Rapid charging method of rechargeable batteries
A technology for fast charging and rechargeable batteries, applied in the direction of secondary battery charging/discharging, secondary battery repair/maintenance, etc., to achieve the effect of fast charging and easy promotion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
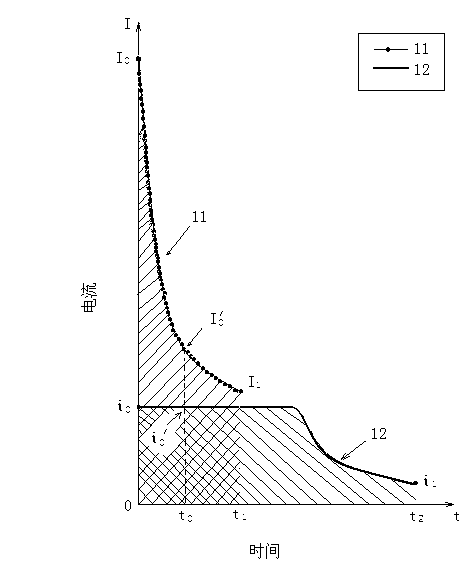
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Example 1: Commercially available 601417HS15QC high-rate 3.7V60mAh polymer lithium-ion battery, the battery system material is lithium cobaltate and carbon system type single battery, the standard charging cut-off voltage U0=4.2V, ΔU=0.05*N, select when When N=0, ΔU=0, the selected constant voltage U=U0+ΔU=4.2V, the cut-off current I1 is numerically equal to 0.5C and 1C, and C is the charging rate, which is numerically equal to the rated capacity of the battery. The rated capacity of the battery is 60mAh, and the initial charging voltage is 3.0V.
[0039] Table 1
[0040] Charging method Charging system Actual charging initial current I0 (mA) Actual charging time (min) 1C discharge to 3V discharge capacity (mAh)
[0041] 1 60mA (1C) constant current charging to 4.2V to constant voltage charging, the current drops to 3mA (0.05C) to stop. 60 81.3 61.3
[0042] 2 Select U= 4.2V constant voltage charging, stop charging until the current decreases to 30mA (0.5C)...
Embodiment 2
[0045] Example 2: Commercially available 452026Fe15C fast charge type 3.2V100mAh polymer lithium ion battery, the battery system material is lithium iron phosphate and carbon system type single battery, the standard charge cut-off voltage U0=3.6V, ΔU=0.05*N, select when When N=0, ΔU=0, the selected constant voltage U=U0+ΔU=3.6V, the cut-off current I1 is numerically equal to 0.5C and 1C, and C is the charging rate, which is numerically equal to the rated capacity of the battery. The rated capacity of the battery is 100mAh, and the initial charging voltage is 2.0V.
[0046] Table 2
[0047] Charging method Charging system Actual charging initial current I0 (mA) Actual charging time (min) 1C discharge to 3V discharge capacity (mAh)
[0048] 1 100mA (1C) constant current charging to 3.6V to constant voltage charging, the current drops to 6.5mA (0.05C) to stop. 100 76.8 110.2
[0049] 2 Select U= 3.6V constant voltage charging, stop charging until the current decreases...
Embodiment 3
[0052] Example 3: Commercially available 452026HS10QC fast charge type 3.7V130mAh polymer lithium ion battery, the battery system material is lithium cobalt oxide and carbon system type single battery, the standard charge cut-off voltage U0=4.2V, ΔU=0.05*N, select when When N=-1, ΔU=-0.05V, the selected constant voltage U= U0+ΔU=4.15V, the cut-off current I1 is numerically equal to 0.5C and 1C respectively, and C is the charging rate, which is numerically equal to the rated value of the battery capacity. The rated capacity of the battery is 130mAh, and the initial charging voltage is 3.0V.
[0053] table 3
[0054] Charging method Charging system Actual charging initial current I0 (mA) Actual charging time (min) 1C discharge to 3V discharge capacity (mAh)
[0055] 1 130mA (1C) constant current charging to 4.2V to constant voltage charging, the current drops to 6.5mA (0.05C) to stop. 130 77.6 134.5
[0056] 2 Select U= 4.15V constant voltage charging, stop chargin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com