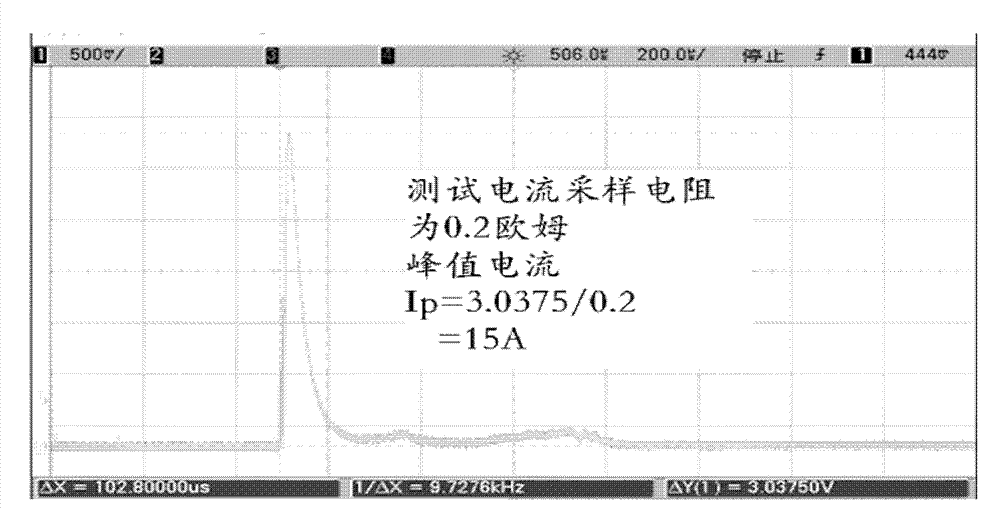
Battery protecting device and protecting method
A battery protection device and discharge control technology, applied in emergency protection circuit devices, circuit devices, emergency protection circuit devices for limiting overcurrent/overvoltage, etc. , battery pole piece carbonization and poor contact, etc., to achieve the effect of prolonging storage time, suppressing transient high current, and preventing fire from hurting people
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
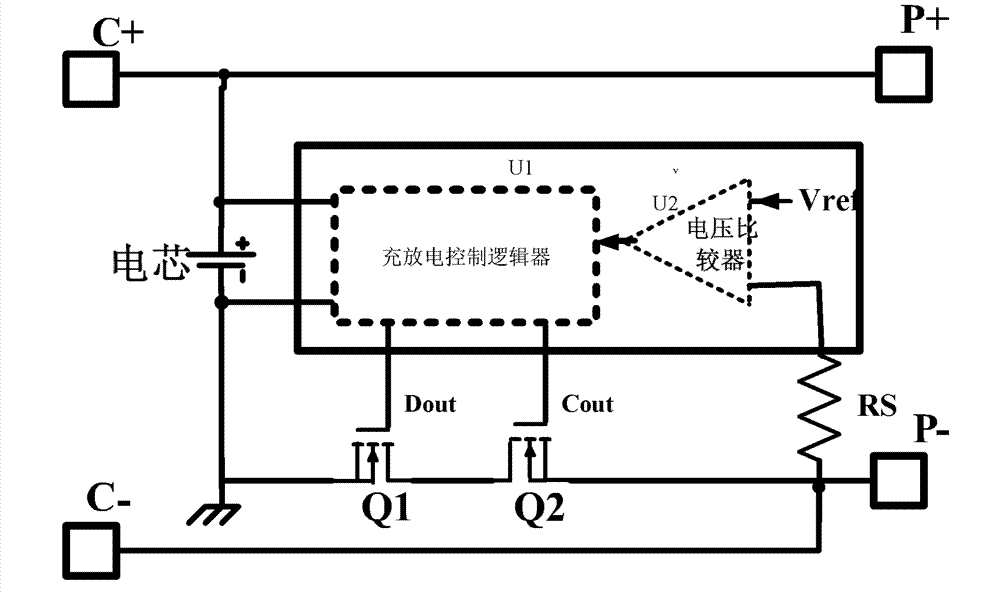
[0035] see Figure 4, shows the first embodiment of the battery protection device of the present invention, which includes a charge and discharge control logic U1, one end of the charge and discharge control logic U1 is connected to the negative electrode C- of the battery charging port through a resistor RS, and one output end of the charge and discharge control logic U1 is connected to the discharge terminal. The gate of MOS transistor Q1, the other output end is connected to the gate of charging MOS transistor Q2; the source of discharging MOS transistor Q1 is connected to the negative pole of the cell, the drain is connected to the source of charging MOS transistor Q2, the positive pole of the discharge port P+, and the charging port The positive pole C+ is connected to the positive pole of the cell;
[0036] It also includes a feedback terminal S connected to the positive pole P+ of the discharge port. The discharge control unit 11 includes a MOS transistor Q3, a MOS tran...
no. 2 example
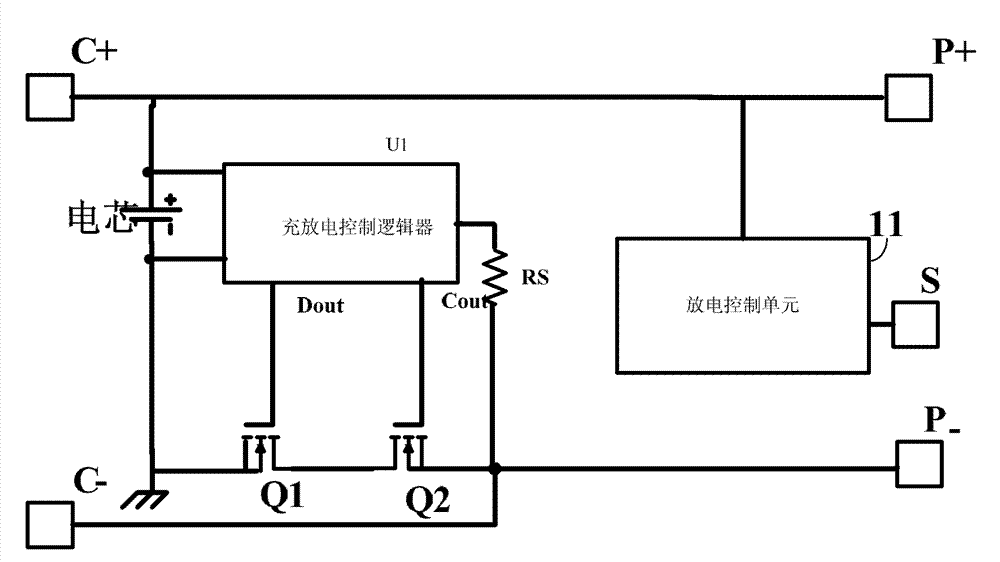
[0041] see Figure 5 , shows the second embodiment of the battery protection device of the present invention, including a charge and discharge control logic U1, one end of the charge and discharge control logic U1 is connected to the negative pole P- of the battery discharge port through a resistor RS, and one output end of the charge and discharge control logic U1 is connected to the discharge port The gate of the MOS transistor Q1, and the other output terminal is connected to the gate of the charging MOS transistor Q2; the source of the discharging MOS transistor Q1 is connected to the negative pole of the cell, the drain is connected to the source of the charging MOS transistor Q2, and the positive pole of the discharge port P+ is connected to the battery. the positive pole of the core;
[0042] It also includes a feedback terminal S connected to the positive pole P+ of the discharge port. The discharge control unit 11 includes a MOS transistor Q3 and a MOS transistor Q4. ...
no. 3 example
[0046] see Image 6 , shows the third embodiment of the battery protection device of the present invention, including a charge and discharge control logic U1, one end of the charge and discharge control logic U1 is connected to the negative pole P- of the battery discharge port through a resistor RS, and one output end of the charge and discharge control logic U1 is connected to the discharge port The gate of the MOS transistor Q1, and the other output terminal is connected to the gate of the charging MOS transistor Q2; the source of the discharging MOS transistor Q1 is connected to the negative pole of the cell, the drain is connected to the source of the charging MOS transistor Q2, and the positive pole of the discharge port P+ is connected to the battery. the positive pole of the core;
[0047] It also includes a feedback terminal S connected to the positive pole P+ of the discharge port. The discharge control unit 11 includes a MOS transistor Q5, the source of the MOS tran...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com