Low-energy consumption sleeping monitoring method synchronous relative to time of wireless sensor network
A wireless sensor network, relative time technology, applied in the direction of synchronization device, wireless communication, energy consumption reduction, etc., can solve the problems of increasing the number of dedicated synchronization packet transmission, affecting the short preamble length, increasing communication energy consumption, etc., to achieve communication saving overhead, saving energy overhead, and reducing synchronization overhead
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0036] The present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
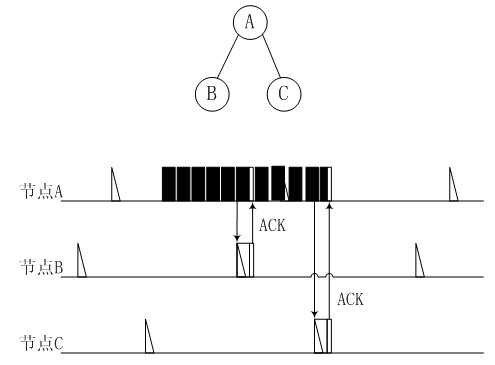
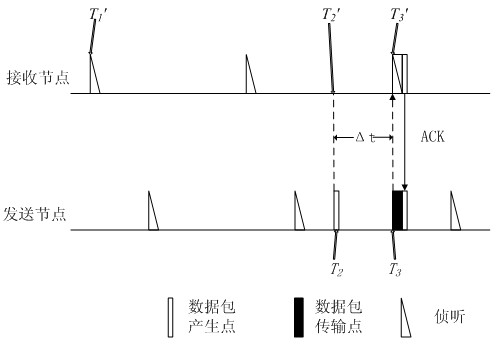
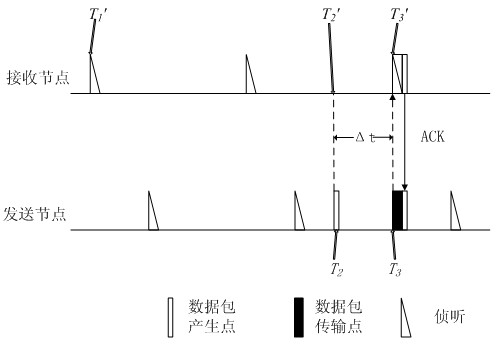
[0037] The low-energy-consumption sleep listening method for relative time synchronization of wireless sensor network of the present invention requires a new node to establish a relative synchronization table in the wireless sensor network, wherein the relative synchronization table includes the latest time of neighbor nodes. Wake-up time, clock offset and clock drift of neighbor nodes, and sleep period of neighbor nodes, according to which relative synchronization between nodes can be achieved; The data packet transmission of the destination node, so as to achieve the purpose of reducing the energy consumption of the sending node.
[0038] like figure 1As shown, nodes B and C are nodes newly joining the network. When the new nodes B and C establish a relative synchronization table, node A broadcasts its own synchronization information by means of a long pr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com