Multi-phase light-assisted Fenton catalyst and preparation method thereof
A catalyst, fec2o4 technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, physical/chemical process catalysts, chemical/physical processes, etc., can solve the problems of low catalytic activity, difficult to degrade non-dye organic pollutants, etc., and achieve high catalytic activity Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] r-TiO 2 Preparation of HAP-coated r-TiO by immersion in artificial simulated body fluids to induce HAP deposition 2 (HAP-TiO 2 ), wherein the coating amount of HAP is 2.9%; then the HAP-TiO 2 Placed in 0.0055 mol / L FeC 2 o 4 In the solution, stir well, and evaporate all the water in a water bath at 100 °C to obtain a mixed powder, in which Fe and TiO 2 The mass ratio of the mixture is 2:100; finally, the mixed powder is heated in a tube furnace at a temperature of 400 °C, and the furnace is filled with an argon atmosphere to obtain Fe-HAP-TiO 2 .
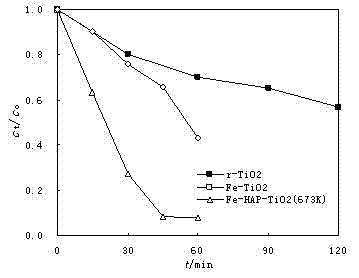
[0043] figure 1 Indicates that different catalysts can catalyze H 2 o 2 Degradation of atrazine. show that r-TiO 2 When used as a catalyst, the degradation rate of atrazine was only 40% after 120 min of reaction, but for r-TiO 2 For loading Fe treatment, that is, Fe-TiO 2 When used as a catalyst, the degradation rate is nearly 60% after 60 minutes of reaction; while the Fe-HAP-TiO prepared at a calcination tempera...
Embodiment 2
[0046] As described in Example 1, the mixed powder is heated in a tube furnace at a temperature of 300-900° C., wherein an argon atmosphere is passed through the furnace to obtain Fe-HAP-TiO2 samples at different calcination temperatures, wherein Fe-loaded The amount is 2%.
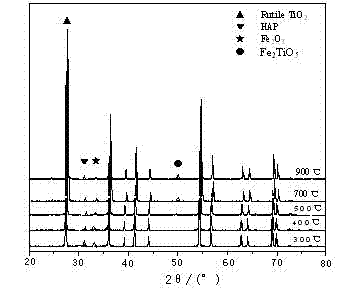
[0047] The TiO 2 The crystal forms of all exist in the rutile form, which is different from the precursor TiO 2 The crystal form distribution is consistent; image 3 As shown, the characteristic diffraction peak of HAP appears at about 31 (°) of the sample 2θ, and the characteristic diffraction peak of α-Fe appears at about 33 (°). 2 o 3 The characteristic diffraction peaks indicate that the sample generated HAP and α-Fe 2 o 3 A new phase; when the calcination temperature reaches 600 ℃ and 700 ℃, the sample appears α-Fe at 2θ=33.1 (°) 2 o 3 The characteristic diffraction peak of is slightly weakened, and Fe appears at 2θ=48.7(°) 2 TiO 5 The new characteristic diffraction peak of , that is, Fe has...
Embodiment 3
[0051] As described in Example 1, first prepare HAP-TiO with 2.9% HAP coating 2 , then HAP-TiO 2 Place 0.0055 mol / L FeC in different proportions with Fe 2 o 4 In the solution, stir well, and evaporate all the water in a water bath at 100 °C to obtain a mixed powder, in which Fe and TiO 2 The mass ratios are 0, 1, 2, 4, 5:100 respectively; finally, the mixed powder is heated in a tube furnace at a temperature of 400 °C, and an argon atmosphere is passed through the furnace to obtain Fe with different Fe loads. -HAP-TiO 2 sample.
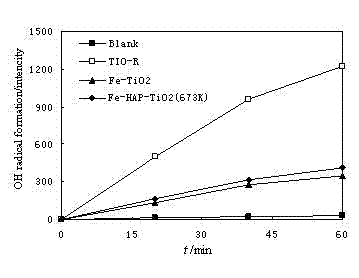
[0052] Figure 6 showed that, for HAP-TiO 2 For loaded Fe treatment, its catalytic activity is low; 2% Fe-loaded Fe-HAP-TiO 2 The sample has better catalytic activity, while Fe-HAP-TiO with higher Fe loading 2 Samples, such as 3-5%, the catalytic activity began to decline.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com