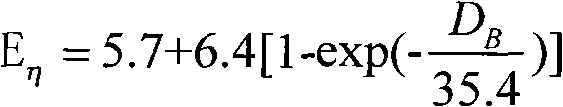Method for measuring content of short-chain branches in polyethylene copolymer
A technology of polyethylene copolymer and measurement method, which is applied in the direction of measuring devices, flow characteristics, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of limitations, failure to reflect the overall structure of samples, and high requirements for test sample preparation conditions, and achieve the effect of low requirements and easy operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] 1.1 Determination of the content of short chain branches in polyethylene copolymer standard samples
[0041]The standard sample used is a randomly selected polyethylene copolymer, and the infrared spectroscopic method is used according to the literature "infrared spectroscopic practical characterization of PE microstructure" [Xie Kan, Chen Dongmei, Cai Xia, etc. Synthetic Resin and Plastics, 2005, 22 (1) : 48-52], the method measures each ethylene and different monomer (butene, hexene) copolymer short chain branch content value, and each standard sample prepares 5 samples, and the result of testing respectively is averaged and set Set as the true value of the short chain branch content of the standard sample. The specific test steps are:
[0042] 1) Press the pellet or powder sample into a 0.4mm thick sheet at 170°C in a metal mold lined with aluminum foil;
[0043] 2) Use the MAGNA-IR 760 infrared spectrometer of Nigoli Company of the United States to test the sample...
Embodiment 2
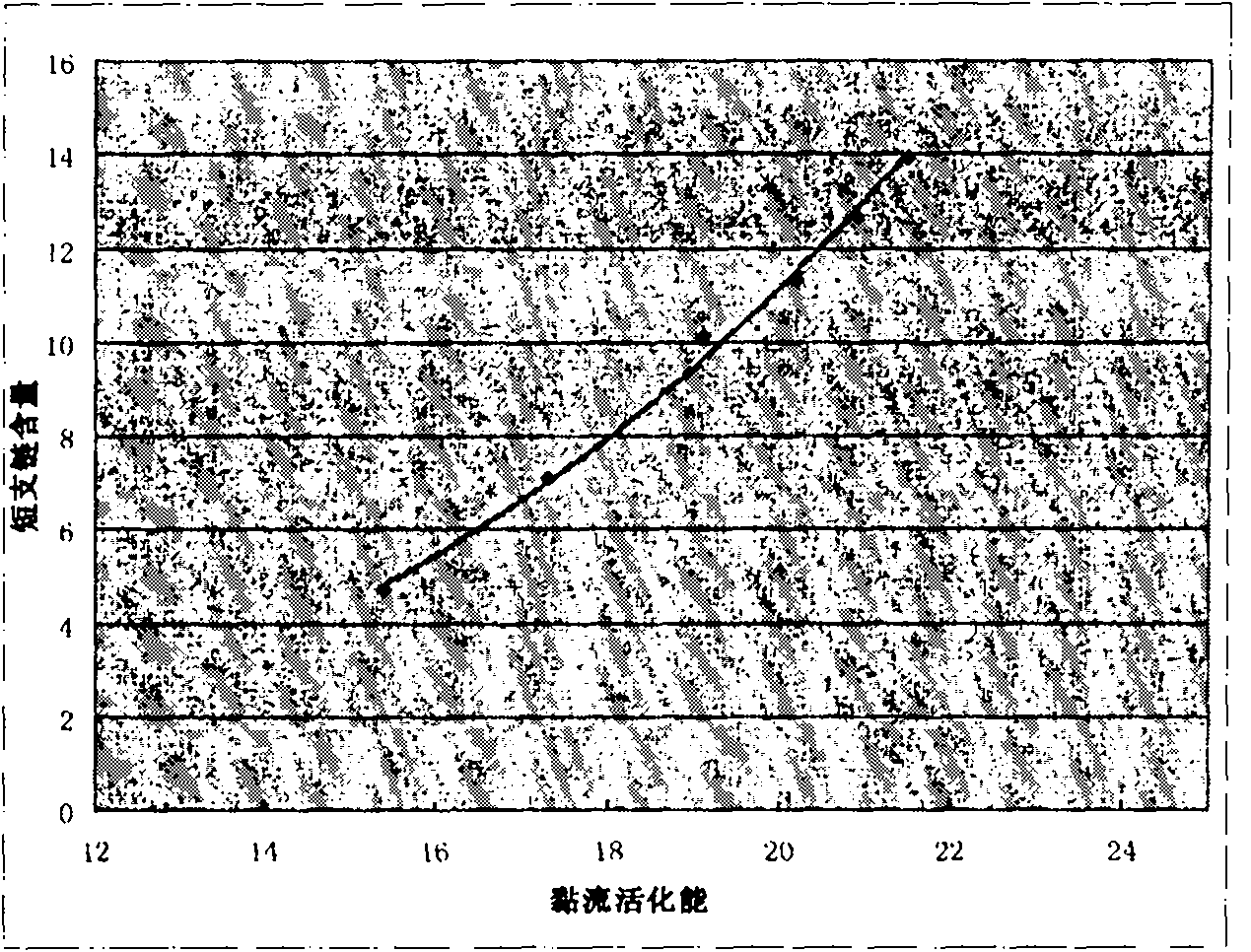
[0078] Viscous flow activation energy E of polyethylene copolymer at extremely low frequency η The assay method is with embodiment 1. According to E η Find the corresponding short chain branch content from the working curve, or put E η The value is to be entered into the regression equation to calculate the short chain branch content of the sample.
[0079] 2.1 Determination of short-chain branch content in ethylene-butylene copolymer
[0080] sample
15#
16#
17#
E. η / (KJ·mol -1 )
15.8
19.2
21.5
D B
5.01
9.39
13.50
D. B (IR)
5.1
9.3
13.6
absolute error
-0.09
0.09
-0.1
Relative error
1.76%
0.97%
0.74%
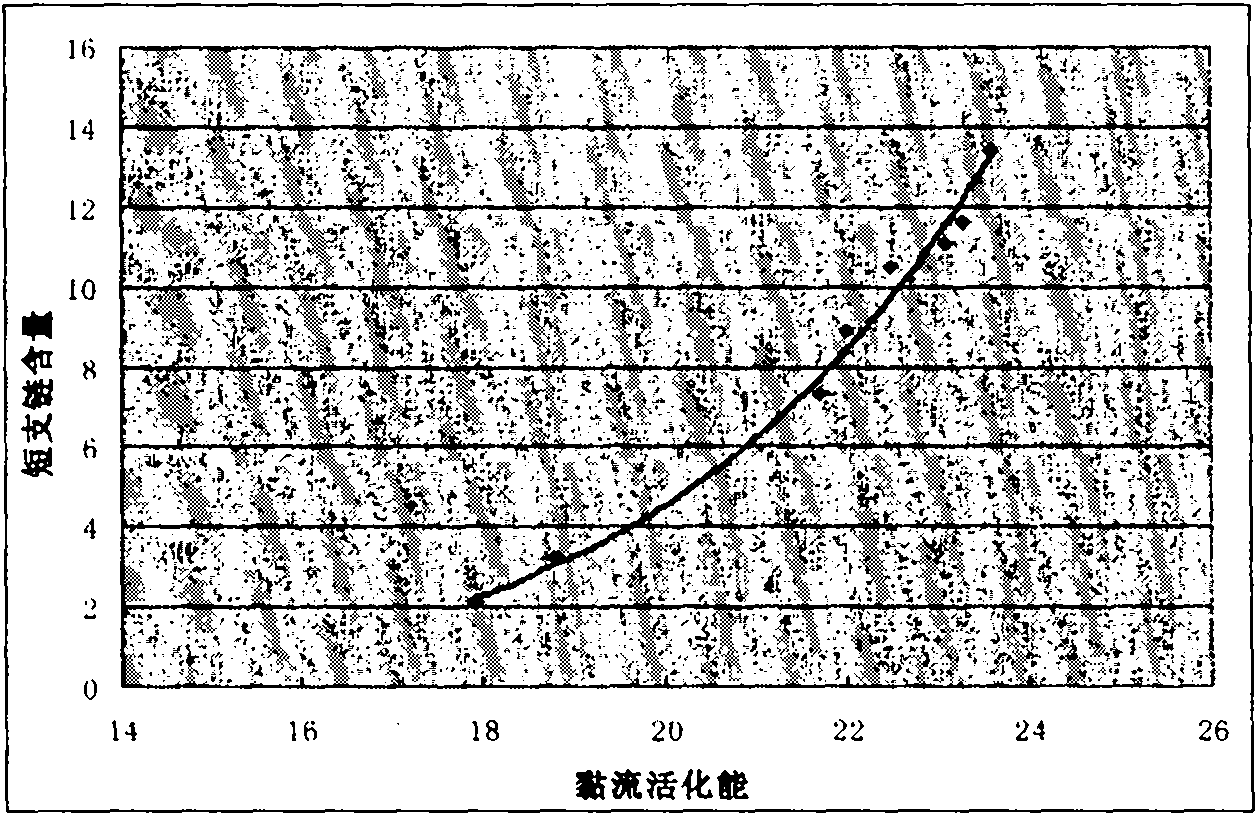
[0081] 2.2 Determination of short-chain branched chain content in ethylhexyl copolymer
[0082] sample
Embodiment 3
[0084] Viscous flow activation energy E of polyethylene copolymer at extremely low frequency η The assay method is with embodiment 1. The assay method of polyethylene copolymer short chain branch content is the same as embodiment 2. Prepare different samples for the same sample to test the reliability of the method.
[0085] 3.1 Determination of short-chain branched content in ethylene-butylene copolymer
[0086] sample
16#-1
16#-2
16#-3
16#-4
16#-5
E. η / (KJ·mol -1 )
19.1
19.2
19.3
19.0
19.1
D B
9.22
9.39
9.54
9.07
9.22
absolute error
-0.17
0
0.15
-0.32
-0.17
[0087] Average 9.29
[0088] Mean absolute error 9.29-9.39=-0.1
[0089] Relative error 0.1 / 9.39*100%=1.1%
[0090] 3.2 Determination of short-chain branched chain content in ethylhexyl copolymer
[0091] sample
19#-1
19#-2
19#-3
19#-4
19#-5
[0092] ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com