Substrate processing device and method
A technology of a substrate processing device and a substrate processing method, which is applied in the directions of optics, instruments, and optomechanical equipment, and can solve problems such as reduction, poor development, resist pattern film thickness deviation, resist pattern dimensional accuracy, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
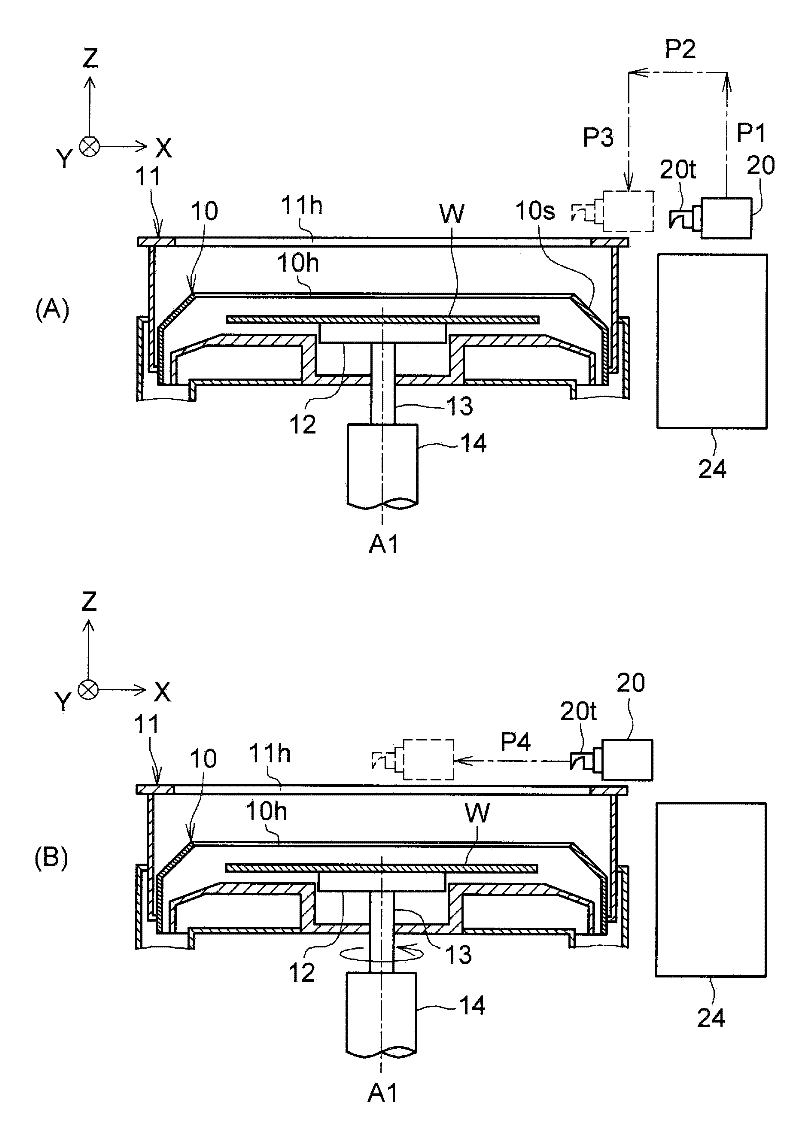
[0050] figure 1 is a diagram schematically showing the main configuration of a developing device 1 as a substrate processing device according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention, figure 2 is showing figure 1 A plan view of a part of the developing device 1 is shown. shown in schematic section figure 1 part of the structure. Such as figure 1 As shown, the developing device 1 has: a rotary disk (support member) 12 supporting the back surface of a semiconductor wafer W (hereinafter, simply referred to as “wafer W”); The developing device 1 is a device for performing development treatment by a spray development method on a photosensitive resin film (not shown) which is a film to be processed formed on the upper surface of the wafer W. As shown in FIG. The photosensitive resin film is a resist film formed by applying, for example, a spin coating method. Before the wafer W is loaded into the developing device 1, it is exposed with light passing through the mask blank by ...
Embodiment approach 2
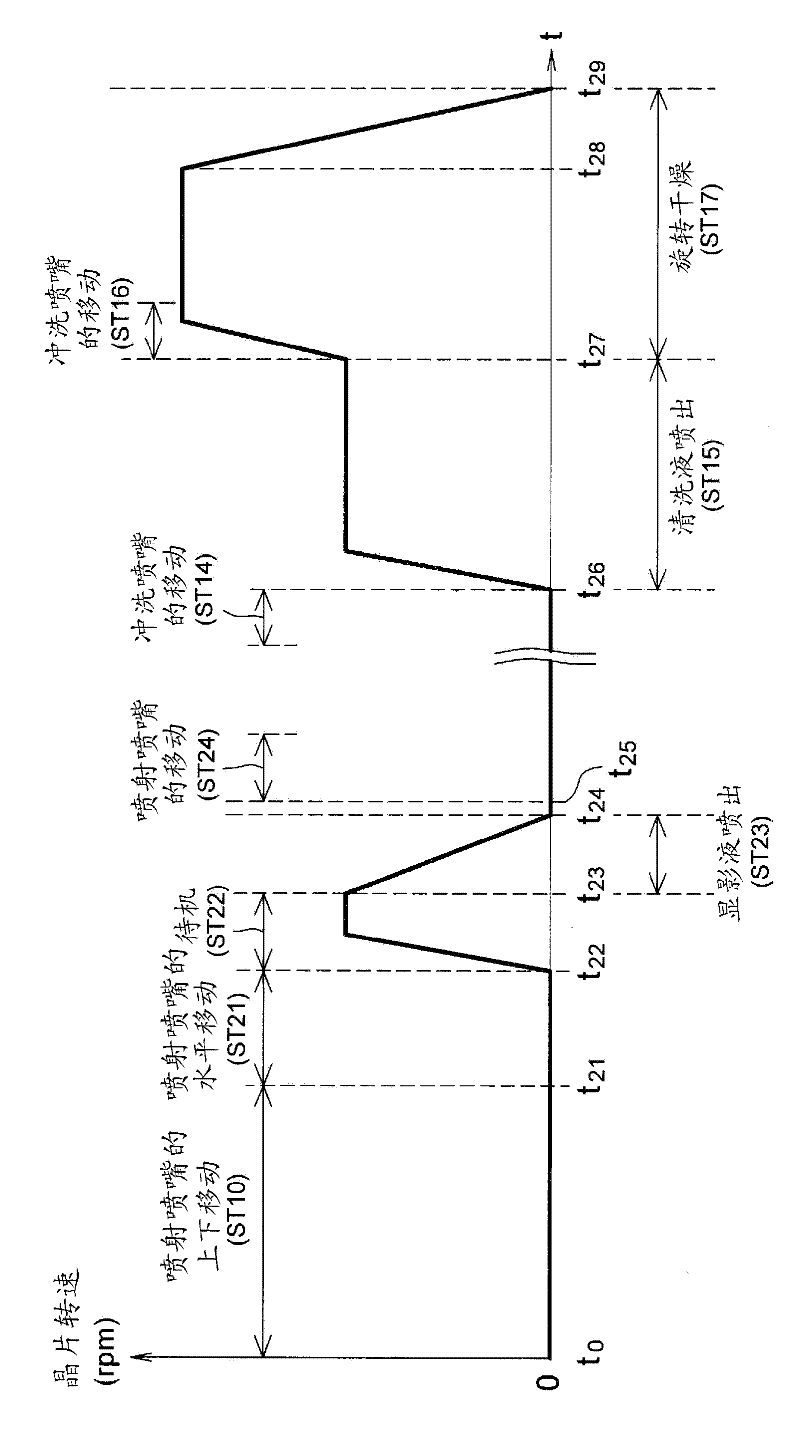
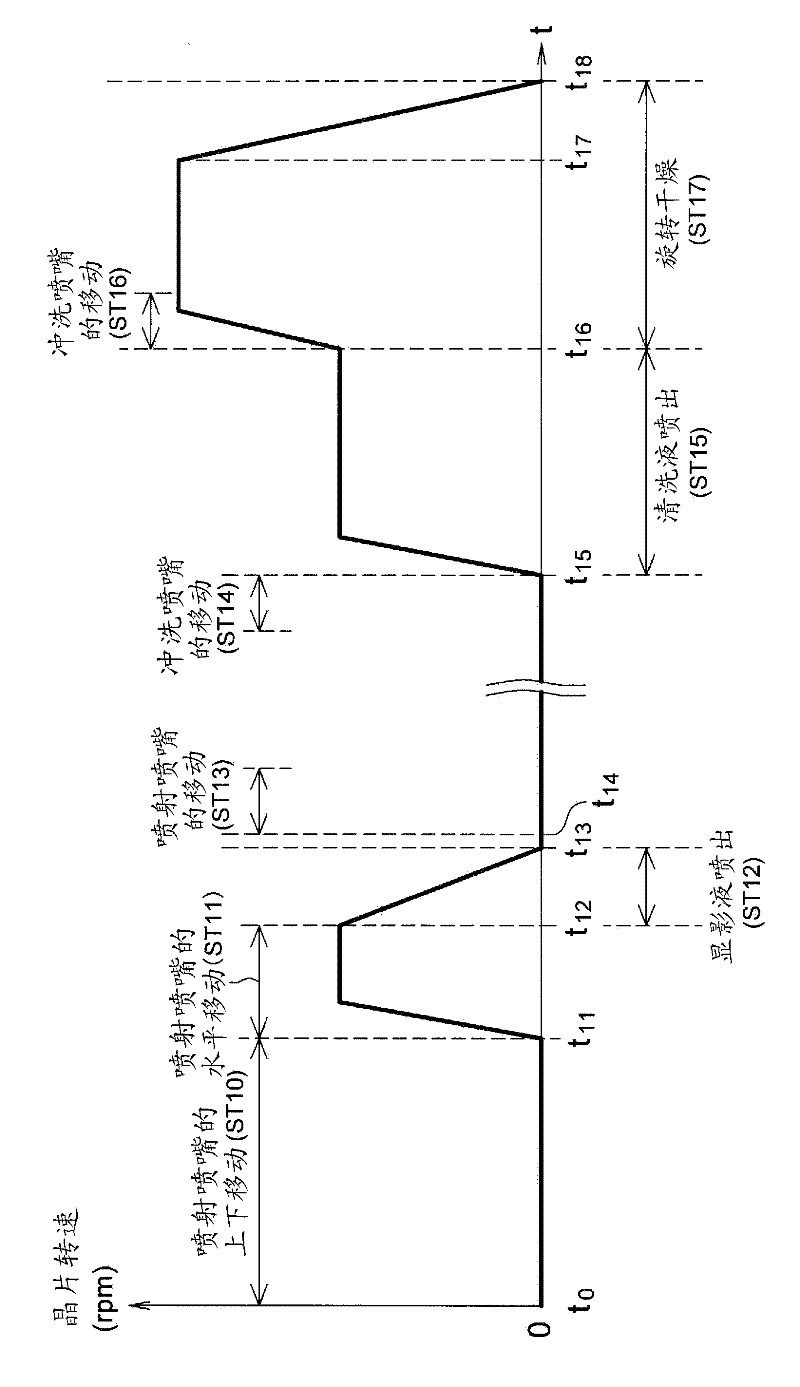
[0072] Next, Embodiment 2 of the present invention will be described. The developing device of Embodiment 2 has the same configuration as that of the developing device of Embodiment 1 except for the order of the developing process. Figure 8 It is a timing chart schematically showing an example of the sequence of the development process in the second embodiment.
[0073] As in the case of Embodiment 1, when the sequence starts, the spray nozzle moving mechanism 21 moves the spray nozzle 20 up and down (step ST10 ). Specifically, as Figure 4 As shown in (A), the ejection nozzle moving mechanism 21 raises the ejection nozzle 20 on the path P1, moves it horizontally on the path P2, and lowers the ejection nozzle 20 to a position outside the outer edge of the wafer W on the path P3.
[0074] Then, the ejection nozzle moving mechanism 21 moves the ejection nozzle 20 in the horizontal direction so that the tip portion 20t of the ejection nozzle 20 is located at the ejection posit...
Embodiment approach 3
[0079] Next, Embodiment 3 of the present invention will be described. The developing device of Embodiment 3 has the same configuration as that of the developing device 1 of Embodiment 1 except for the order of the developing process. Figure 9 It is a timing chart schematically showing an example of the sequence of the developing process in the third embodiment.
[0080] Such as Figure 9 As shown in , the developer discharge control unit 44 reaches the discharge position at a predetermined time t after the spray nozzle 20 reaches the discharge position. 33 Time t advanced by offset time (offset time) δ (for example, 0.5 seconds) 32 The developer is started to be ejected from the ejection nozzle 20 (step ST12B). Other aspects are the same as those of Embodiment 1 image 3 in roughly the same order.
[0081] In this way, according to Embodiment 3, for example, even when the residual developer adhering to the jet nozzle 20 is scattered on the wafer W due to the impact or in...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com