Myoelectric prosthetic hand force tactile feedback method and tactile feedback myoelectric prosthetic hand system
A technology of tactile feedback and myoelectricity, applied in prosthetics, medical science, artificial arms, etc., can solve problems such as difficulty in adapting to normal life, feedback of force conditions, inability to realize external force perception of prosthetic hands, etc., and restore normal life , Prevent collisions, and improve the effect of normal life
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0043] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with accompanying drawing and specific embodiment
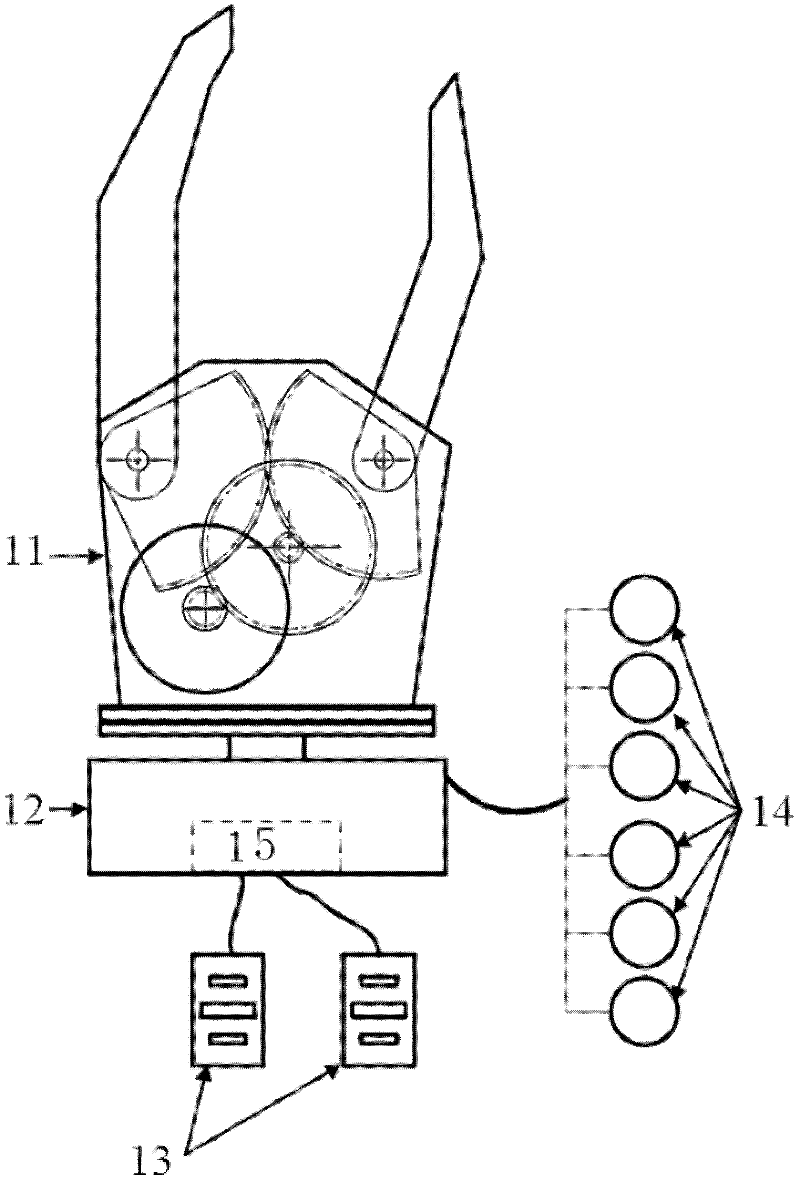
[0044] A kind of myoelectric artificial hand force tactile feedback method comprises steps:
[0045] 1) First use the three-dimensional force sensor installed on the base of the mechanical prosthetic hand to collect the three-dimensional force information on the mechanical prosthetic hand;
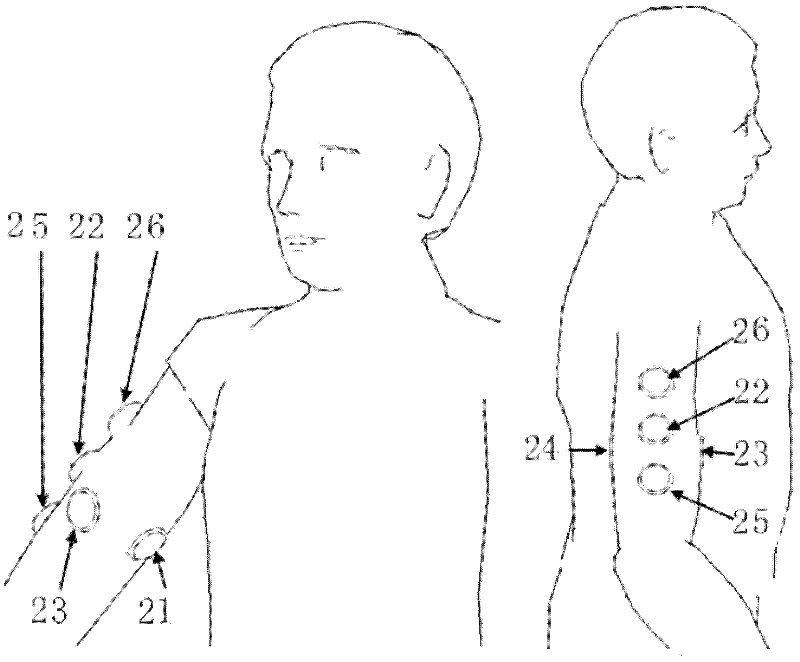
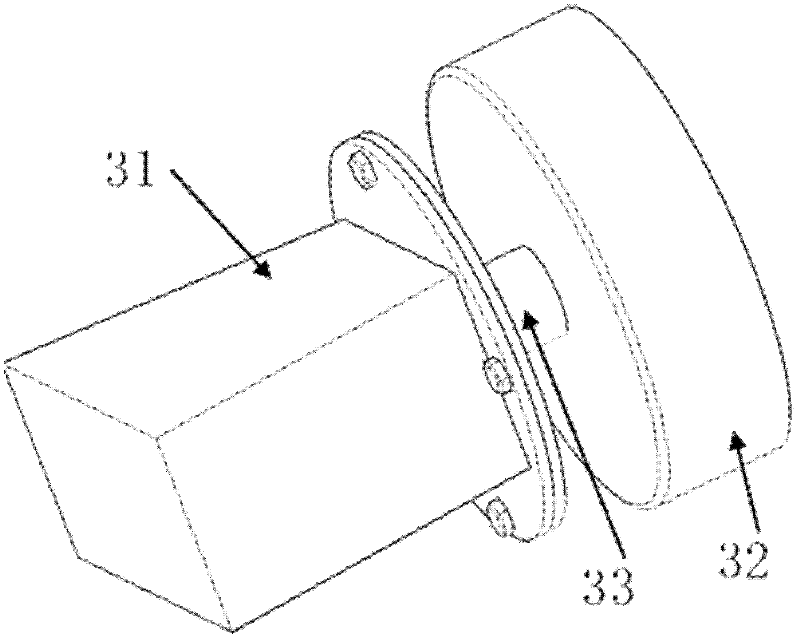
[0046] 2) Then convert the three-dimensional force information into a vibration signal, and drive the vibrator installed on the user; when the mechanical prosthetic hand is subjected to a three-dimensional force, the vibrator will vibrate on behalf of the corresponding force direction, and the vibration intensity and force magnitude Proportional.
[0047] There are 6 vibrators in total, which respectively represent the force in the positive direction of the X-axis, the force in the negative direction of the X-axis, the force in the positive direction of the Y-axi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com