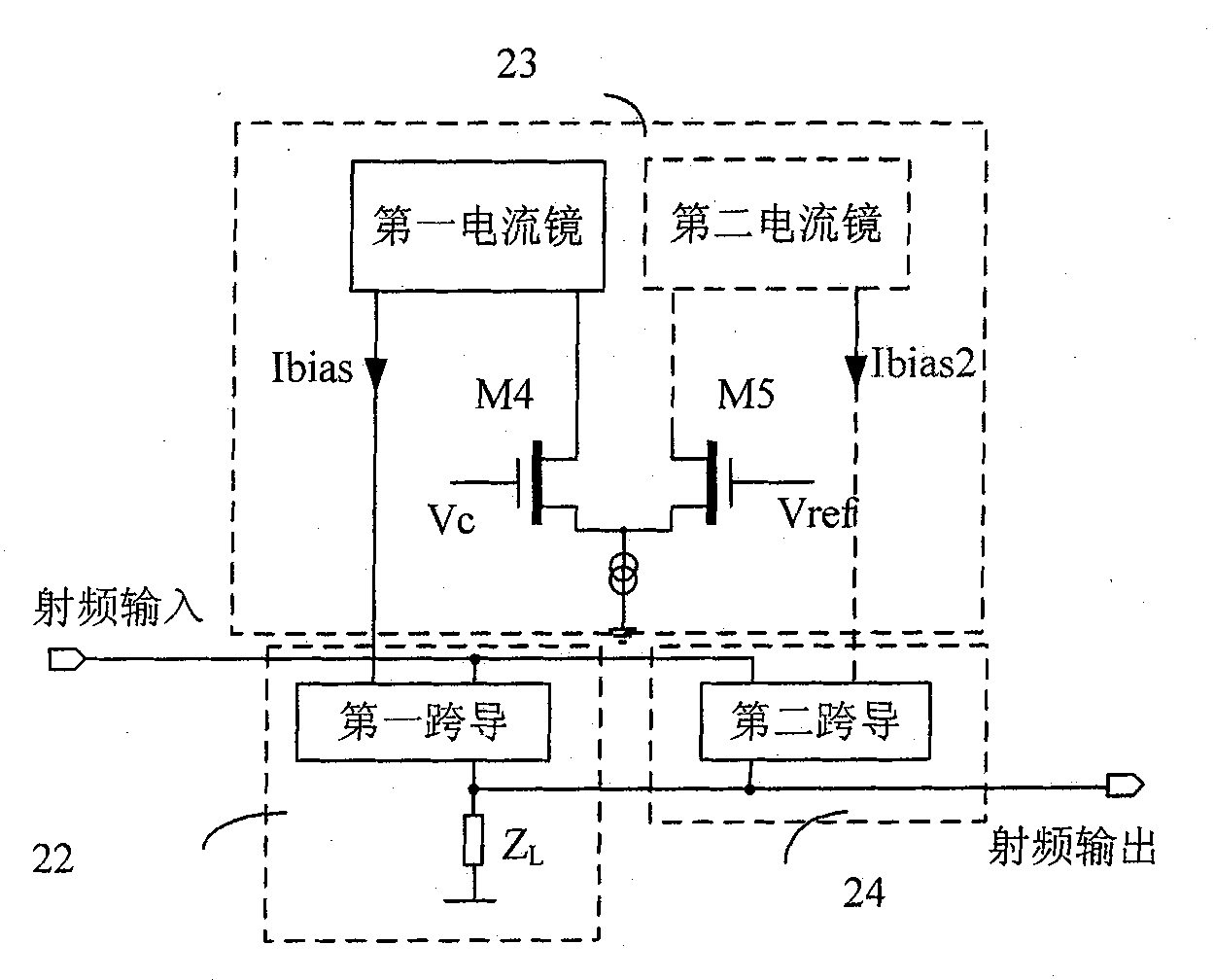
[0045] adjustable-gain low-noise amplifiers, such as figure 2 As shown, including an adjustable gain block (22), a predistorter (23) and a minimum gain block (24):
[0046] The radio frequency is input to the adjustable gain module (22) and the minimum gain module (24);
[0047] After the predistorter (23) compares the gain control voltage Vc with the reference voltage Vref, it is converted into a first bias current Ibias, and the first bias current Ibias is provided to the adjustable gain module (22);
[0048] The minimum gain module (24) provides minimum gain control, and the minimum gain module (24) inputs the second bias current Ibias2 to adjust its gain;
[0049] The output of the adjustable gain module (22) and the output of the minimum gain module (24) are combined as the radio frequency output of the adjustable gain low noise amplifier.
[00...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com