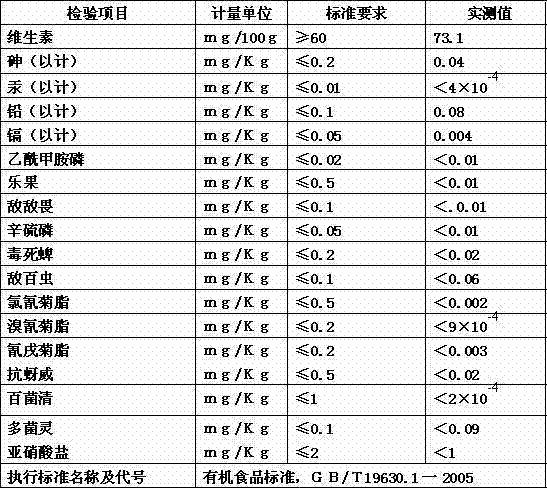
Technology for cultivating organic fruit and vegetable matrix
A substrate cultivation, organic substrate technology, applied in cultivation, soilless cultivation, organic fertilizer and other directions, can solve the problems of restricting popularization and application, mastering, not formulating water and fertilizer, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0056] Example 1: Standardized management of fertilizer requirements of different economic crops
[0057] Taking nitrogen and potassium in a crop of solanaceous vegetables for 18 weeks as an example, nitrogen 3.5 kg×40 m 3 ×16.9% (release rate)=23.66kg, potassium 2.2 kg×40 m 3 × 65% (release rate) = 57.2kg, which is the level of fertilizer supply, which is enough to meet the nutrient requirement of 10,000kg per mu of tomato crop.
[0058] The amount of fertilizer required for 1000kg of output of various economic crops Unit: kg
[0059] crop type Nitrogen (N%) Phosphorus (P205%) Potassium (K20%) tomato 2.2~2.8 0.5~0.8 4.2~4.8 cucumber 2.8~3.2 1.0 4.0 pumpkin 3.7-4.2 1.8-2.2 6.5~7.3 chili 3.5~5.4 0.8~1.3 5.5~7.2 winter melon 1.3~2.8 0.6~1.2 1.5~3.0 watermelon 2.5-3.3 0.8-1.3 2.9-3.7 Chinese cabbage 1.77 0.81 3.73 cauliflower 7.7~10.8 2.1~3.2 9.2~12.0 frame beans 8.1 2.3 6.8 ...
Embodiment 2
[0061] Embodiment 2: matrix cultivation groove example
[0062] The structure of standard cultivation tanks for solanaceous, melon and other vines is: length ≤ 40m, inner diameter width 48cm, height ≥ 15cm, clear distance between tanks 72cm; standard cultivation tank structure for leafy vegetables and other fast-growing fruits and vegetables: length ≤ 40m, inner diameter The width is 96cm, the height is ≥10cm, and the clear distance between the tanks is 48cm.
[0063] Application Effect and Cost Comparison of Several Typical Materials of Cultivation Groove
[0064] material One-time investment (yuan) Depreciation cost (yuan / year) Appearance apply effects brick 2000~4000 100~200 generally most cement board 2000~4000 100~200 it is good generally foam tank 5000~6000 500~600 most it is good Phosphopic soil tank 4000~5000 400~500 better it is good
Embodiment 3
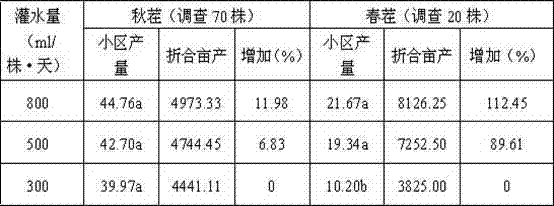
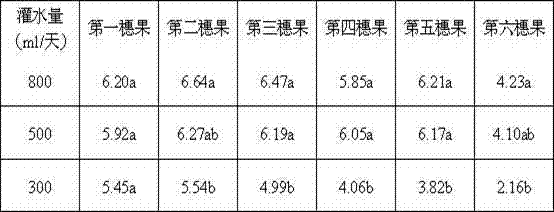
[0065] Example 3: Standardized management of irrigation volume for different crops in different growth periods
[0066] The amount of irrigation can significantly affect the growth and yield of tomatoes. Affected by the external climate, the impact of different irrigation amounts on the growth and yield of tomatoes in spring crops is more obvious than that in autumn crops.
[0067] The effect of different irrigation amounts in spring on the size of tomato fruit Unit: cm
[0068]
[0069] Effects of different irrigation amounts on the stem diameter of spring crop tomato Unit: cm
[0070]
[0071] Effect of different irrigation amounts on tomato yield Unit: kg
[0072]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com