Passive optical network
A technology of passive optical network and optical network unit, which is applied to the selection device, electrical components, selection device and other directions of the multiplexing system to achieve a convenient number and transmission distance of optical signals, increase the number of wavelengths, and improve the uplink access bandwidth. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0019] The technical solutions of the present invention will be described in further detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
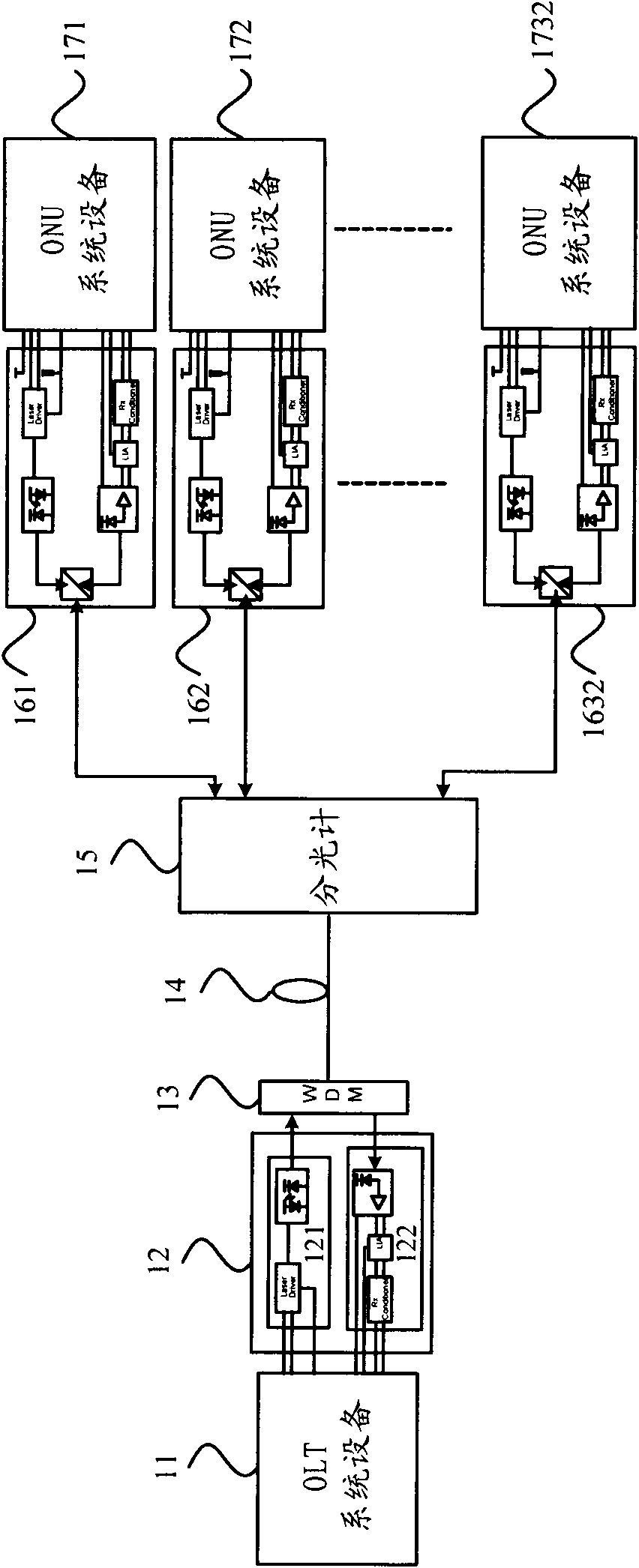
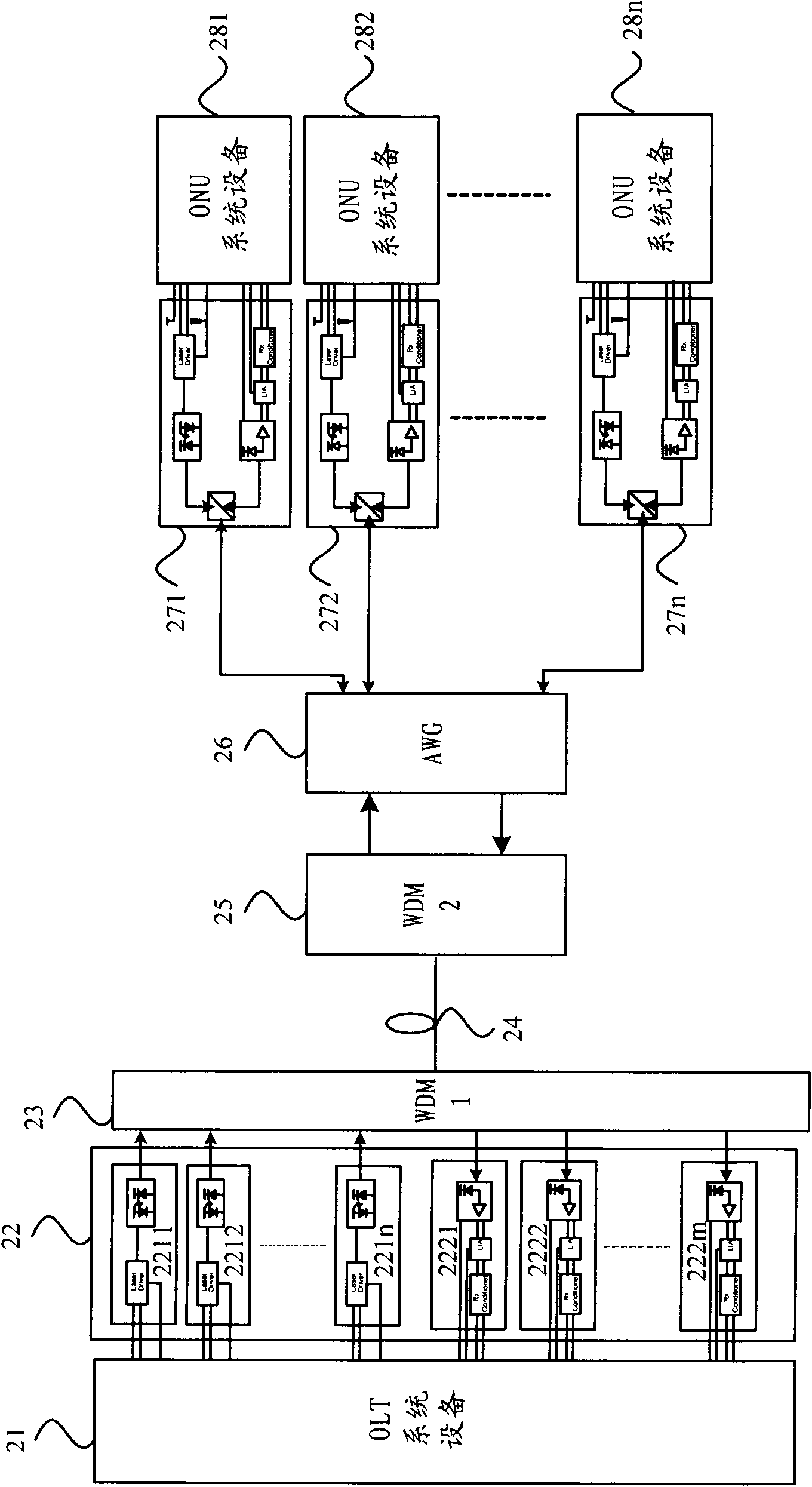
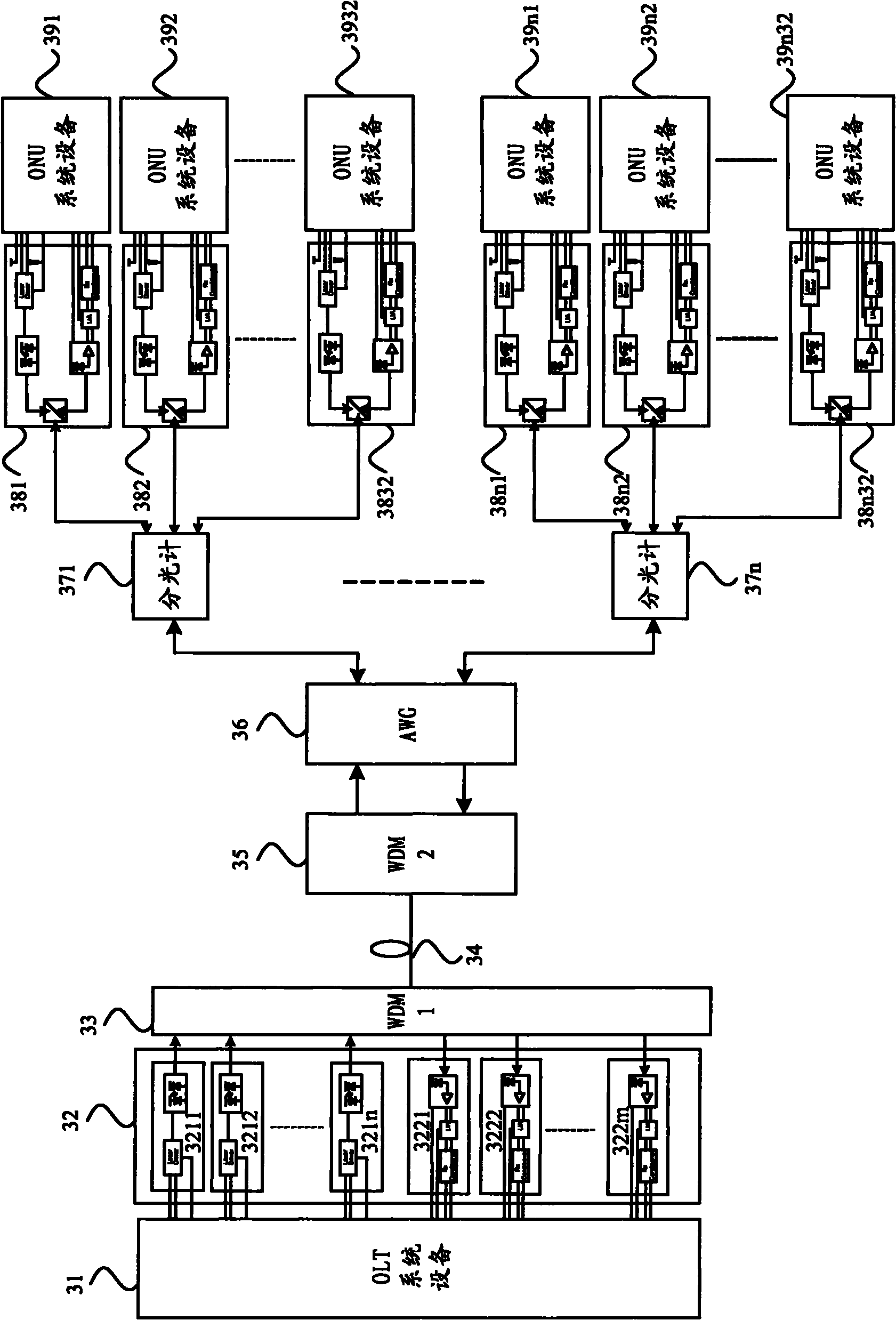
[0020] The present invention starts from the layout structure of the existing passive optical network, and considers that the existing passive optical network generally adopts an OLT to carry a plurality of ONUs through a spectrometer, and adopts a downlink optical signal of one wavelength and an uplink optical signal of one wavelength for signalling The transmission structure has shortcomings such as small ONU access bandwidth, large optical loss, and inconvenience to expand the number of ONUs. A new passive optical network is proposed, which can effectively solve the problems of existing passive optical networks.
[0021] figure 2 and image 3 The schematic structural diagrams of two embodiments of the passive optical network of the present invention are respectively shown.
[0022] First refer to figur...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com