System and method for recycling magnesium and magnesium alloy waste
A recovery system and magnesium alloy technology, applied in metal processing equipment, process efficiency improvement, ingot casting workshop, etc., can solve the problem of difficult to control the effect of impurity removal, high chlorine content, damage to product mechanical properties and corrosion resistance, etc. question
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0034] The present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings, so that those skilled in the art can implement it with reference to the description.
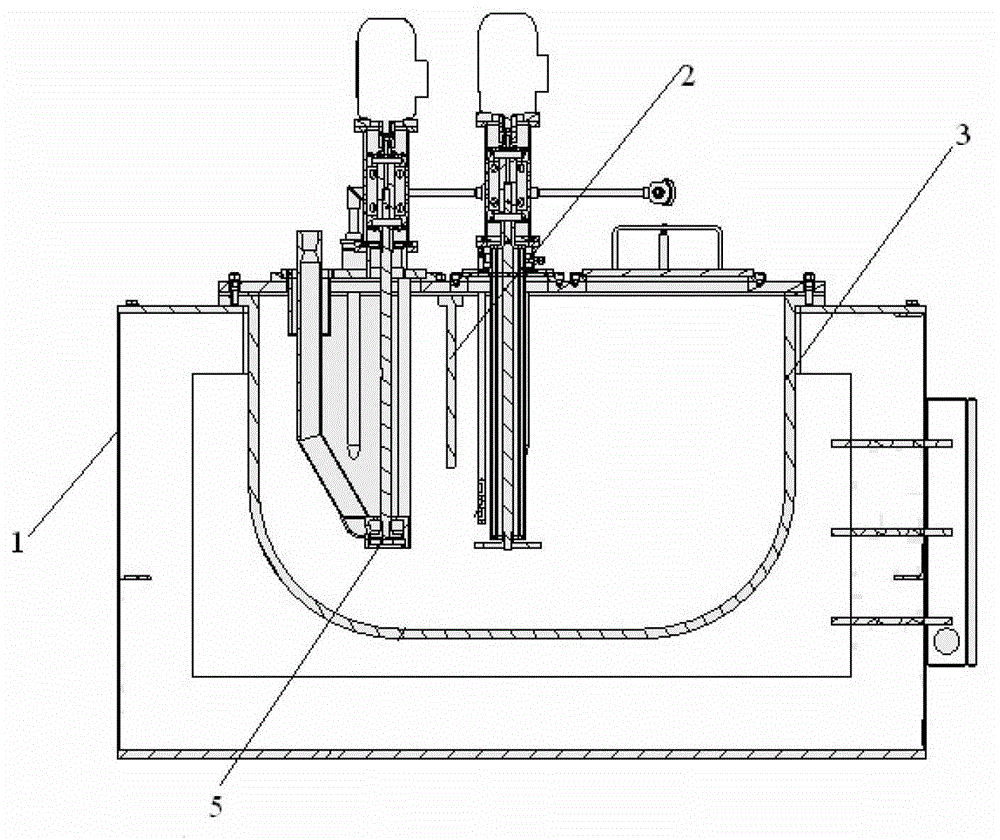
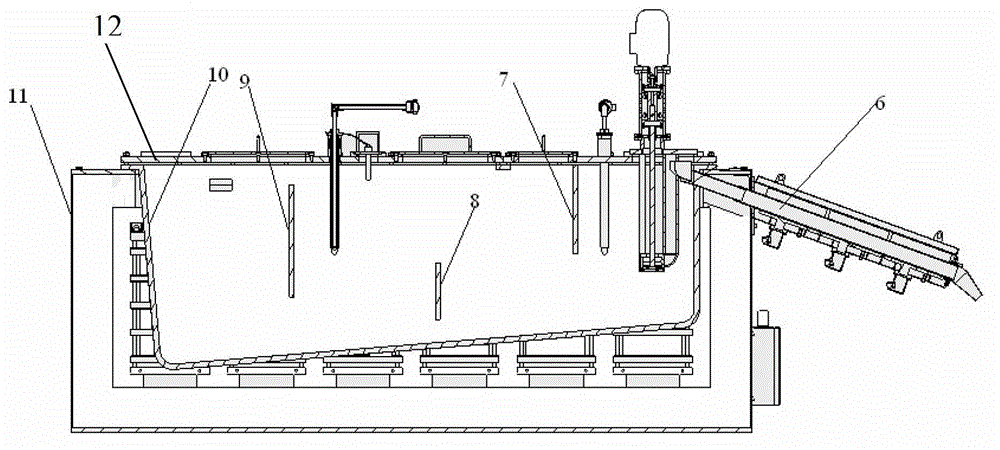
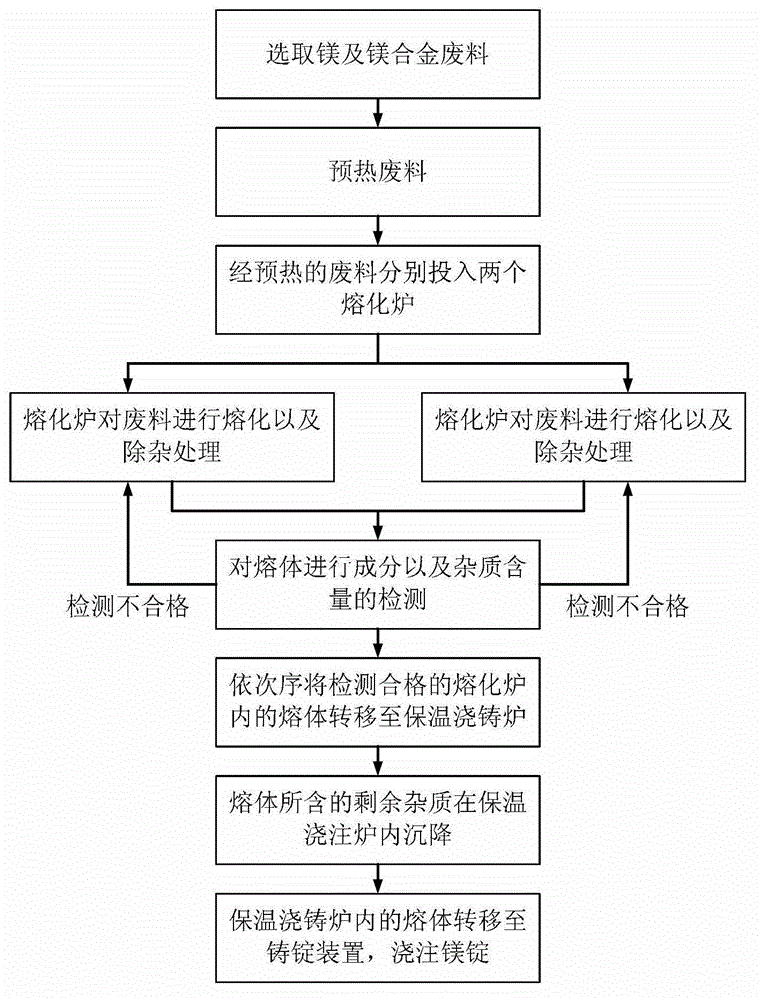
[0035] Such as figure 1 and figure 2 As shown, the present invention provides a recovery system for magnesium and magnesium alloy waste, comprising: at least one melting furnace 1, the first liquid outlet pipe 5 of any melting furnace is connected to the first crucible 3 inside of the melting furnace near the bottom position, any melting furnace has an inlet device for feeding inert gas into the first crucible of the melting furnace, and the inlet device is connected to a position close to the bottom of the first crucible of the melting furnace; the insulation casting furnace 11, The bottom of the second crucible of the heat preservation casting furnace is inclined relative to the horizontal plane, and the direction of inclination of the bottom of the second crucible is: the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com