Oblique incident laser particle analyzer
A laser particle size analyzer and oblique incidence technology, applied in the field of particle size analyzer, can solve the problems of small angle range, low sensitivity and resolution, and achieve the effect of expanding the receiving angle, increasing the sensitivity and resolution, and improving the particle size distribution range.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
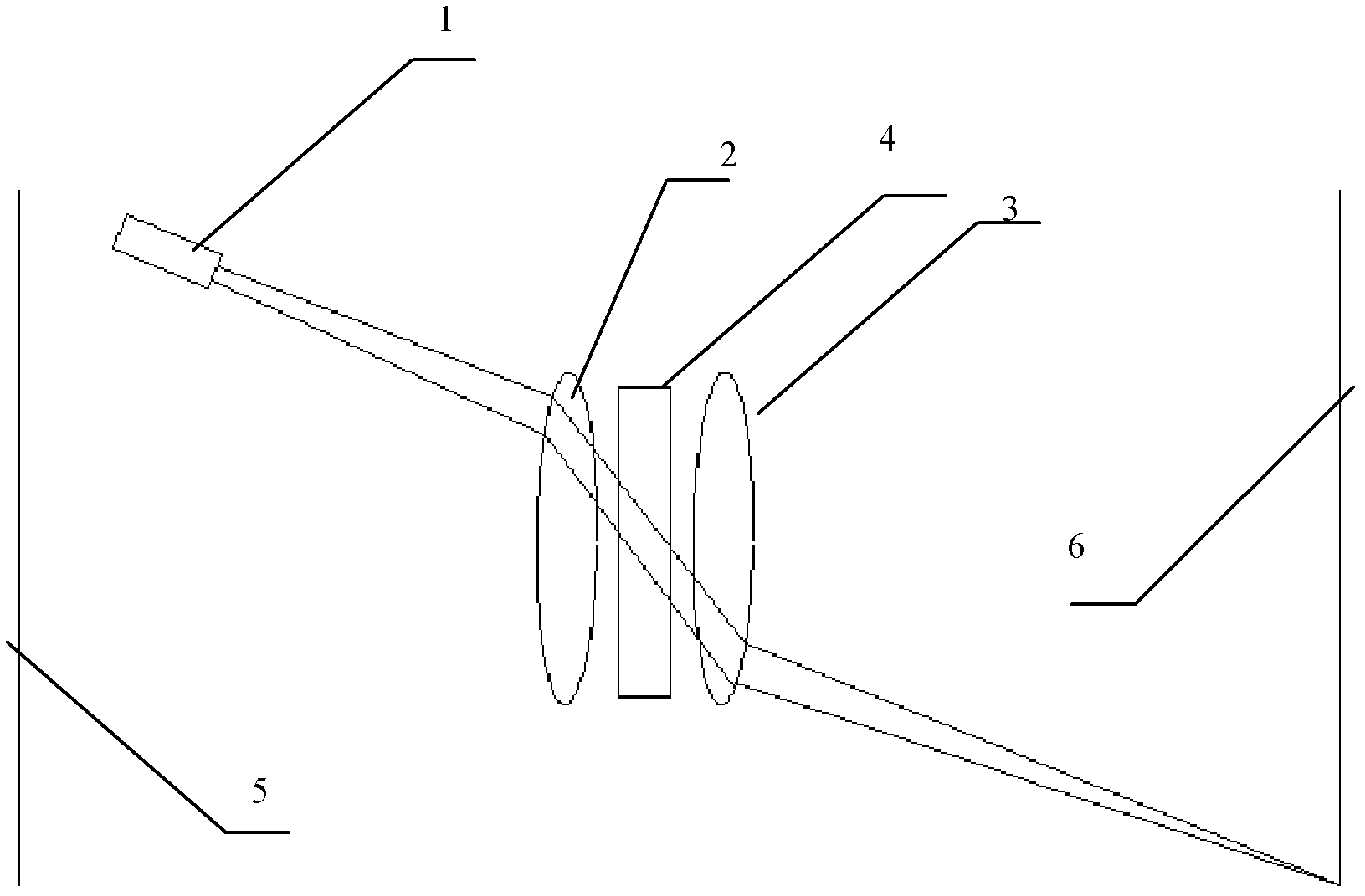
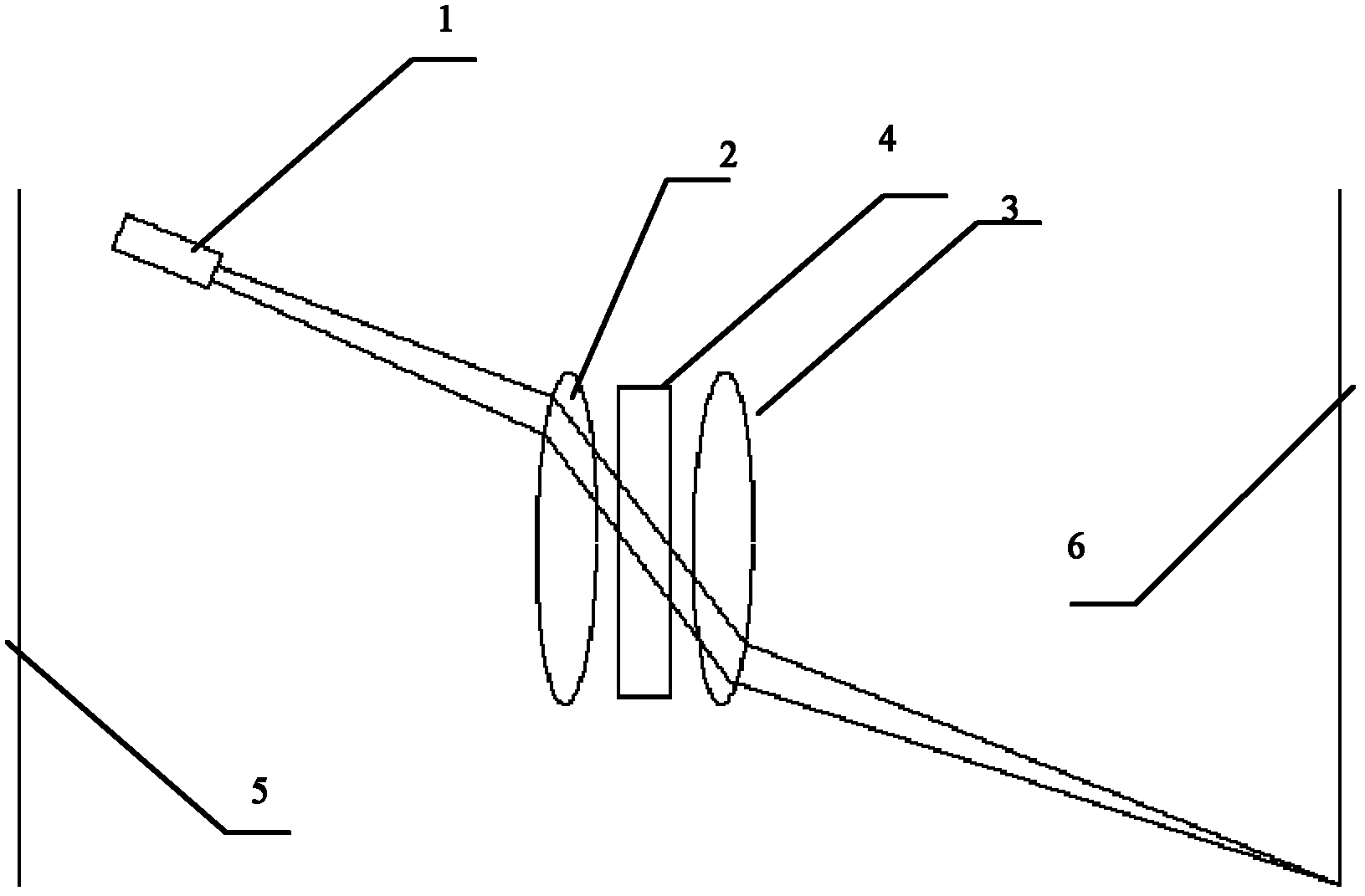
[0022] Such as figure 1 Shown, the structure diagram of oblique incident laser particle size analyzer of the present invention, this particle size analyzer comprises laser 1, lens group, sample cell 4 and viewfinder, lens group is made up of front lens 3 and rear lens 2 of the same optical axis, front lens 3 and the rear lens 2 are respectively placed on the front and rear sides of the sample cell 4; the sample cell 4 is a rectangular sample cell, and the center of the sample cell 4 is placed on the optical axis of the lens group when placed. The laser 1 is placed above the optical axis and placed obliquely on the rear side of the rear lens 2. The height of the laser 1 from the optical axis and the angle of inclination ensure that the laser light emitted by the laser 1 passes through the edge of the rear lens 2 and enters the center of the sample pool obliquely; The "edge part" mentioned here means that the laser beam is not vertically incident, and the position where the lase...
Embodiment 2
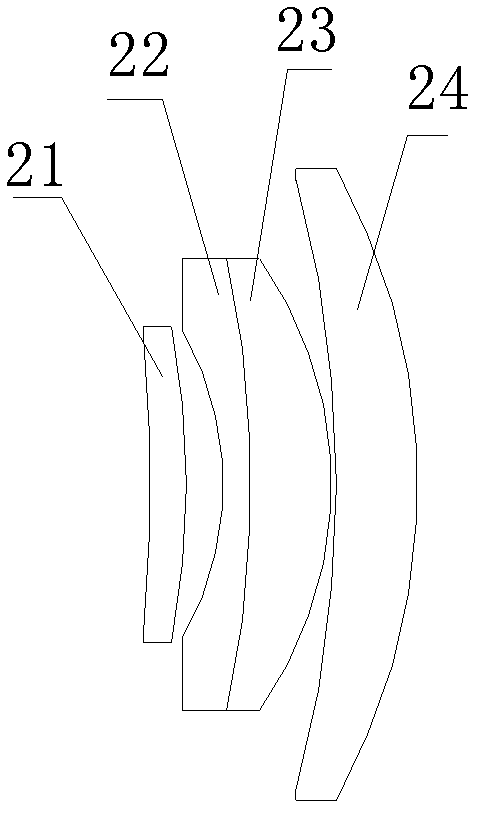
[0029] The difference with Embodiment 1 is that the angle between the laser along the optical path direction and the optical axis of the lens group is 47°, the ratio of the curvature radius of the front surface of the lens I to the radius of curvature of the rear surface is 2; the curvature of the front surface of the lens II The ratio of the radius of curvature to the radius of curvature of the back surface is 4.5; the ratio of the radius of curvature of the front surface of lens III to the radius of curvature of the back surface is 0.4; the ratio of the radius of curvature of the front surface of lens IV to the radius of curvature of the back surface is 0.6.
[0030] The diameter ratios of lens II, lens III and lens IV to lens I are: 1:1, 1.6:1 and 4:1, respectively.
[0031] When the present invention is in use, the laser beam passes through the rear lens, and the rear lens acts as a collimating lens to convert the divergent beam into a parallel beam and then enters the samp...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com