Direct-current offset cancelling circuit applied to low-frequency variable gain amplifier
A technology of gain amplifier and DC offset, applied in the direction of amplification control, gain control, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of affecting the compensation of DC offset accuracy, increasing area, increasing power consumption, etc., to reduce power consumption, eliminate DC offset, effect of reducing design complexity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0029] Specific embodiments of the present invention are described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings:
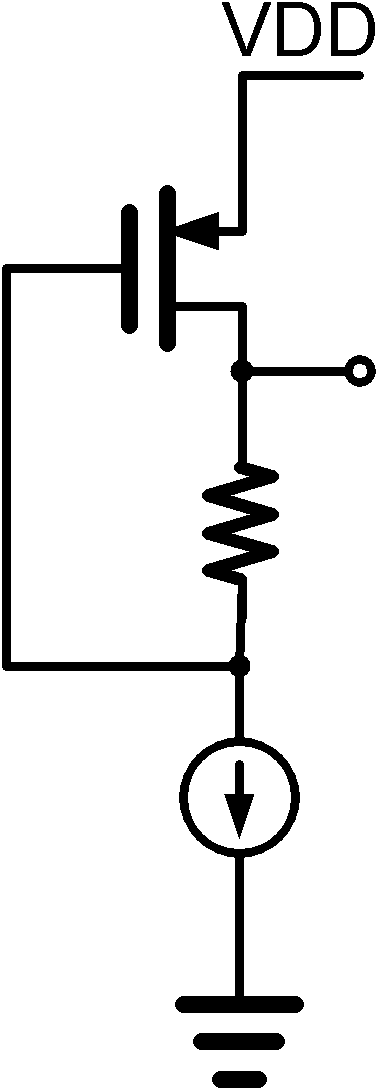
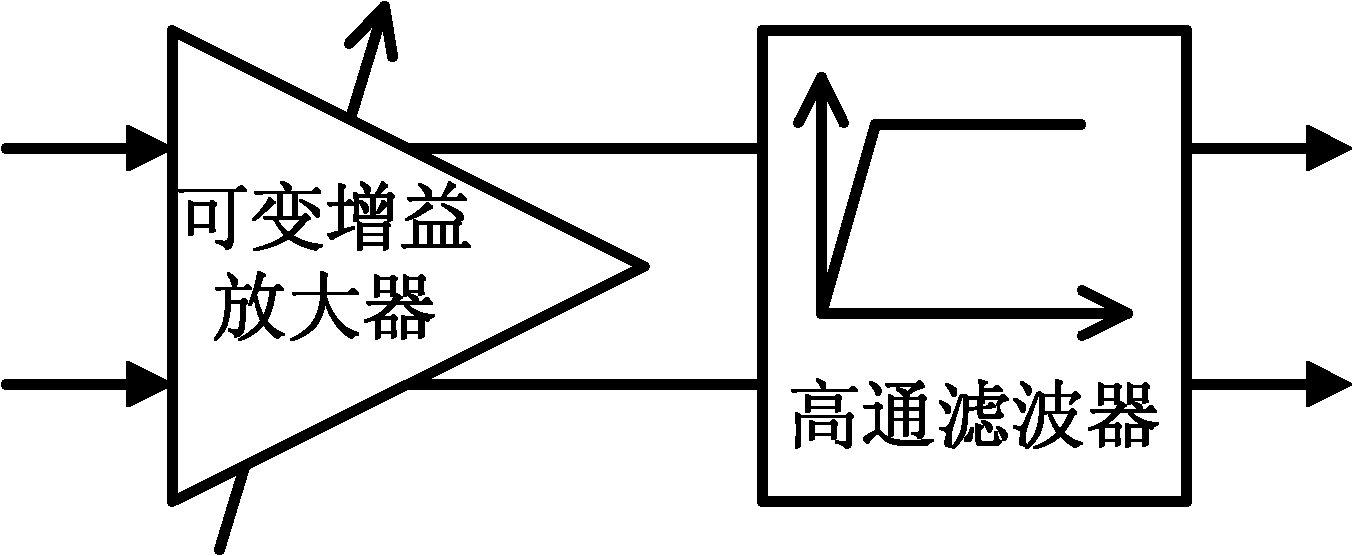
[0030] figure 1 A circuit diagram of a very small current source; figure 2 A circuit block diagram for the traditional high-pass filter to eliminate DC offset; image 3 A circuit block diagram for conventional DC offset removal using digital signal processing.
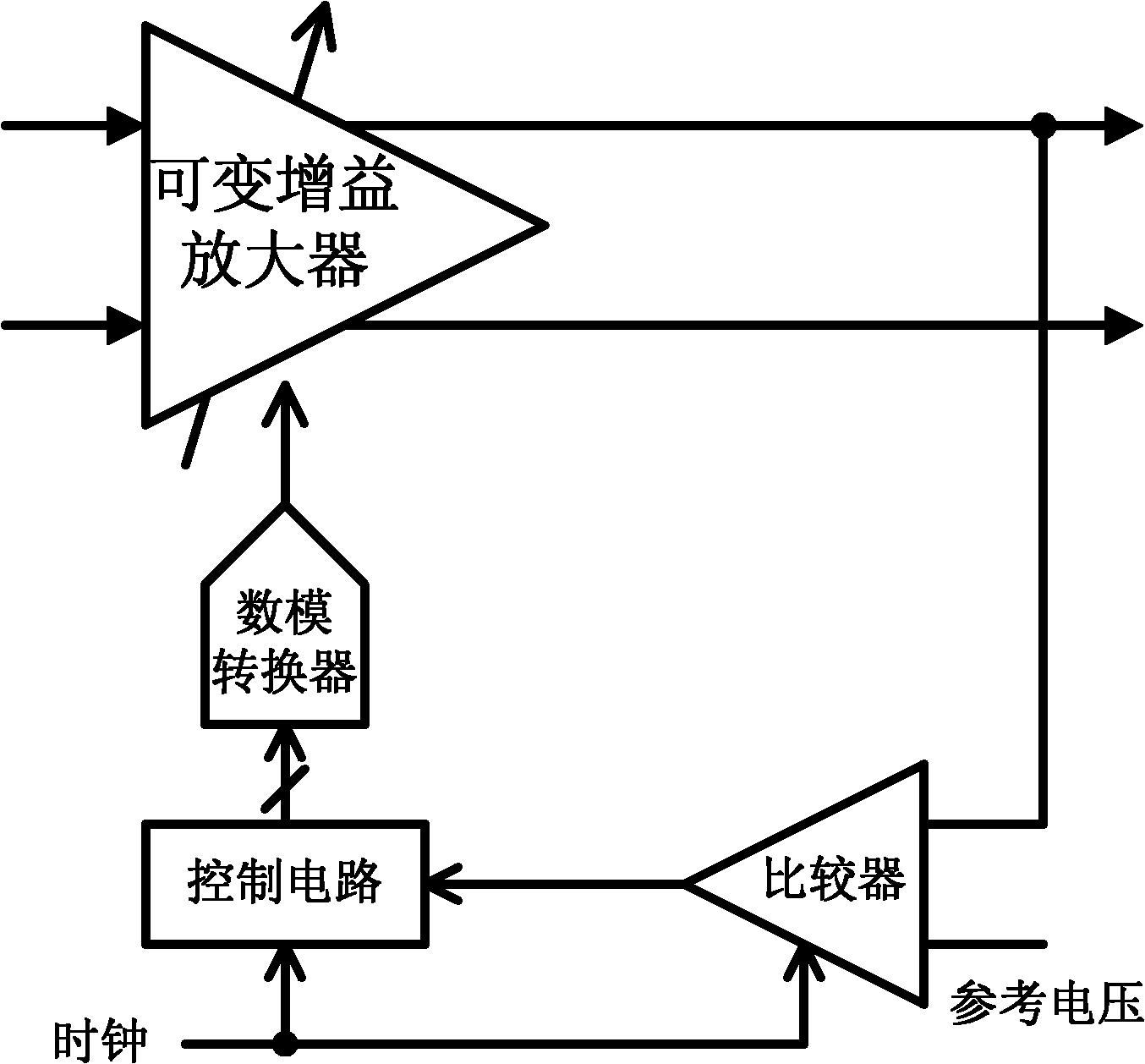
[0031] see Figure 4 As shown, the present invention is applied to the circuit block diagram of the embodiment of the low-frequency variable gain amplifier; including: a differential input pair, a current buffer, and a common-source output stage. Figure 4 The structure of variable gain amplifier using DC offset canceling circuit is given. The DC offset cancellation circuit consists of: a transconductance amplifier and a very small current source bias; the input of the transconductance amplifier is connected to the output of the variable gain amplifier for converting the output DC offset voltag...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com