Phase change energy storage material
A technology of phase change energy storage materials and nucleating agents, which is applied in the field of energy storage materials, can solve the problems of large supercooling degree of phase change energy storage materials, and achieve the effect of large latent heat of phase change
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Put 400g of calcium chloride crystalline hydrate into a 500ml beaker and heat to 40°C, then add 2g of barium sulfate and 4g of strontium chloride hexahydrate as nucleating agents while stirring, and continue to add 0.4g after the nucleating agents are completely dissolved Carboxymethyl cellulose and 0.4g hydroxyethyl cellulose, after stirring evenly, add 0.4g white graphite, after the white graphite is added and completely dissolved, the temperature is lowered and cooled to obtain a phase change energy storage material, which is put into a plastic container as a finished product to be prepared. use.
[0036] Perform performance measurement on the phase change energy storage material prepared in this embodiment:
[0037] The temperature drop method is used to test the phase change energy storage material, and the paperless recorder records the temperature, specifically:
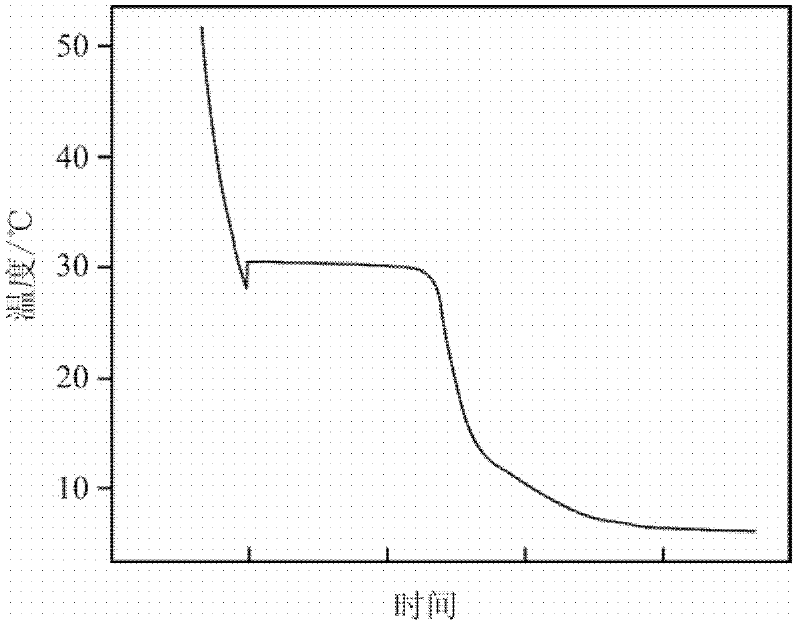
[0038] Heat the phase-change energy storage material prepared in this example to 60°C, then put it ...
Embodiment 2
[0040] Put 400g of Antarctica into a 500ml beaker and heat to 50°C, then add 2g of barium sulfate and 4g of strontium chloride hexahydrate as nucleating agents while stirring, and continue to add 0.4g of carboxymethyl fiber after the nucleating agents are completely dissolved Add 0.4g of white graphite and 0.4g of hydroxyethyl cellulose, stir evenly, then add 16g of ammonium chloride and 4g of magnesium hydroxide, cool down and cool down after the addition of the additives is completed and completely dissolved, and a phase change energy storage material is obtained. Put it into a plastic container to become a finished product for use.
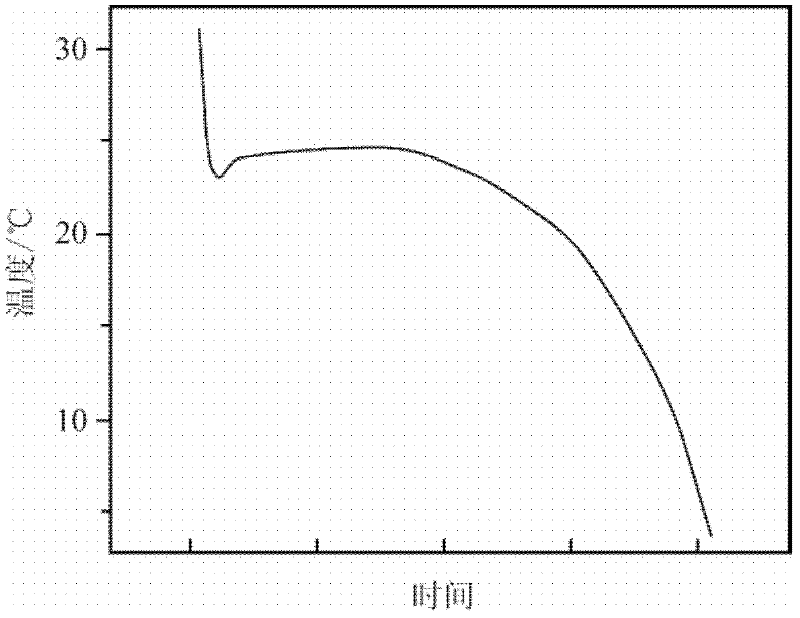
[0041] The same method as in Example 1 is used to measure the performance of the phase-change energy storage material prepared in this example, figure 2 The cooling curve of the phase-change energy storage material prepared for this example can be seen from the figure, the phase-change energy storage material is supercooled to 23.8°C and begin...
Embodiment 3
[0043] Put 400g of Antarctica into a 500ml beaker and heat to 45°C, then add 3g of barium sulfate and 6g of strontium chloride hexahydrate while stirring, and continue to add 0.6g of carboxymethylcellulose and 0.6g of Hydroxyethyl cellulose, after stirring evenly, add 0.4g of white graphite, after the addition of additives is completed and completely dissolved, the temperature is lowered and cooled to obtain a phase change energy storage material, which is put into a plastic container to become a finished product for use.
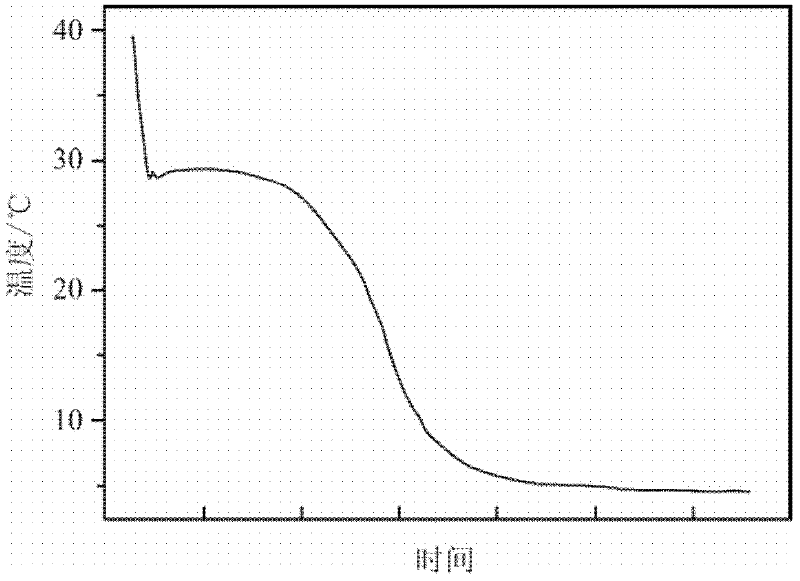
[0044] The same method as in Example 1 was used to measure the performance of the phase-change energy storage material prepared in this example. The phase-change energy storage material was heated to 40° C., put into a freezer and started to cool, and the liquid cooled rapidly. Such as image 3 Shown is the cooling curve of the phase change energy storage material prepared in this example. It can be seen from the figure that the phase change energy storage ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| phase transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com