A catalyst and process for the manufacture of ultra-low sulfur distillate product
A technology for hydrodesulfurization and distillate oil, applied in the field of preparation of ultra-low sulfur distillate products, distillate oil hydrodesulfurization catalysts
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0029] The process of the present invention for preparing the catalyst of the present invention provides a more economical method of preparing hydroprocessing catalysts than many prior art preparation methods. The novel process includes a single step for mixing the catalyst components to incorporate the hydrogenation metal and the promoter into the mixture in this single step. On the other hand, many prior art methods use multiple steps to incorporate the catalytic component into the composition, such as first preparing the support structure followed by a separate impregnation step. Indeed, the process of the present invention does not desirably involve the use of molybdenum salts or solutions thereof to incorporate the molybdenum component into the catalyst of the present invention. Typically, the prior art teaches the use of molybdenum salt solutions for the incorporation of molybdenum into the support structure of the catalyst. The process of the present invention can be m...
Embodiment I
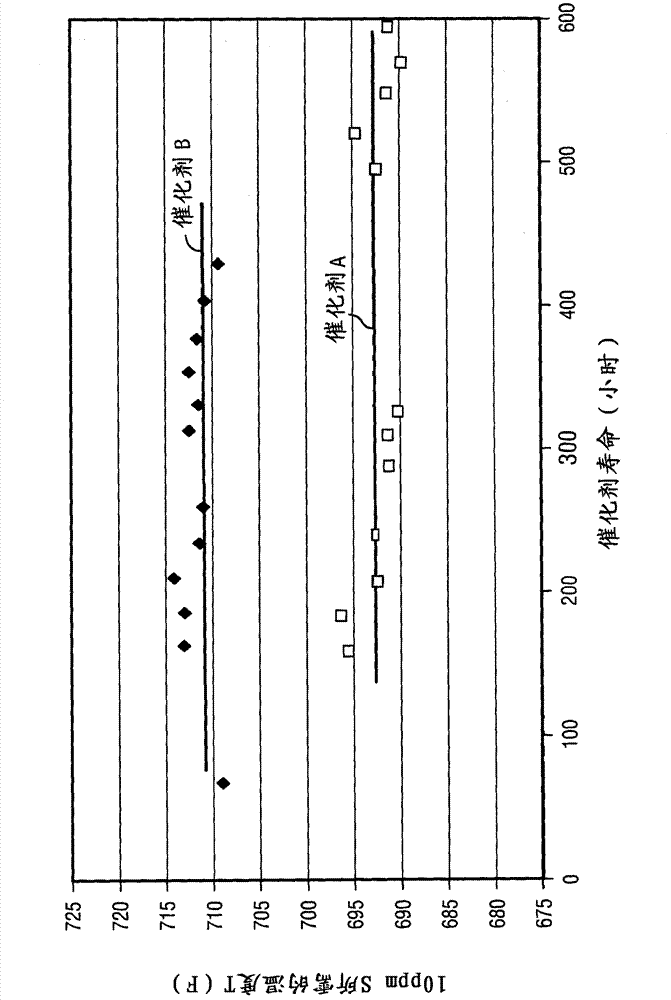
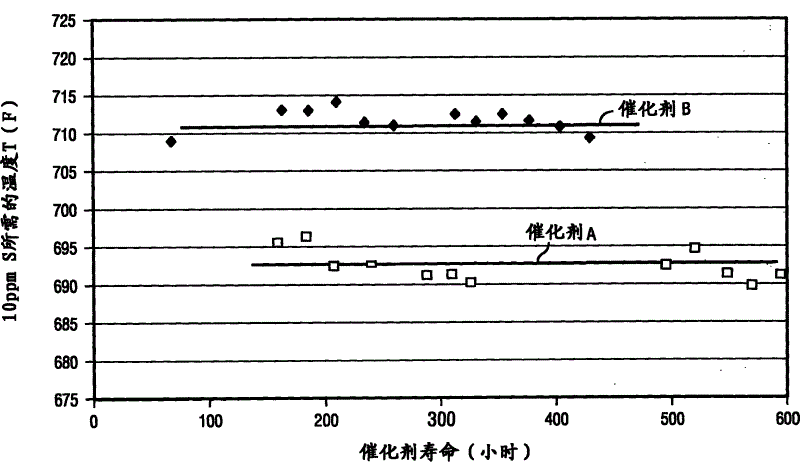
[0052] This example describes the preparation of Catalyst A and Comparative Catalyst B.
[0053] Catalyst A
[0054] Prepare catalyst A by the following steps: first dissolve 724.71 parts by weight of cobalt nitrate (Co(NO) in 316.4 parts by weight of deionized water by heating 3 ) 2 ·6H 2 O) forming an aqueous cobalt solution and then cooling the aqueous cobalt solution. The aqueous cobalt solution was mixed with 3134.8 parts by weight of 2% silica-alumina, 680.3 parts by weight of fresh Co / Mo / P / Ni hydrotreating catalyst (2.9 wt% Co, 12.0 wt% Mo, 0.09 wt% %P and 0.02wt% Ni), 301.1 parts by weight of molybdenum trioxide powder, 30 parts by weight of commercially available extrusion aids, 3465.7 parts by weight of deionized water and nitric acid were mixed. The mixture was extruded using a 1.3 mm clover die. The extrudates were dried at 100°C.
[0055] Aliquots of the dried extrudate pellets were calcined in air at temperatures of 593°C (1100°F) and 677°C (1250°F) for 2 h...
Embodiment II
[0064] This example describes the method used in testing the catalyst described in Example I. The process is used to remove the sulfur content of a distillate feedstock to obtain a product having less than 100 ppm sulfur.
[0065] The test was carried out using a single reactor tube system. The heating section containing the tubular 50 inch x 5 / 8 inch ID stainless steel (317SS) reactor was heated by a 5 zone furnace. Temperature control was based on the internal temperature of the reactor measured by an RTD probe placed axially along the length of the reactor and in the center of the catalyst bed. Each tubular reactor is loaded with a 50cm 3 Catalyst A or Catalyst B in a stacked bed arrangement. A pre-reactor zone and a post-reactor zone containing 6 inches of 70-80 mesh size silicon carbide particles were placed in the bottom and top zones of the reactor. To improve fluid distribution and maximize oil, catalyst, and gas contact, the catalyst was mixed with 70-80 mesh sili...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com