Surface hot dipping and pore sealing method of neodymium-iron-boron permanent magnet material
A permanent magnet material, NdFeB technology, applied in the direction of magnetic materials, inorganic materials, magnetic objects, etc., can solve the problems of poor corrosion resistance of NdFeB permanent magnets
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
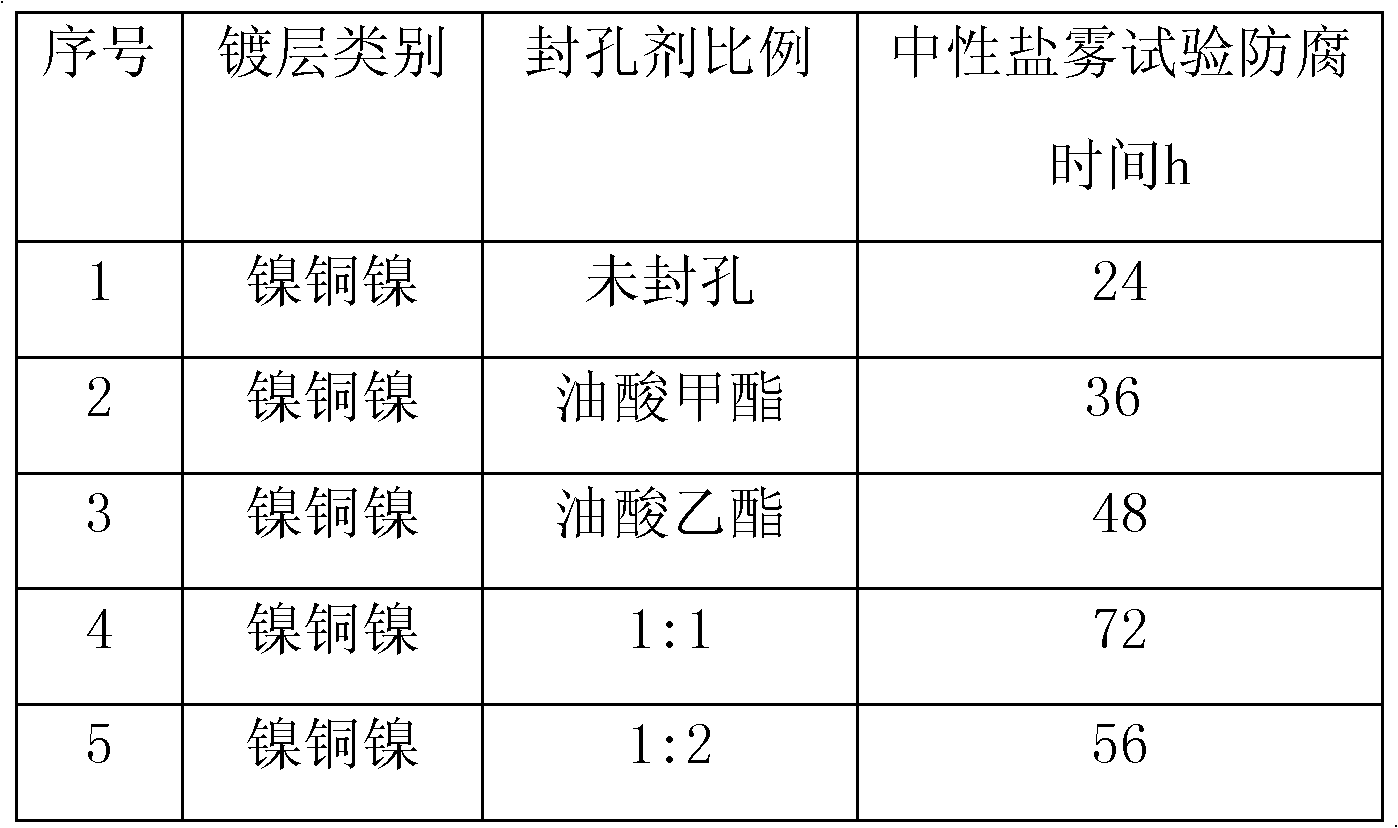
[0013] Example 1: 5 pieces of NdFeB permanent magnets with a brand name of 35SH and a specification of 45×45×8.7mm are used, one of which is directly subjected to mechanical chamfering, degreasing, pickling, and activation pretreatment processes, and then the NdFeB permanent magnet The surface of the boron permanent magnet is plated with nickel-copper-nickel coating. The remaining 4 blocks are operated according to the following process steps:
[0014] (1) One or both of propyl oleate and butyl oleate are prepared into four sealing agents according to the ratio of 1:1 and 1:2;
[0015] (2) Put the NdFeB permanent magnet into the oven to heat, the heating temperature is 200°C, and count for 2 hours after reaching the set temperature;
[0016] (3) Take out the NdFeB permanent magnets from the oven, completely immerse the four permanent magnets in the four sealing agent solutions, and take them out after the surface temperature of the permanent magnets is lower than 40°C;
[00...
Embodiment 2
[0022] Five pieces of NdFeB permanent magnets with the brand name of 35SH and a specification of 45×45×8.7mm are used, one of which is directly subjected to mechanical chamfering, degreasing, pickling, and pre-activation pretreatment processes, and then on the surface of the NdFeB permanent magnet. Nickel-copper-nickel plating. The remaining 4 blocks are operated according to the following process steps:
[0023] (1) Prepare a sealing agent with propyl oleate and butyl oleate in a ratio of 1:1;
[0024] (2) Put four NdFeB permanent magnets into the oven to heat, the heating temperature is 120, 160, 200, 240 ℃ respectively, and count for 2 hours after reaching the set temperature;
[0025] (3) Take out the NdFeB permanent magnets from the oven, completely immerse the remaining four permanent magnets in the sealing solution, and take them out after the surface temperature of the magnets is lower than 40°C;
[0026] (4) Carry out mechanical chamfering, degreasing, pickling, act...
Embodiment 3
[0031] Five pieces of NdFeB permanent magnets with the brand name of 35SH and a specification of 45×45×8.7mm are used, one of which is directly subjected to mechanical chamfering, degreasing, pickling, and pre-activation pretreatment processes, and then on the surface of the NdFeB permanent magnet. Nickel-copper-nickel plating. The remaining 4 blocks are operated according to the following process steps:
[0032] (1) Prepare a sealing agent with propyl oleate and butyl oleate in a ratio of 1:1;
[0033] (2) Put the NdFeB permanent magnet into the oven to heat, the heating temperature is 200 ℃, and after reaching the set temperature, time the heating for 1h, 1.5h, 2h, 2.5h respectively;
[0034] (3) Take out the NdFeB permanent magnets from the oven, completely immerse the remaining four permanent magnets in the sealing agent solution, and take them out after the surface temperature of the magnets is lower than 40°C;
[0035] (4) Perform mechanical chamfering, degreasing, pic...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com