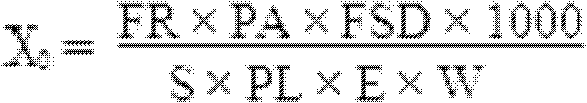Emulsion breaking method for aftosa oil emulsion inactivated vaccine
A technology of inactivated vaccines and oil emulsions, applied in the field of quality inspection of foot-and-mouth disease vaccines, can solve the problems of high capital expenditure, high requirements for experimental facilities, and long time consumption, and achieve high recovery rate, good antigen separation effect, and stability.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0015] The demulsification method of embodiment one foot-and-mouth disease oil emulsion inactivated vaccine
[0016] Take 100ml of commercial foot-and-mouth disease vaccine emulsified with ISA 206 adjuvant, put it into a 250ml separating funnel, add 6-20ml of demulsifier n-amyl alcohol (or choose any one of benzyl alcohol, chloroform, and n-hexanol), and fully suspend for 1 Minutes or more; put the separatory funnel into a refrigerator at 4°C, and let it stand for more than 30 minutes, oil and water can be seen to separate; separate about 34ml of the water phase layer, which contains the 146S antigen.
Embodiment 2
[0017] The recovery and content determination test of the 146S antigen after embodiment two foot-and-mouth disease oil emulsion inactivated vaccine demulsification
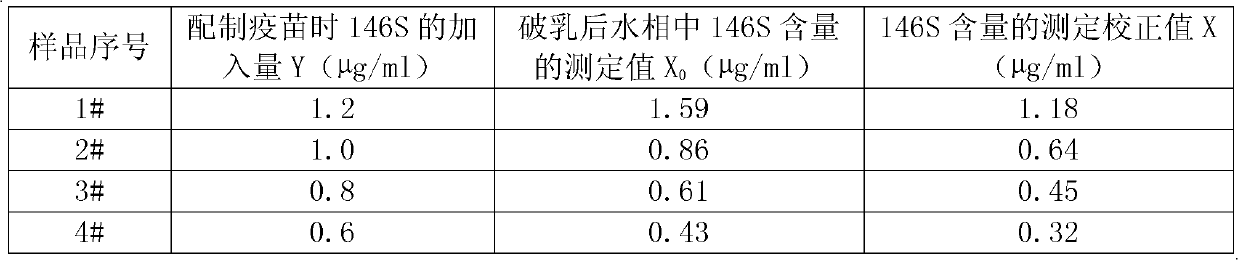
[0018] Get 4 parts of foot-and-mouth disease oil emulsion inactivated vaccine samples, respectively numbered as 1#-4#, according to the method in embodiment 1 for demulsification; get the water phase obtained after demulsification, that is, 146S antigen solution, according to the invention patent of application number 200910092779 The described sucrose density gradient ultraviolet light quantitative method detects the content of 146S antigen, and the specific steps are as follows:
[0019] 1. Concentration of 146S antigen solution: Ultracentrifuge containing 146S antigen solution, resuspend to 1 / 10 of the original volume with PBS solution to obtain concentrated antigen solution, and put it in a refrigerator at 2-8°C for later use;
[0020] 2. Prepare 15%-45% sucrose gradient: prepare 5 tubes of 15%-45% uniform lin...
Embodiment 3
[0035] 146S antigen content determination in embodiment three foot-and-mouth disease oil emulsion inactivated vaccines
[0036] The content determination method of 146S antigen in the foot-and-mouth disease oil emulsion inactivated vaccine is as follows:
[0037] (1) get the commercial foot-and-mouth disease inactivated vaccine of 100ml ISA 206 adjuvant emulsification, demulsify by the method in embodiment one, obtain containing 146S antigen aqueous phase about 34ml;
[0038] (2) Detect the 146S antigen content in the aqueous phase according to the sucrose density gradient ultraviolet light quantitative method described in Example 2 (X 0 ) was 0.78 μg / ml, and the corrected value (X) of 146S antigen content was further obtained as 0.58 μg / ml;
[0039] (3) According to the formula Y=-1.0343X 2 +2.244X-0.0082, the calculated 146S antigen content (Y) in the vaccine is 0.94 μg / ml.
[0040]It is known that the amount of 146S antigen added to the vaccine sample during preparation ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com