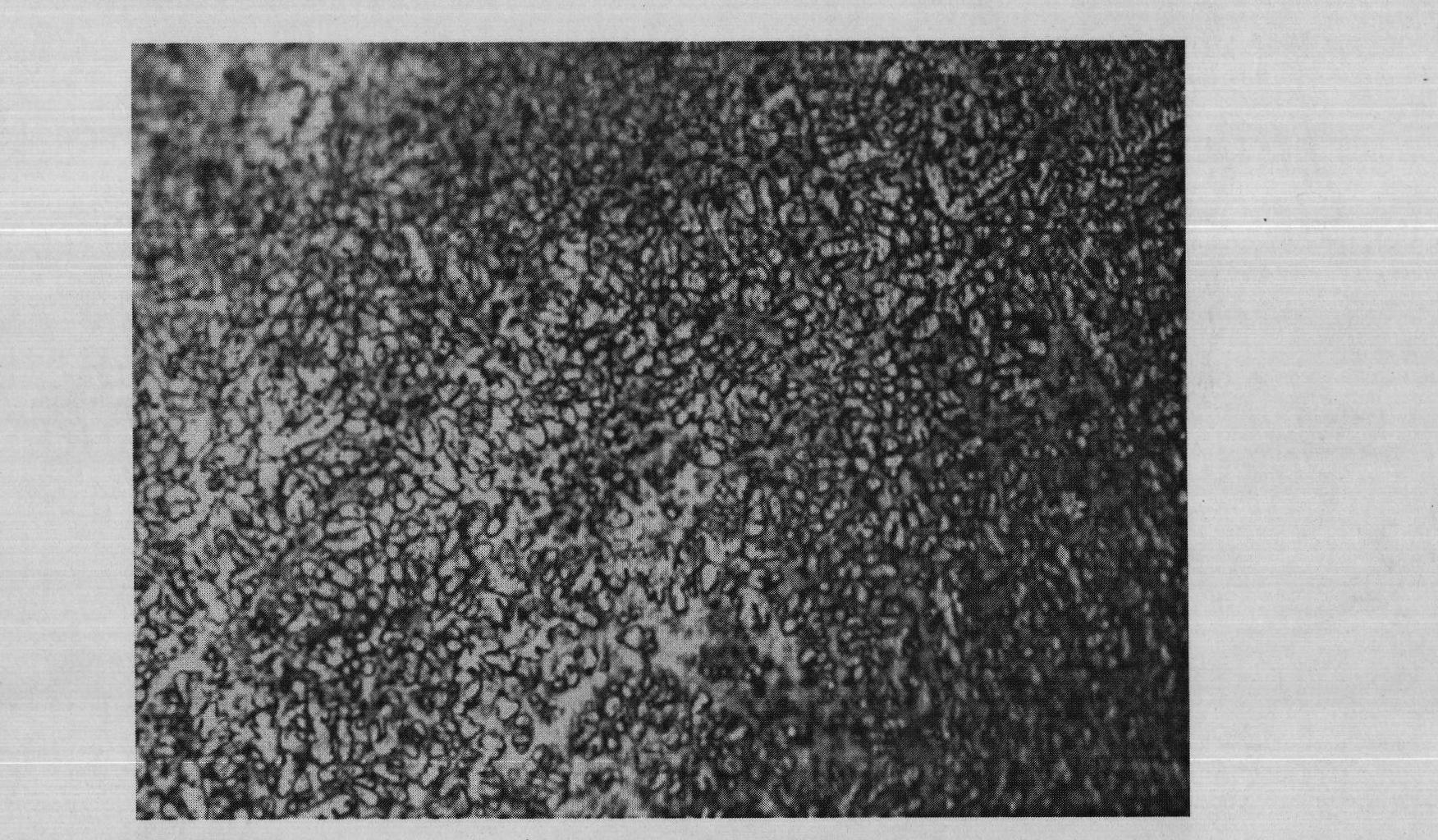
Metallographic corrosive agent for amorphous alloys and observation method for metallographic structures of amorphous alloys
A technology of amorphous alloy and metallographic structure, which is applied in the field of observation of amorphous alloy metallographic corrosion agent and amorphous alloy metallographic structure, can solve the problems of harmful environment, inconvenient observation of crystal phase, complicated preparation and use process, etc., and achieves The effect of fast corrosion speed, improved contrast, and easy identification
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
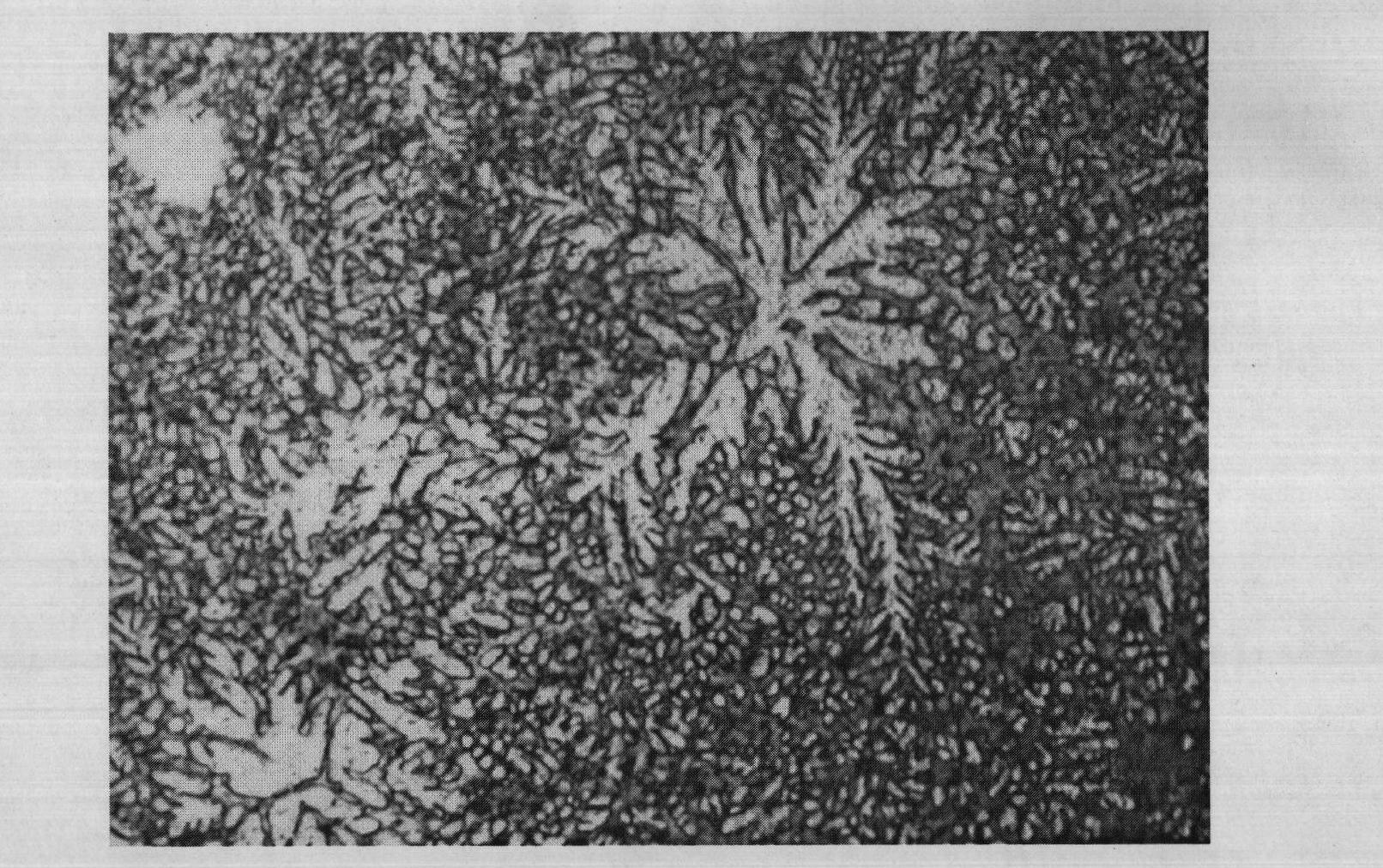
[0034] The sample is composed of Zr 56.2 Ti 13.8 Cu 6.9 Ni 5.6 be 12.5 Nb 5.0 After grinding and polishing the observation surface of the amorphous alloy sample, select a mixed solution containing 0.12mol / L hydrofluoric acid, 0.74mol / L phosphoric acid, 1.05mol / L oxalic acid, and water balance Etching for 60s, and then using 10 grams of KCl 3 , 0.3 g FeCl 3 Wipe with a mixed solution of 100ml of water for about 10s, and finally wash the metallographic observation surface with absolute ethanol, and dry it with a hair dryer to obtain an amorphous alloy sample A1.
Embodiment 2
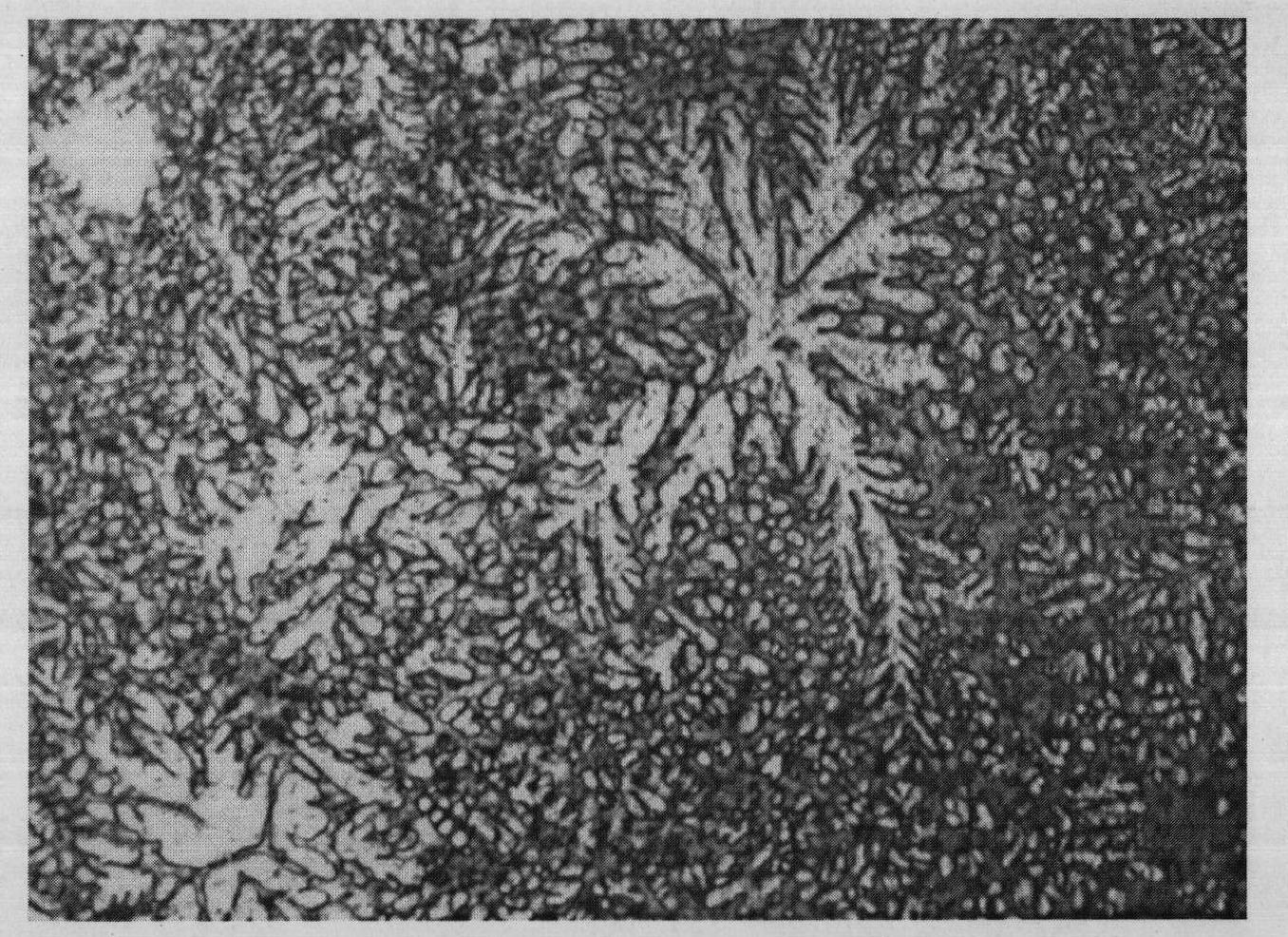
[0036] The sample is composed of Zr 56.2 Ti 13.8 Cu 6.9 Ni 5.6 be 12.5 Nb 5.0 After grinding and polishing the observation surface of the amorphous alloy sample, select a mixed solution containing 0.25mol / L hydrofluoric acid, 0.35mol / L phosphoric acid, 1.5mol / L oxalic acid, and water balance Etched for 50s, and then used containing 5 grams of KCl 3 , 1.0 g FeCl 3 Wipe with a mixed solution of 100ml of water for about 10s, and finally clean the metallographic observation surface with absolute ethanol, and dry it with a hair dryer to obtain an amorphous alloy sample A2.
Embodiment 3
[0038] The sample is composed of Zr 41.2 Ti 13.8 Cu 12.5 Ni 10 be 22.5 After the observation surface of the amorphous alloy is ground and polished, it is dipped in a mixed solution containing 0.45mol / L hydrofluoric acid, 0.74mol / L phosphoric acid, 1.70mol / L oxalic acid and the rest of the water. Eclipse for 30s, and then use 3.5 grams of KCl 3 , 1.5 g FeCl 3 Wipe with a mixed solution of 100ml of water for about 10s, and finally wash the metallographic observation surface with absolute ethanol, and dry it with a hair dryer to obtain an amorphous alloy sample A3.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com