Double-end double-wavelength self-compensation distributed optical fiber temperature sensor
A distributed optical fiber, temperature sensor technology, applied in thermometers, thermometers with physical/chemical changes, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of inability to obtain the accurate cutting information of the sensing fiber at the same time, measurement inaccuracy, etc., to improve Raman The effect of scattered light intensity, improving temperature measurement accuracy, and increasing signal-to-noise ratio
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
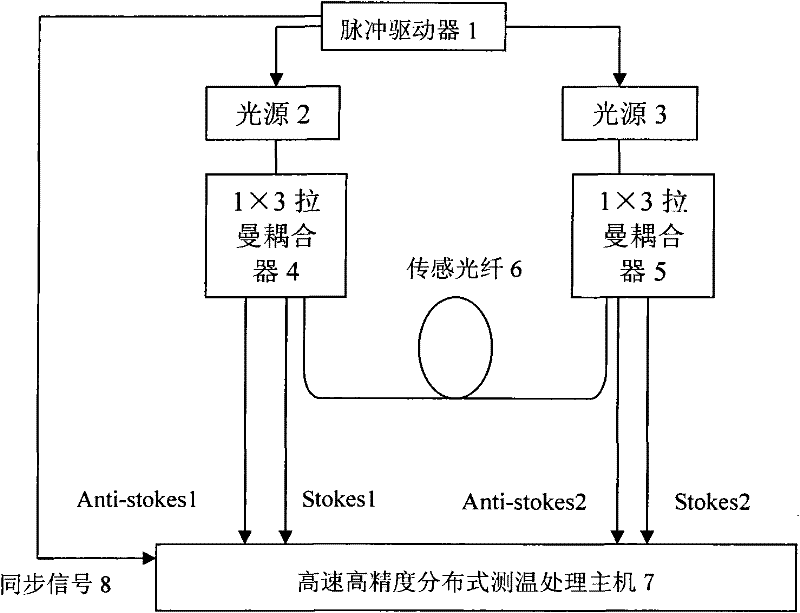
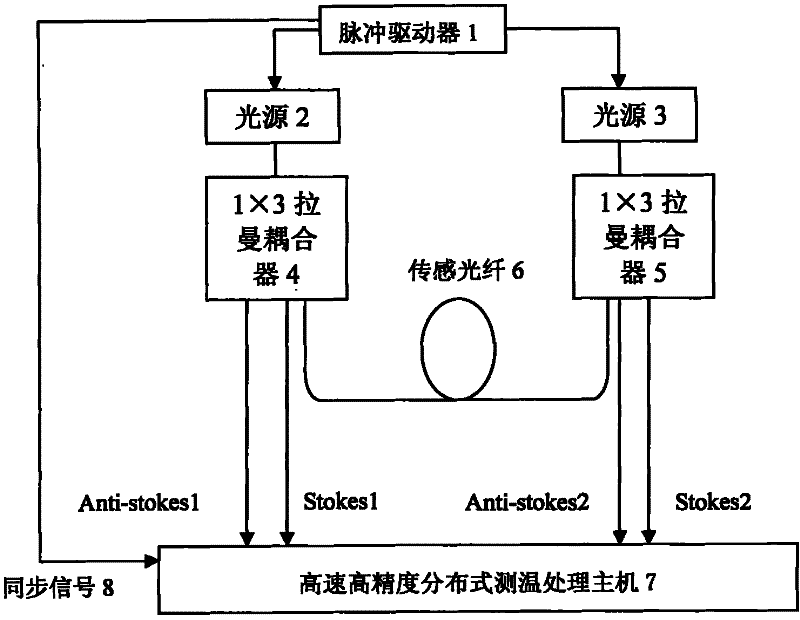
[0015] Embodiment 1: as figure 1 As shown, the pulse driver 1 is connected to two light sources 2 and 3, the light sources 2 and 3 are respectively connected to 1×3 Raman couplers 4 and 5, and the output ends of the two 1×3 Raman couplers are respectively connected to the sensing fiber 6 One end and the other two output ends are connected to a high-speed, high-precision distributed temperature measurement and processing host 7 through optical fibers.
[0016] The light source 2 and the light source 3 emit two pulsed lights with different wavelengths under the action of the pulse driver 1, and the two beams of pulsed light are injected into the two ends of the sensing fiber 6 through two 1×3 Raman couplers. Backward Raman scattering occurs during transmission in the optical fiber, and the obtained backward Raman scattered light returns from both ends of the sensing fiber to the 1×3 Raman coupler, because the 1×3 Raman coupler itself has the function of filtering light , so in ...
Embodiment 2
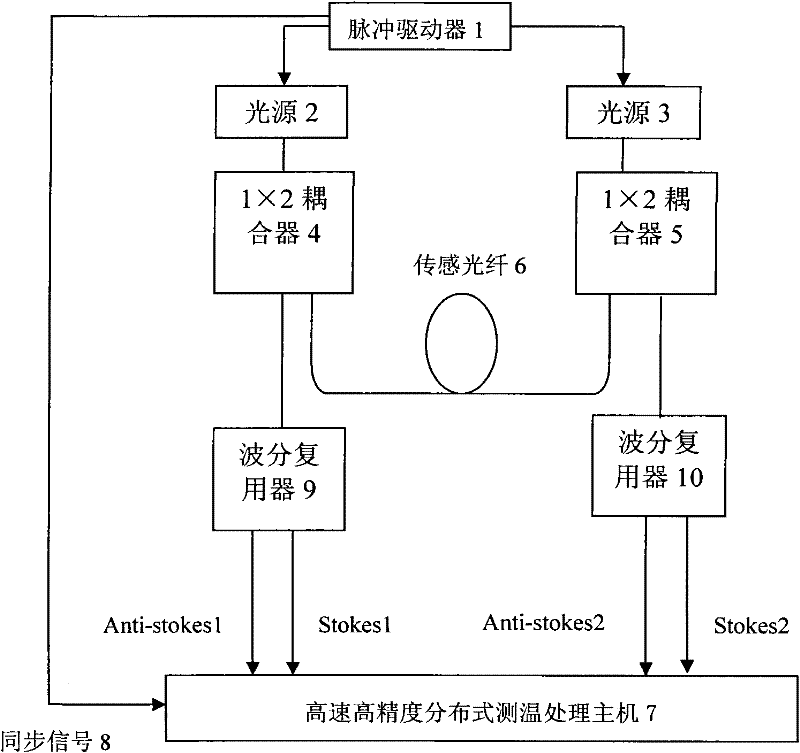
[0018] Embodiment 2: as figure 2 As shown, the pulse driver 1 is connected to two light sources 2 and 3, and the light sources 2 and 3 are respectively connected to 1×2 couplers 4 and 5, and one output end of the two 1×2 couplers is respectively connected to one end of the sensing fiber 6, and the other One output end is respectively connected to a wavelength division multiplexer 9 and 10, and the two wavelength division multiplexers are connected to a high-speed and high-precision distributed temperature measurement and processing host 5 through an optical fiber.
[0019] The light source 2 and the light source 3 emit two kinds of pulsed light with different wavelengths under the action of the pulse driver 1, and the two beams of pulsed light are injected into the two ends of the sensing fiber 6 through two 1×2 couplers, and the pulsed light is in the sensing fiber Back Raman scattering occurs during transmission, and the obtained back Raman scattered light returns to two 1×...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com