Light-emitting diode packaging structure
A technology for light-emitting diodes and packaging structures, applied in electrical components, electrical solid-state devices, circuits, etc., can solve problems such as inability to implement mass production, perishable packaging structures, and shortening the life of LEDs, and is suitable for mass production. It is not easy to be broken and the contact area is increased.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0042] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the embodiments with reference to the accompanying drawings.
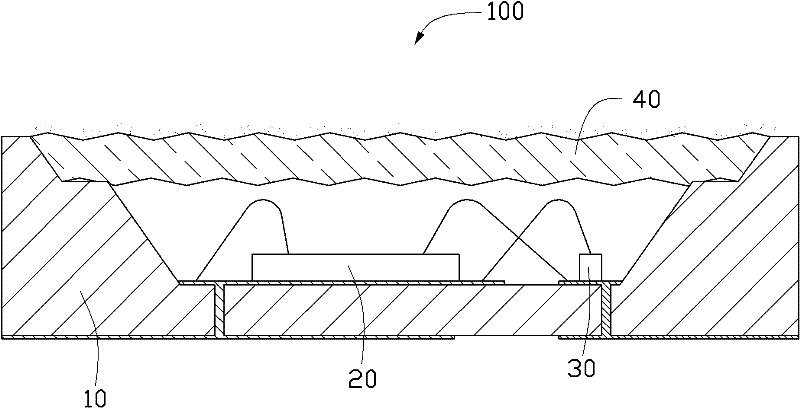
[0043] figure 1 Shown is a light emitting diode packaging structure 100 in the first embodiment of the present invention, the light emitting diode packaging structure 100 includes a substrate 10, an LED chip 20 disposed on the substrate 10, a stable structure fixed on the periphery of the LED chip 20 A voltage diode 30 and a lens 40 covering the LED chip 20 and the Zener diode 30.
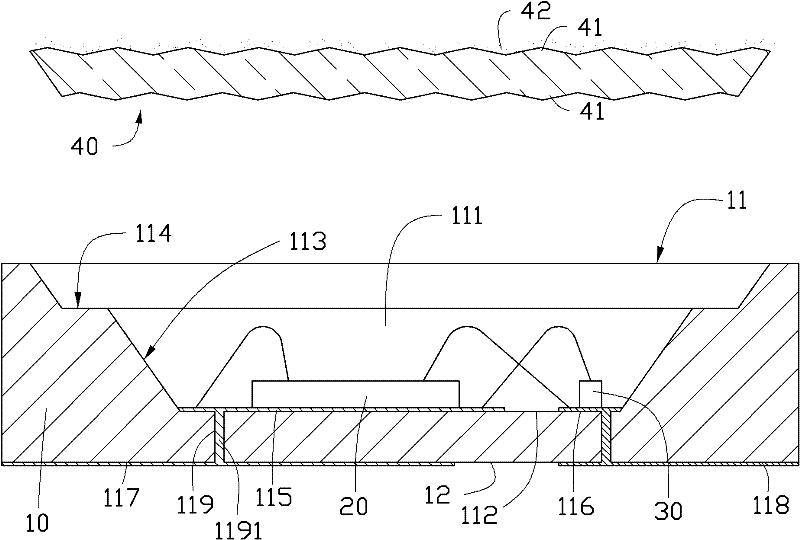
[0044] Please refer to figure 2 , the substrate 10 is a silicon substrate, which can be low resistance or high resistance. To further illustrate, the high-resistance silicon substrate has a resistivity (resistivity) of about 1 to 30,000 ohm-centimeters (ohm-centimeter) and can be doped with boron (B) or phosphorus (P), while the low-resistance silicon substrate has a resistance of The ratio is about 0.001 to 0.02 ohm-cm and can be doped with boron (B), ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com