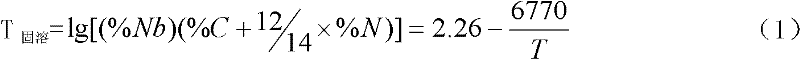Hot rolling process capable of improving high-grade thick pipeline steel fracture toughness
A fracture toughness and thick gauge technology, which is applied to the hot rolling process of high-grade steel above X70, thick gauge pipe steel above 15mm, and the hot rolling process of high-grade thick gauge pipeline steel, which can solve the problem of poor stability and poor DWTT performance. ideals etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
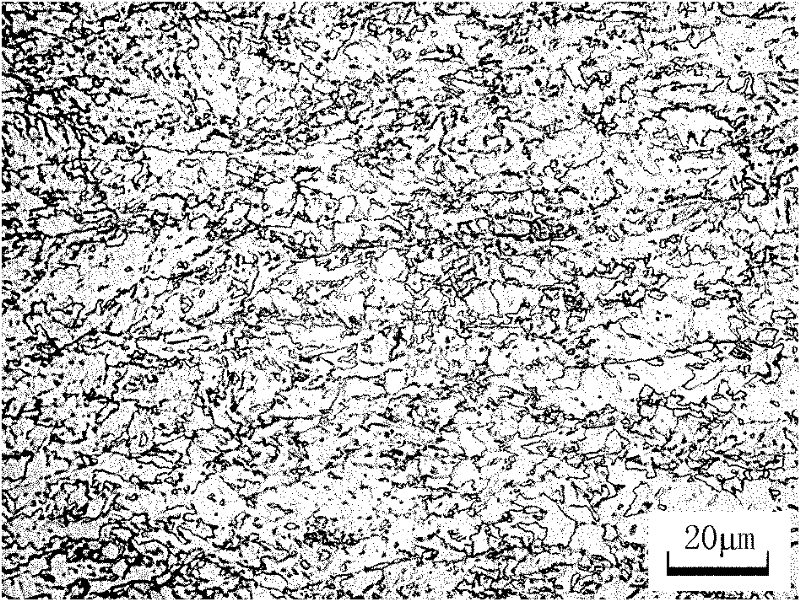
[0023] The carbon content in the steel slab is 0.05%, the niobium content is 0.06%, the nitrogen content is 0.0040% and other alloy elements, and the produced product requires X70 hot-rolled steel strip with a thickness of 15.9mm.
[0024] The hot rolling process sequentially includes the slab heating section process, hot rolling section process, plate coiling section process and cooling section process. The specific process parameters of each section process are:
[0025] (1) Slab reheating section process: slab heating temperature = T 固溶 +30~80℃, where T 固溶 is the complete solid solution temperature of niobium carbonitride in steel, so the slab reheating temperature is 1180°C;
[0026] (2) The relationship between the time in the furnace and the thickness of the slab is: the total time in the furnace = 1 / 2×t+30~50min, where t is the thickness of the slab in mm; the temperature difference between the upper and lower surfaces of the slab after reheating is ≤ 30°C;
[0027] ...
Embodiment 2
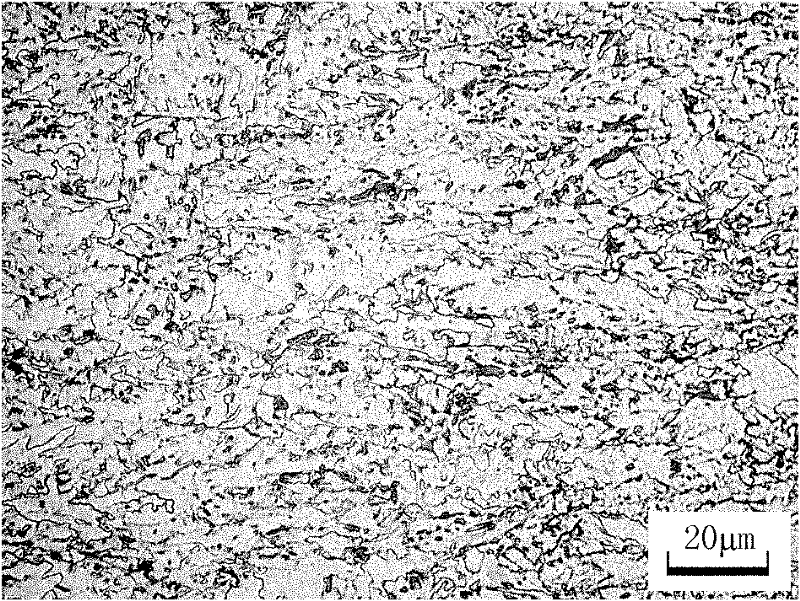
[0032] The difference from Example 1 is that the carbon content in the steel slab is 0.03%, the niobium content is 0.09%, the nitrogen content is 0.0045% and other alloy elements, and the produced product requires a X80 hot-rolled steel strip with a thickness of 18.4mm. The specific process parameters of each process are as follows:
[0033] (1) The slab reheating temperature is 1200°C;
[0034] (2) The rough rolling single pass reduction rate is 21%;
[0035] (3) The final rolling temperature is 830°C;
[0036] (4) The cumulative reduction rate of finishing rolling is 70%;
[0037] (3) The coiling temperature is 450°C;
[0038] (4) The cooling rate is 17°C / s.
[0039] The mechanical properties of the hot-rolled steel strip produced by the method described in Example 2 are shown in Steel 2 in Table 1.
Embodiment 3
[0041] The difference from Example 1 is that the carbon content in the steel slab is 0.05%, the niobium content is 0.06%, the nitrogen content is 0.0050% and other alloy elements, and the produced product requires a X70 hot-rolled steel strip with a thickness of 17.5mm. The specific process parameters of each process are as follows:
[0042] (1) The slab reheating temperature is 1180°C;
[0043] (2) The rough rolling single pass reduction rate is 20%;
[0044] (3) The final rolling temperature is 800°C;
[0045] (4) The cumulative reduction rate of finishing rolling is 71%;
[0046] (3) The coiling temperature is 550°C;
[0047] (4) The cooling rate is 15°C / s.
[0048] The DWTT performance of the hot-rolled steel strip produced by the method described in Example 3 is shown in Steel 3 in Table 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com