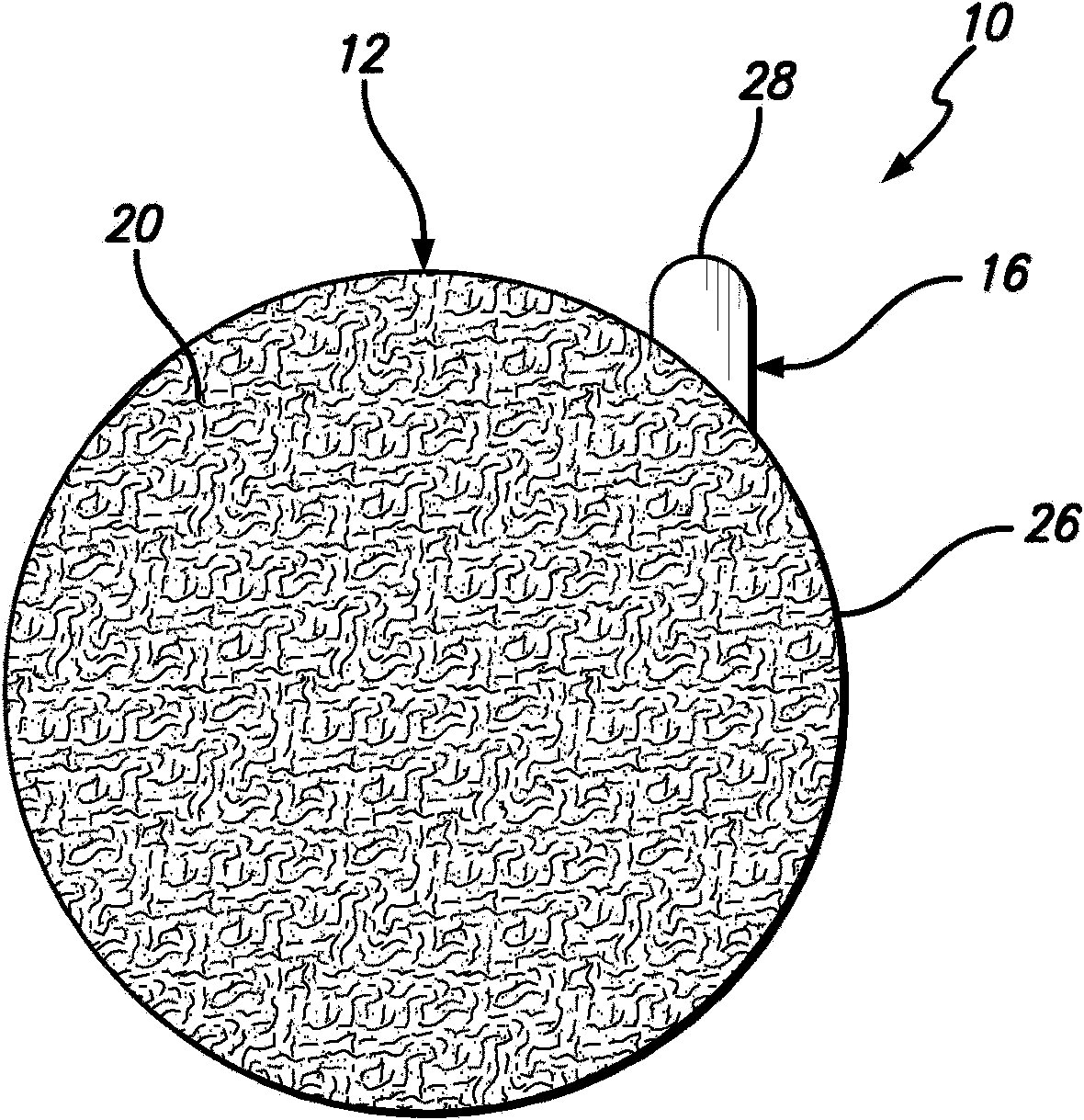
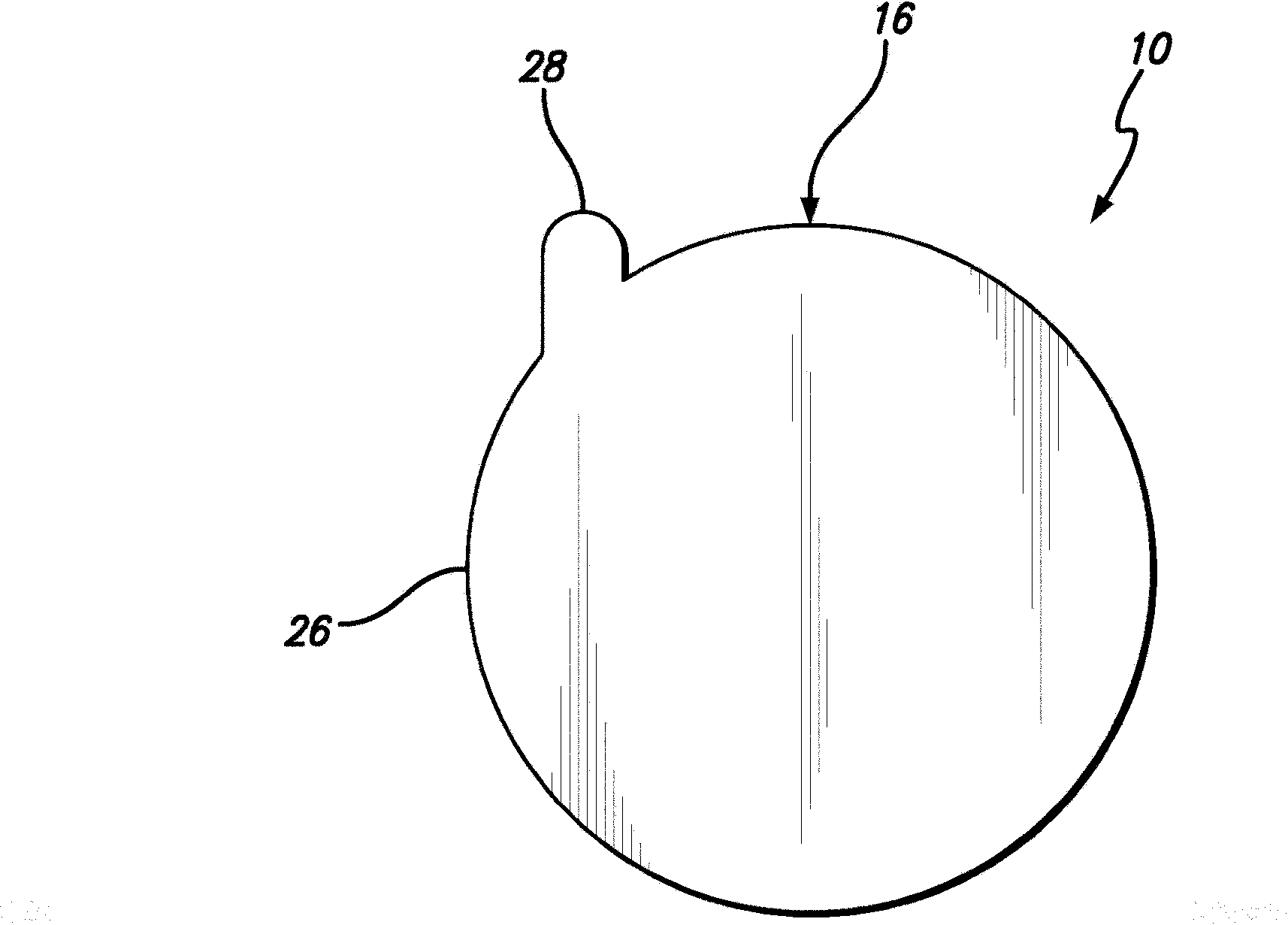
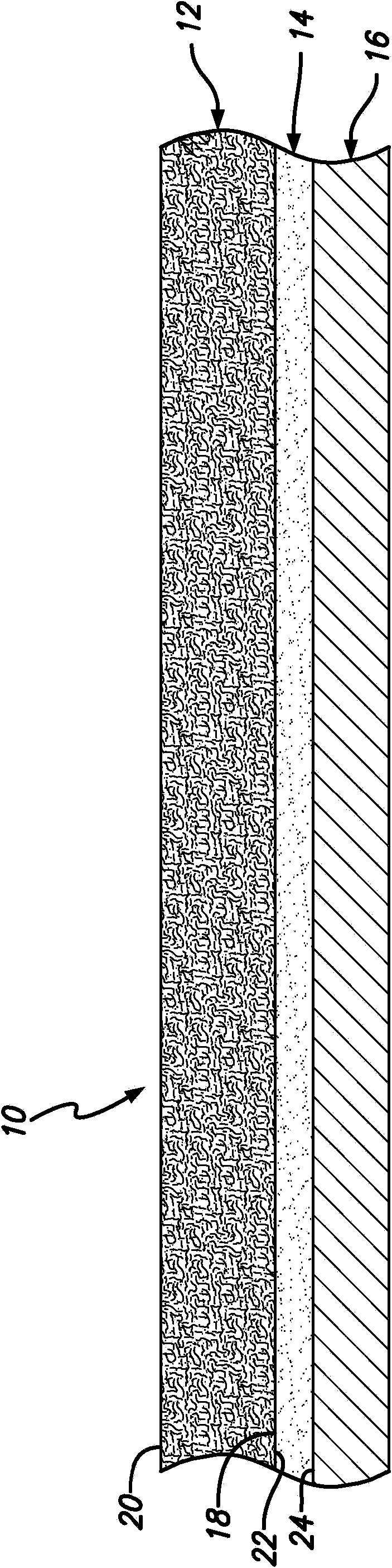
Dry sanitizing patch for decreasing human pathogen transmission
A pathogen and patch technology, applied in the field of dry disinfection patches used to reduce the spread of human pathogens, can solve the problems of unavailable and time-consuming facilities
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0059] Preparation of sulfated rayon fabric
[0060] According to one embodiment of the present invention, sulfated rayon is prepared according to the following steps of the present invention. First, 60 mL of isopropanol was cooled on ice, and 0.2 g of MgSO 4 Water was removed by adding to isopropanol. Next, 240 mL of sulfuric acid, previously ice-cooled, was added to the isopropanol. Then, with a density of 70 g / m 2 A non-woven (non-woven) rayon fabric was cut into 17.5 cm x 22.5 cm rectangles and laid on a polypropylene mesh of approximately the same size. Next, the rayon fabric on the mesh was immersed in ice-cold acetic acid for 15 minutes. Then, the isopropanol / sulfuric acid mixture was poured into a polyethylene box (approximately 30 cm x 37.5 cm) placed on ice. Next, the rayon fabric on a polyethylene mesh was immersed in an isopropanol / sulfuric acid mixture for 5 or 10 minutes and rinsed first in cold isopropanol and then in cold isopropanol containing 3 grams of ...
Embodiment 2
[0062] Preparation of sulfonated rayon fabric
[0063] According to one embodiment of the present invention, the sulfonated rayon fabric is prepared according to the following steps of the present invention. First, a solution was prepared by adding 30 grams of sodium sulfate to 600 grams of distilled water, followed by the addition of 4 grams of CI Reactive Blue 21 dye (a sulfonated binding substance). Then, 30 grams of density of 70 g / m 2 A non-woven (non-woven) rayon fabric is added to the solution and gently agitated until uniformly submerged and wetted. Then, 12 g of sodium carbonate were added with stirring, and the mixture was kept at 30° C. for 35 minutes. Next, the temperature was raised to 70°C for an additional 60 minutes to produce a sulfonated rayon fabric (using CI Reactive Blue 21 dye as a binding substance). The sulfonated rayon fabric was then rinsed under running water until no free dye was eluted, and the sulfonated rayon fabric was allowed to dry.
Embodiment 3
[0065] Contains substances that disrupt the disease-causing ability of one or more than one human pathogen
[0066] Preparation of fabrics of one or more than one substance
[0067] According to one embodiment of the present invention, according to the following steps, the sulfated cellulose fabric prepared according to Example 1 or the sulfonated cellulose fabric prepared according to Example 2 is made to contain one or more substances other than the binding substances. An additional substance that destroys the disease-causing ability of one or more than one human pathogen. First, a sulfated rayon fabric was prepared according to the method disclosed in Example 1 or a sulfonated rayon fabric was prepared according to the method disclosed in Example 2 (using CI Reactive Blue 21 dye as a binding substance). Then, using the concentration of lg metal salt / 100ml water, through aerosol at 40μl / cm 2 Fabric (amount) Copper sulfate and zinc acetate, both divalent metal salts, were a...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com