Magnesium-based hydrogen storage alloy composite material with added metal sulfide
A magnesium-based hydrogen storage alloy and metal sulfide technology, which is applied in the field of magnesium-based hydrogen storage alloy composite materials, can solve the problems that the hydrogen desorption rate has not been significantly improved, the hydrogen desorption kinetics has not been significantly improved, and the kinetic performance is not ideal. , to achieve the effects of easy industrialization and promotion, easy operation and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
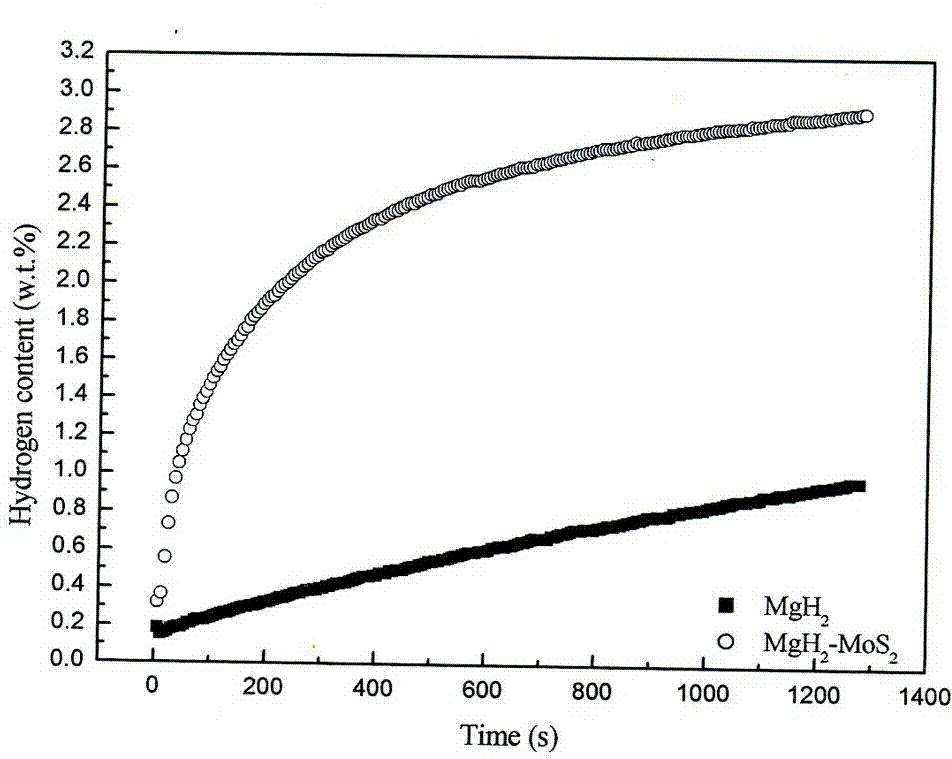
[0025] In an argon atmosphere, an appropriate amount of magnesium powder with a particle size of 100 mesh was weighed and placed in a hydrogenation reactor. The temperature was kept at 400 °C and a hydrogen pressure of 4 MPa for 1 h to convert it into MgH. 2 , naturally cooled to room temperature, taken out under the protection of argon atmosphere, and added to the hydrogenated MgH 2 MoS with a particle size of 100 mesh is added to the powder 2 The powder was mixed uniformly in a mass ratio of 10:1. The mixed powder was placed in a ball mill tank and ball milled under the protection of hydrogen atmosphere. The ball quality was stainless steel. The ball mill was a Pulverisette6 planetary ball mill. The rotation speed of the ball mill tank was 450 r / min , the mass ratio of ball to material is 29:1, the intermittent time is 15 min, and the ball milling time is 1 h. The magnesium-based hydrogen storage alloy composites prepared by ball milling were tested for hydrogen absorption ...
Embodiment 2
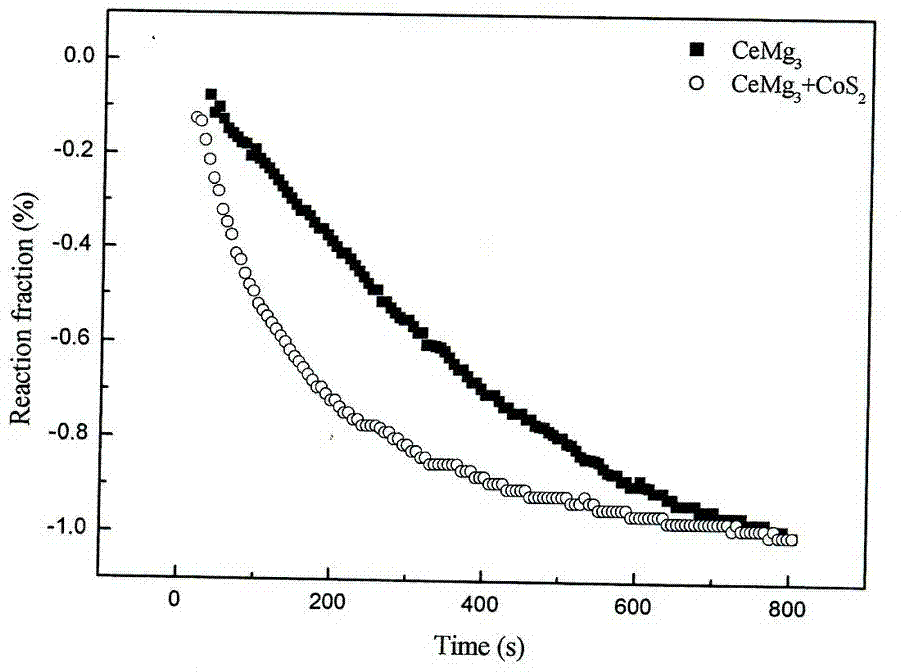
[0027] CeMg 3 The alloy was mechanically pulverized to 40 mesh under the protection of argon atmosphere, and an appropriate amount of powder was weighed and placed in a hydrogenation reactor, kept at 300 °C and 3 MPa hydrogen pressure for 1 h to convert it into CeH 3 and MgH 2 , cooled to room temperature naturally, and taken out under the protection of argon atmosphere. Under the protection of argon atmosphere, CoS with a particle size of 200 mesh was added to the hydrogenated magnesium-based alloy powder 2 The powder was mixed uniformly according to the mass ratio of 10:3. The mixed powder was placed in a ball mill tank and ball milled under the protection of hydrogen atmosphere. The ball quality was stainless steel. The ball mill was a Pulverisette6 planetary ball mill, and the speed of the ball mill tank was 550 r / min , the mass ratio of ball to material is 33:1, the intermittent time is 5 min, and the ball milling time is 3 h. The magnesium-based hydrogen storage alloy...
Embodiment 3
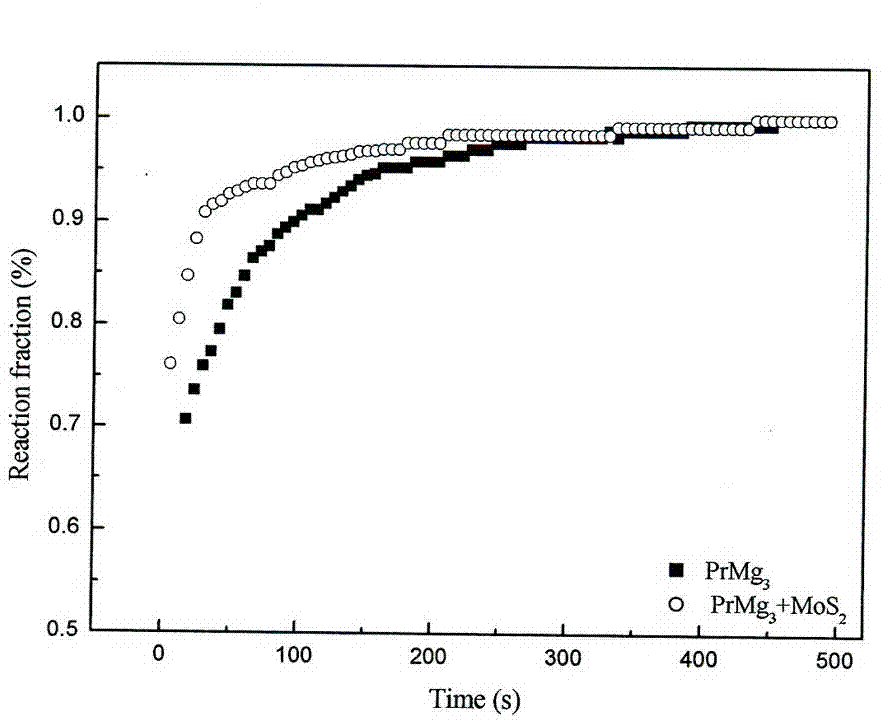
[0029] PrMg 3 The alloy was mechanically pulverized to 70 mesh under the protection of a hydrogen atmosphere, and an appropriate amount of powder was weighed and placed in a hydrogenation reactor. 3 and MgH 2 , cooled to room temperature naturally, and taken out under the protection of argon atmosphere. Under the protection of argon atmosphere, MoS with a particle size of 100 mesh was added to the hydrogenated magnesium-based alloy powder 2 The powder is mixed evenly according to the mass ratio of 5:1. The mixed powder is placed in a ball mill tank and ball milled under the protection of hydrogen atmosphere. The ball quality is stainless steel. The ball mill is a Pulverisette6 planetary ball mill, and the speed of the ball mill tank is 500 r / min. , the mass ratio of ball to material is 31:1, the intermittent time is 30 min, and the ball milling time is 2 h. The magnesium-based hydrogen storage alloy composites prepared by ball milling were tested for hydrogen absorption rat...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size (mesh) | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size (mesh) | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com