Broomcorn glyphosate resistance 5-enolpyruvoyl shikimic acid-3-phosphosynthase (EPSPS) and application thereof
A glyphosate-resistant and glyphosate-tolerant technology, applied in the fields of plant molecular biology and plant genetic engineering, can solve the problems of not selecting EPSPS variants and failing to meet production requirements
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] Example 1. Directed mutagenesis of sorghum 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase.
[0025] 1. Selection of directed mutagen
[0026] A successful glyphosate-tolerant EPSPS variant not only depends on the site of the change, but also depends on the source of the variant. Currently, the most widely commercialized CP4EPSPS is derived from the Agrobacterium CP4 strain. The Ala at the 100th position is converted to Gly, and the conversion of the corresponding Ala of E. coli or Streptococcus pneumoniae to Gly does not confer glyphosate resistance on EPSPS variants (Eschenburg, S. et al. 2002; Sost, D. et al. 1990; Todd Funke et al 2006). The reason for this mainly depends on two points: 1. Whether the Ki of the EPSPS variant is high enough for glyphosate, and 2. The Km for phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) is low enough.
[0027] Although the EPSPS variant (P106S) SEQ ID NO: 2 of maize has a sufficiently low Km to phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) (Km-PEP=17.1±2.8 μM), the Ki to glyp...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Embodiment 2, construction of sorghum EPSPS plant expression vector after modification
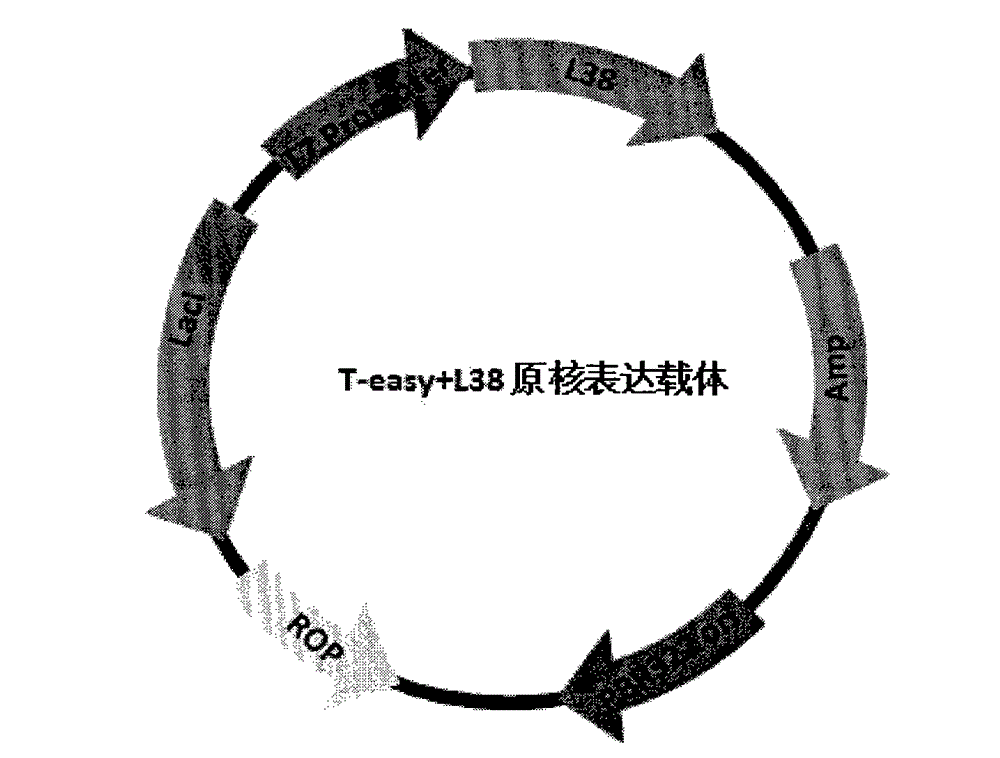
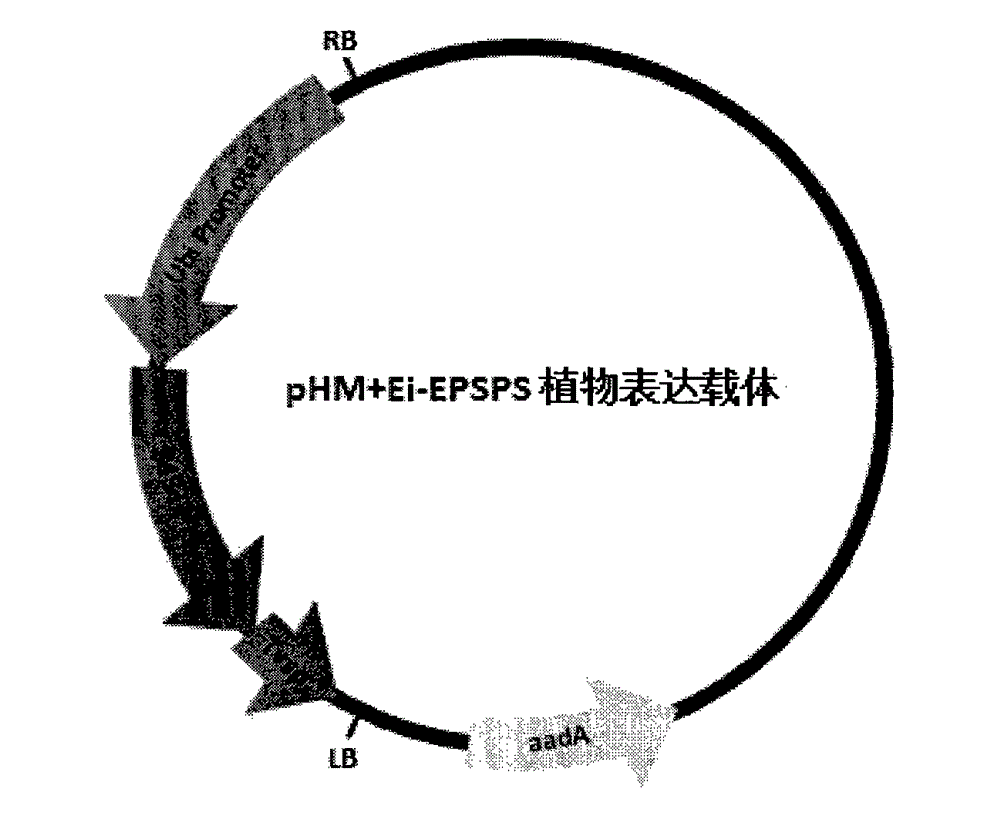
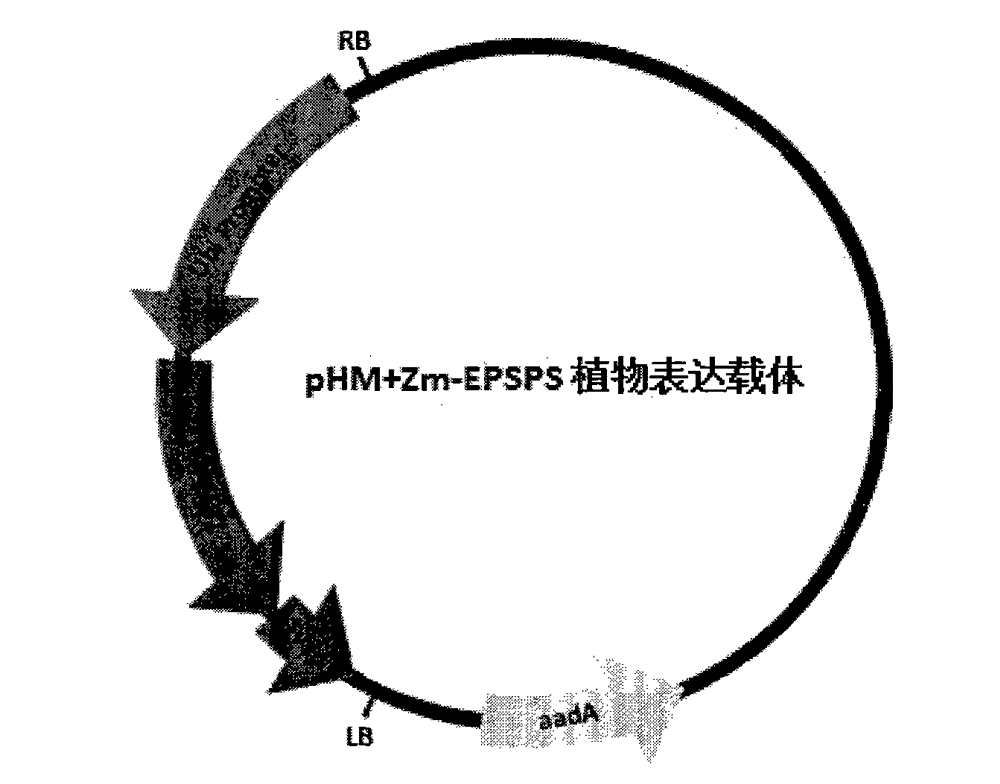
[0034] We added a BglII restriction site to the 5' end of the SEQ ID NO: 6 sequence, and a KpnI restriction site to the 3' end, digested T-easy+CL38 with BglII and KpnI, and recovered the CL38 target fragment. Through the existing plant expression vector pHM102, digest pHM102 with BamHI and Kpn1 respectively. Since the sticky ends produced after digestion with BamHI and BglII are the same, the two fragments can be connected to obtain the modified sorghum EPSPS (P106S) Plant expression vector, named pHM-CL38, see Figure 4 . Modified sorghum EPSPS plant expression vector. We used the same method to construct the plant expression vectors of the EPSPS variants of goosegrass and corn respectively, see figure 2 .Glyphosate-tolerant goosegrass EPSPS plant expression vector named pHM+Ei-EPSPS, image 3 . A glyphosate-tolerant maize EPSPS plant expression vector named pHM+Zm-EPSPS.
Embodiment 3
[0035] Example 3. Expression of glyphosate-resistant gene CL38 in maize.
[0036] 1. Obtaining of transgenic glyphosate-resistant gene CL38 maize
[0037] The method for obtaining the transgenic corn is to introduce the insertion sequence into the callus of the recipient plant by using a gene gun method, and obtain the transgenic plant after screening with 100mg / L of herbicide glyphosate. The specific method is:
[0038] (1), induction of type II callus
[0039] a. Remove the bracts: cut off the top of the ear about 1cm, and insert the ear from the top with tweezers, so that the tweezers can be used as a handle, which is convenient for operation, and then put the ear into a beaker containing disinfectant. Put 4-6 ears in the same beaker.
[0040] b. Add about 700ml of disinfectant solution (50% bleach or 5.25% sodium hypochlorite, and add a drop of Tween20) to the beaker to soak the fruit ears. During the 20-minute disinfection process, rotate the fruit ears from time to ti...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com