Gate driving circuit
A gate drive circuit, gate drive technology, used in instruments, static indicators, etc., to achieve the effect of reducing size and strong output capability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
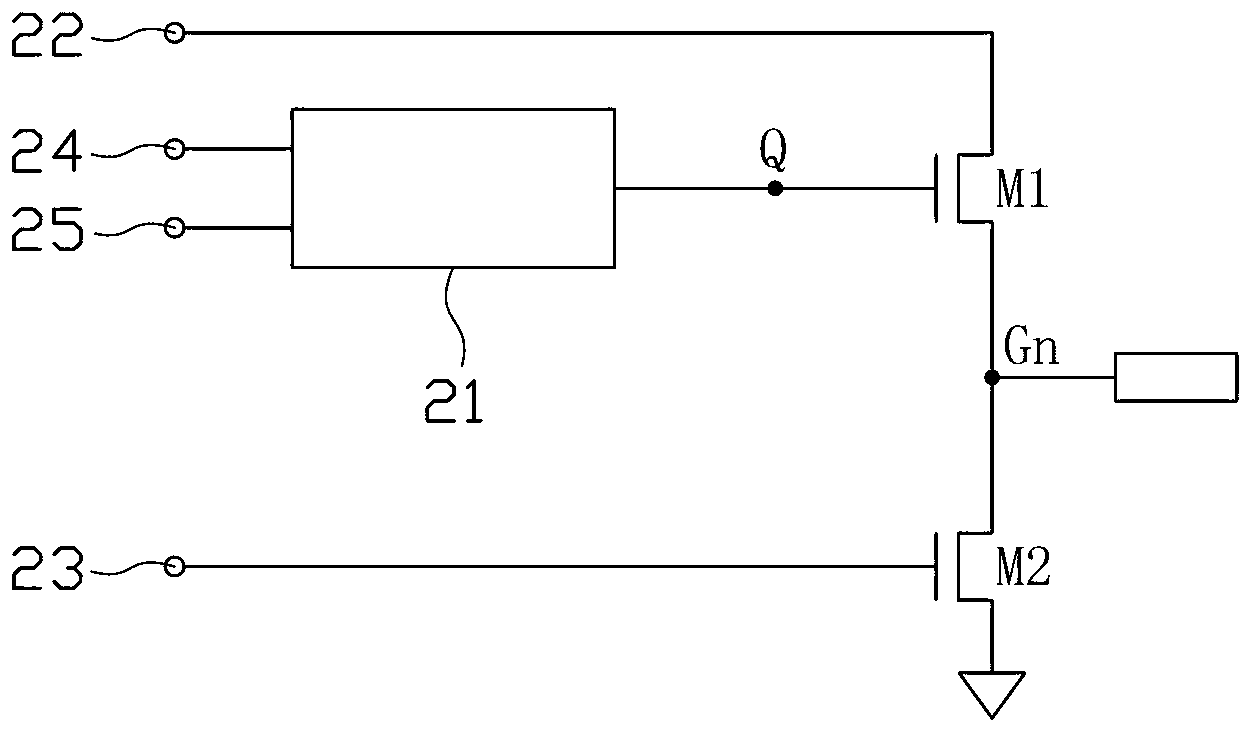
[0051] figure 2 It is a circuit diagram of the gate driving sub-circuit according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention. See figure 2 , which plots the figure 1 The specific circuit structure of the middle latch 21, and this embodiment is a preferred implementation mode of the present invention. The gate driving sub-circuit of this embodiment includes a latch 21 , a pull-up switch element M1 , a pull-down switch element M2 , a pull-up capacitor C3 and a sixth switch element M6 . The first control end of the pull-up switching element M1 is connected to the latch output Q of the latch 21, the first input end of the pull-up switching element M1 is connected to the first timing signal input end 22, and the first pull-up switching element M1 The output terminal serves as the output terminal Gn of the gate driving sub-circuit. The second control end of the pull-down switch element M2 is connected to the second timing signal input end 23, the second output end of the pull-d...
Embodiment 2
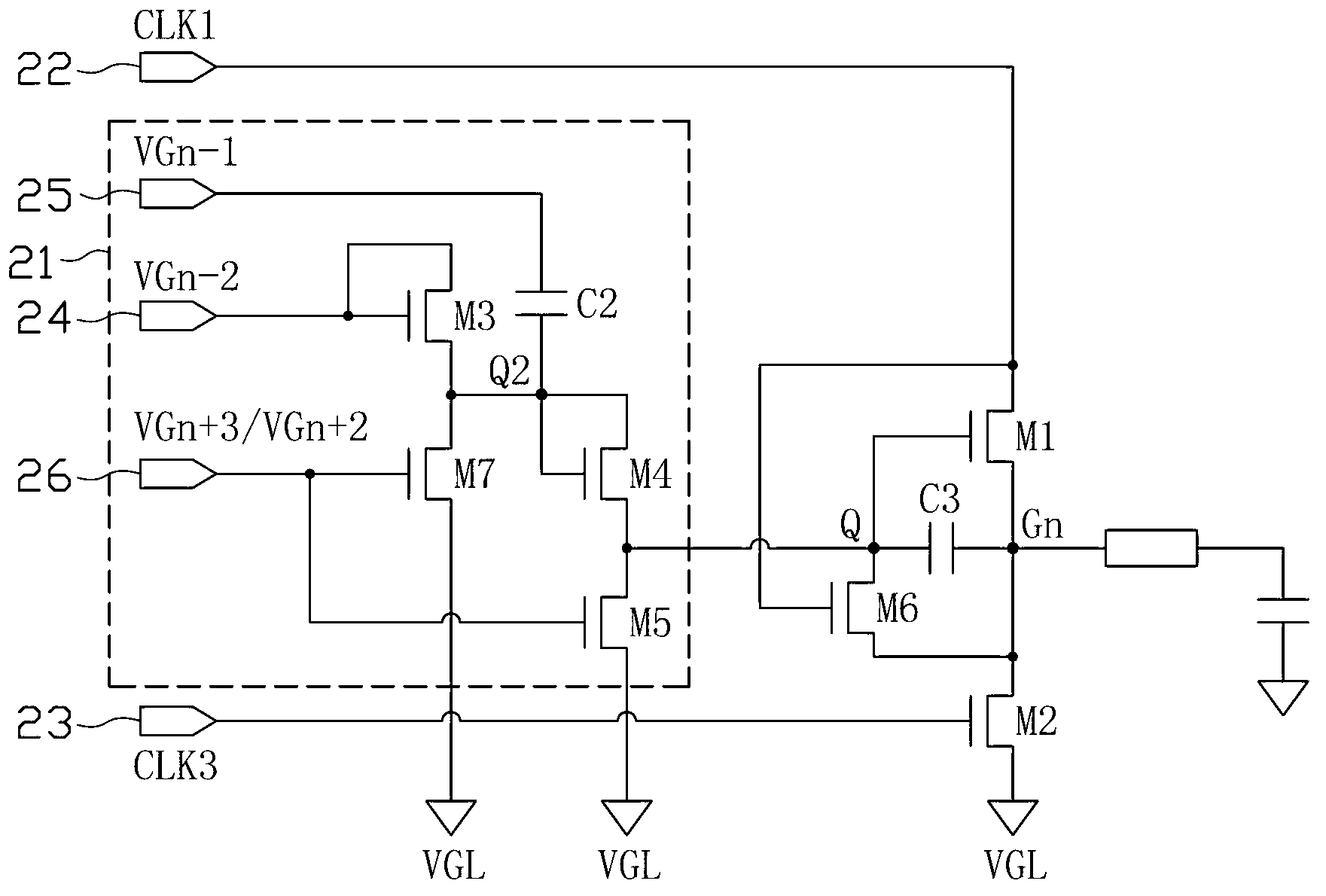
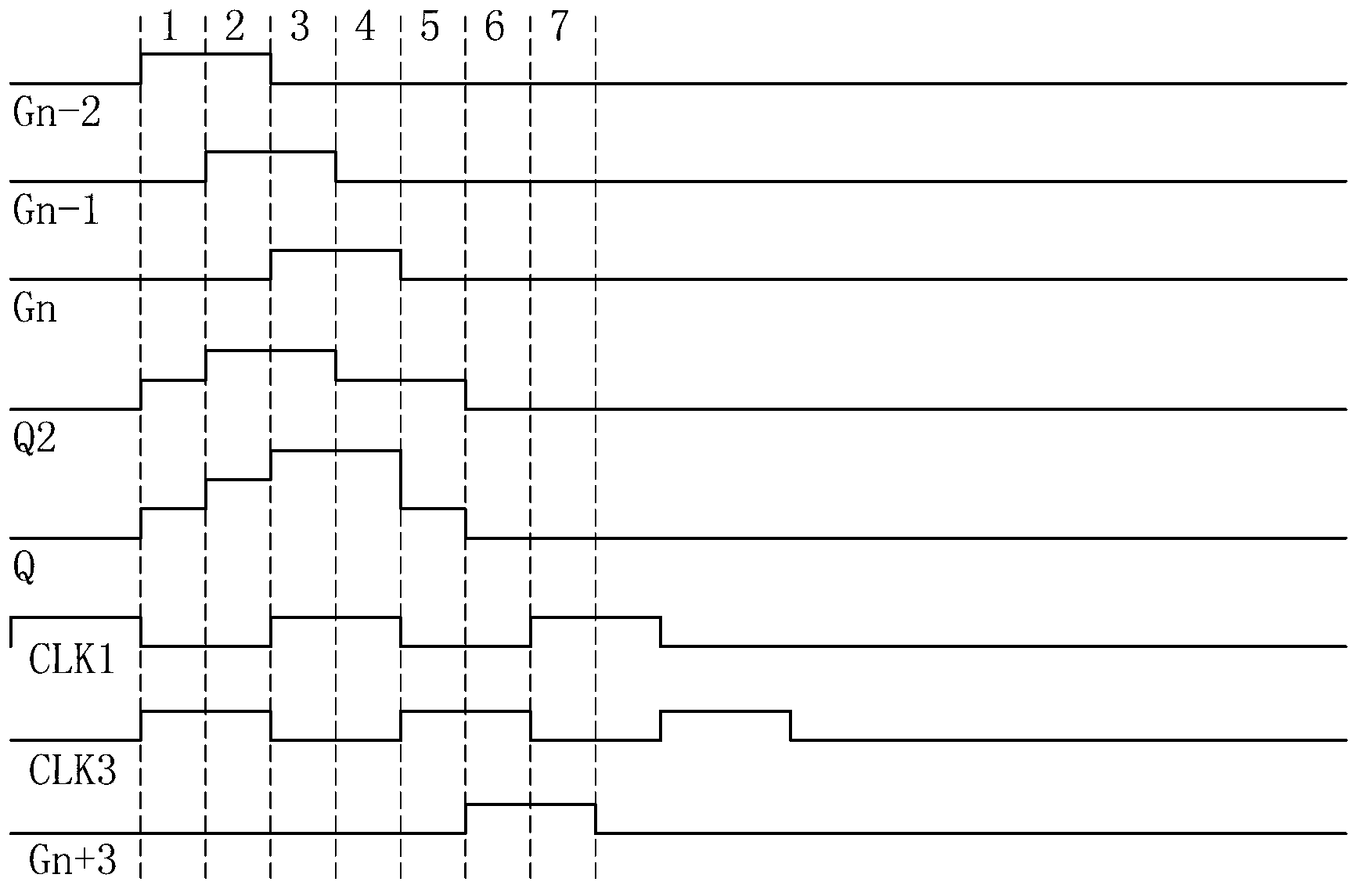
[0073] See Image 6 , which is a circuit diagram of the gate drive circuit in Embodiment 2 of the present invention, and figure 2 The difference is that the figure 2 In the seventh switch element M7, and the third control terminal of the third switch element M3 receives the CLK3 signal input from the second timing signal input terminal 23 ( figure 2 The third control end of the third switch element M3 is connected to the first pull-up signal input end 24). Depend on image 3 As can be seen from the waveform diagram shown in , when the Gn-2 signal is at a high level, the CLK3 signal is also at a high level, so this embodiment can turn on the third switching element M3 at the same time (that is, stage 1), In order to make the first pull-up signal VGn-2 pull up the voltage of point Q for the first time. And the circuit is more concise after the seventh switching element M7 is omitted. Other circuit structures and working principles of this embodiment are the same as fig...
Embodiment 3
[0075] See Figure 7 , which is a circuit diagram of the gate drive sub-circuit in Embodiment 3 of the present invention, and figure 2 The only difference is that the figure 2 The sixth switching element M6 in. The function of the sixth switch element M6 is to transfer the voltage at the stable point Q to the gate drive sub-circuit when the CLK1 high-level signal input by the first timing signal input terminal 22 is output to the output terminal Gn of the gate drive sub-circuit through the third switch element M3. The pole drives the output terminal Gn of the sub-circuit, thereby stabilizing the voltages of the Q point and the Gn point, and also improving the stability of the circuit. It can be seen that the sixth switching element M6 is not a necessary element in the present invention. In the absence of the sixth switching element M6, the circuit of this embodiment can also realize the third switching of the voltage at point Q at the output terminal of the latch 21. leve...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com