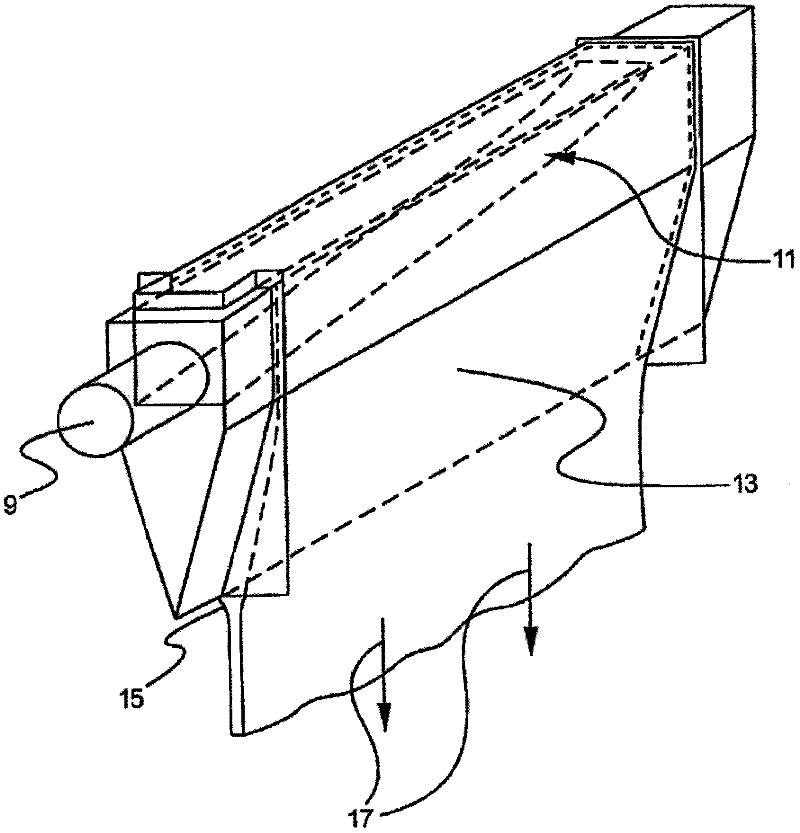
High static fatigue alumina isospipes
A technology of alumina and isobaric tubes, applied in glass forming, glass forming, manufacturing tools, etc., can solve problems such as isobaric tube breakage, unqualified LCD panels, and endangering melting equipment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0130] Incompatibility of Zircon with High Alkali Glass
[0131] This example describes the incompatibility of the zircon material of the '786 patent with peralkali glass. The glass used in this experiment is of the type disclosed in reference to US patent application 12 / 542946, and has an alkali content of more than 10 wt%, specifically 13.75 wt.%, which is mainly Na 2 O and a small amount of K 2 O.
[0132] The glass was heated to 1214°C (viscosity = 35kp), and the zircon sample was rotated inside the molten glass at a superficial velocity of 0.32 cm / sec for 14 days. Figure 11 is a micrograph of the resulting zircon / glass interior surface. In this figure, 110 is glass, 112 is the body of the zircon sample, and 111 is the worm-like or fish-egg-like zirconia that was found to form on the surface of the zircon. The presence of this zirconia results in zirconia defects in the glass, making zircon materials incompatible for use with high alkali glasses.
Embodiment 2
[0134] Compatibility of A1148 with high alkali glass
[0135] This example describes the compatibility of A1148 alumina with high alkali glass. The zircon sample tested in Example 1 was replaced with an A1148 alumina sample and the experiment in Example 1 was repeated. The result is as Figure 12 As shown, among them, 121 is glass, 122 is A1148 alumina. It can be seen that the A1148 material is compatible with high alkali glasses, which did not show any apparent changes over the entire testing period.
Embodiment 3
[0137] Preparation of Alumina with High Static Fatigue Performance
[0138] This example describes the preparation of a high static fatigue alumina material suitable for making the main body of an isopipe (hereinafter referred to as "HSF alumina" for repeated reference).
[0139] The starting material for the preparation of HSF alumina was alumina plate obtained from Coors / Tek, Inc. (Golden, Colorado), sold under the designation AD-998. According to the manufacturer's report, the plates are said to contain 99.8 wt% Al 2 o 3 .
[0140] Figure 13 Shown is the SEM image of the initial grain size of the resulting AD-998. To increase the grain size, the panels were placed on high-purity alumina positioning sand in a high-purity clay box and annealed in air at 1700°C or 1750°C for 72 hours. The results of the annealing process are shown in Figure 14 and 15 ,in Figure 14 It is annealed at 1700℃, Figure 15 It is annealed at 1750°C. It can be seen that the grains of the a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com