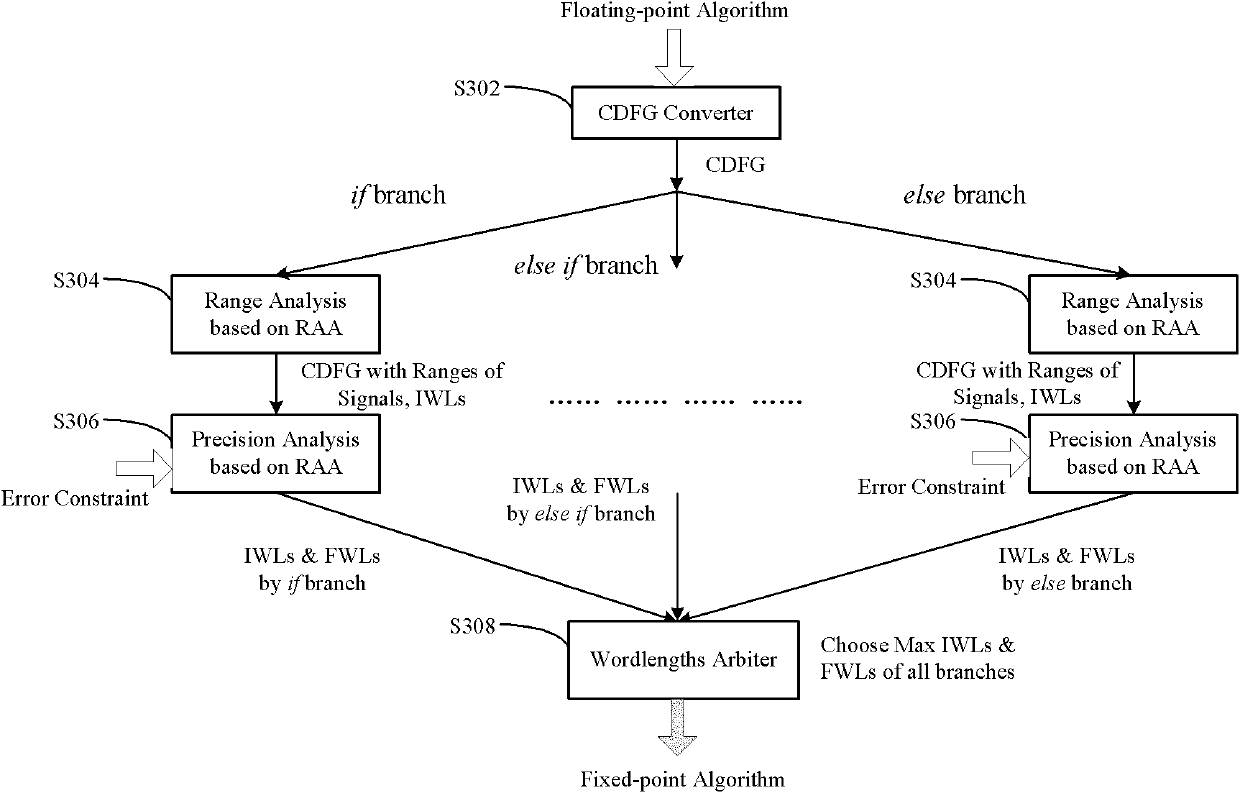
Fixed-point processing method and device
A processing method and a processing module technology, applied in the field of communication, can solve the problems of amplifying fixed-point signal integer bit width and decimal bit width, inaccurate fixed-point processing results, inaccurate analysis of signal variation range, etc., and achieve the effect of improving accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
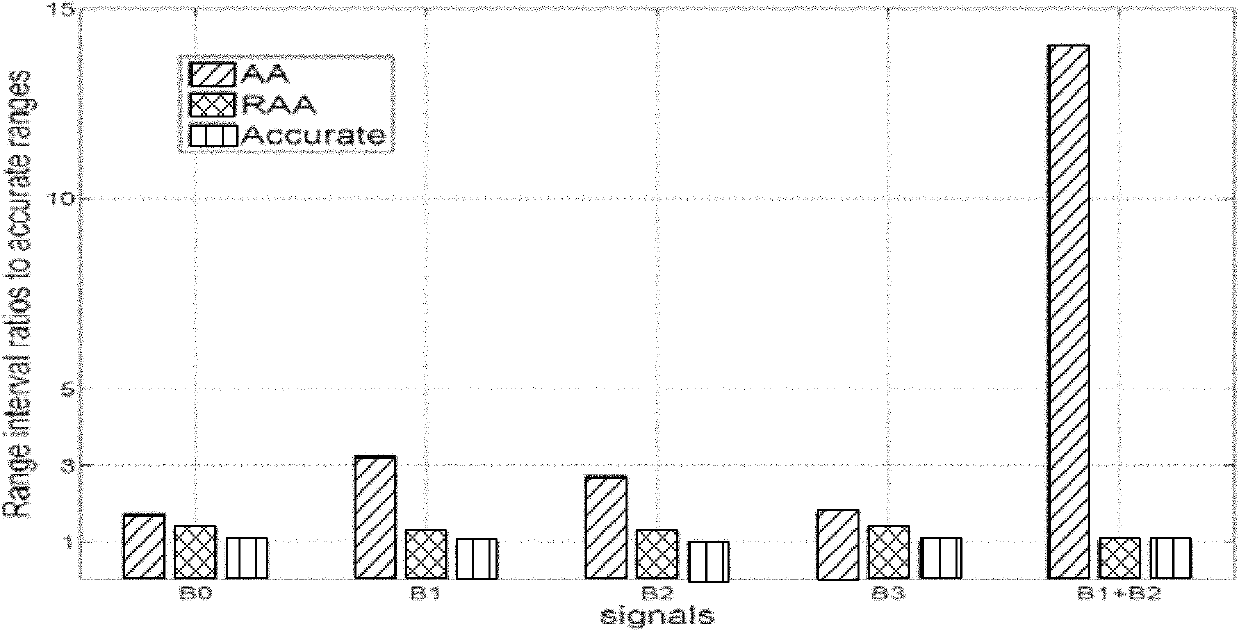
[0050] This embodiment provides an affine algorithm. This embodiment combines the above embodiments and preferred implementation modes therein. In this embodiment, fixed-point processing is performed on the B-splines instance used for image warping.
[0051] In this embodiment, the B-splines basic function B 0 , B 1 , B 2 and B 3 They are defined as follows:
[0052] B 0 ( u ) = 1 6 ( 1 - u ) 3 , B 1 ( u ) = 1 6 ( 3 u 3 - 6 u ...
Embodiment 2
[0069] This embodiment provides an affine algorithm. This embodiment combines the above embodiments and preferred implementation modes therein. In this embodiment, fixed-point processing is performed on 4.2 2×2 matrix multiplication instances.
[0070] In this embodiment, the 2×2 matrix is as follows: y 00 y 01 y 10 y 11 = a 00 a 01 a 10 ...
Embodiment 3
[0097] This embodiment provides an affine algorithm. This embodiment combines the above-mentioned embodiments and preferred implementation modes therein. In this embodiment, the polynomial function instance is subjected to fixed-point processing.
[0098] These 8 polynomial functions in the present embodiment are listed in table 6, wherein " X " of column " Input ranges " represents from x 1 to x m The input signal variation range.
[0099] Table 6 List of polynomial functions
[0100]
[0101] Specifically, the output range analysis results using AA and RAA are listed in Table 7.
[0102] Table 7 Schematic diagram of the output range of polynomial using AA
[0103]
[0104] It can be seen from the results in the table that RAA has found more accurate results of the range of variation for all these 8 polynomial functions, and the output integer bit width obtained by RAA is the same as the real integer required by the output obtained by numerical methods or nonlinear p...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com