Method for detecting and eliminating narrow-band interference by GNSS receiver
A narrowband interference and receiver technology, applied in the field of signal processing, can solve the problems of large amount of calculation and high complexity, and achieve the effect of small amount of calculation, reduced complexity, and reduced capture time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
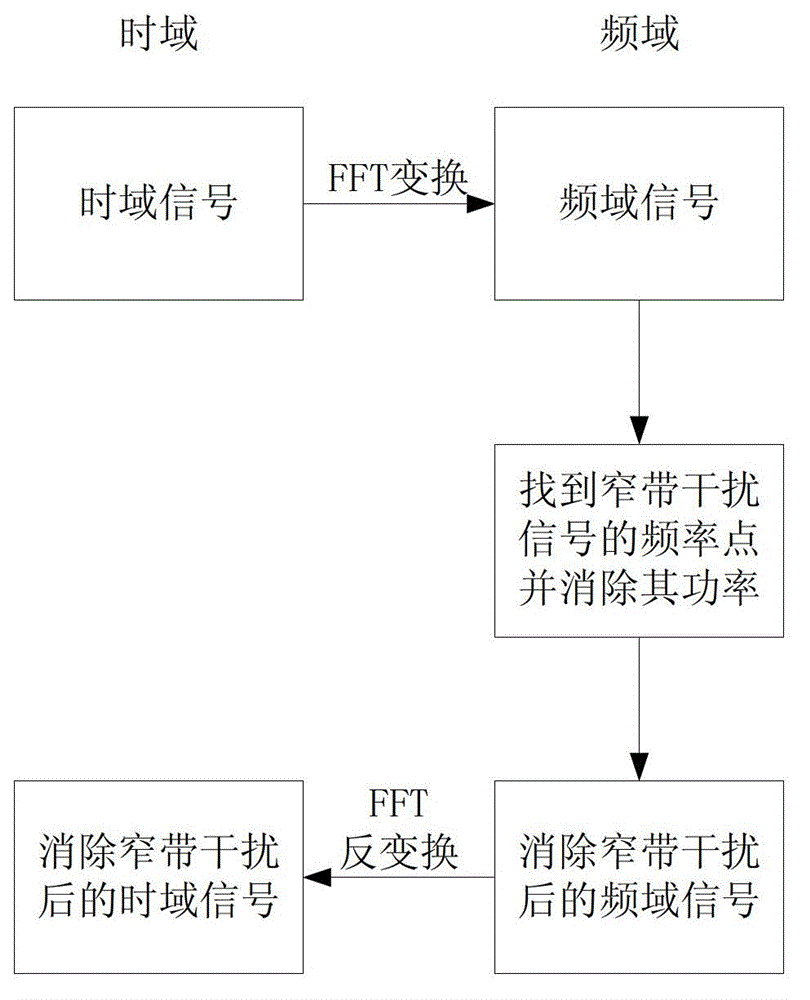
[0033] see Figure 4 , the method for detecting and eliminating narrowband interference by the GNSS receiver of this application is:
[0034] First, the receiver transforms the received time-domain signal into a frequency-domain signal through FFT.
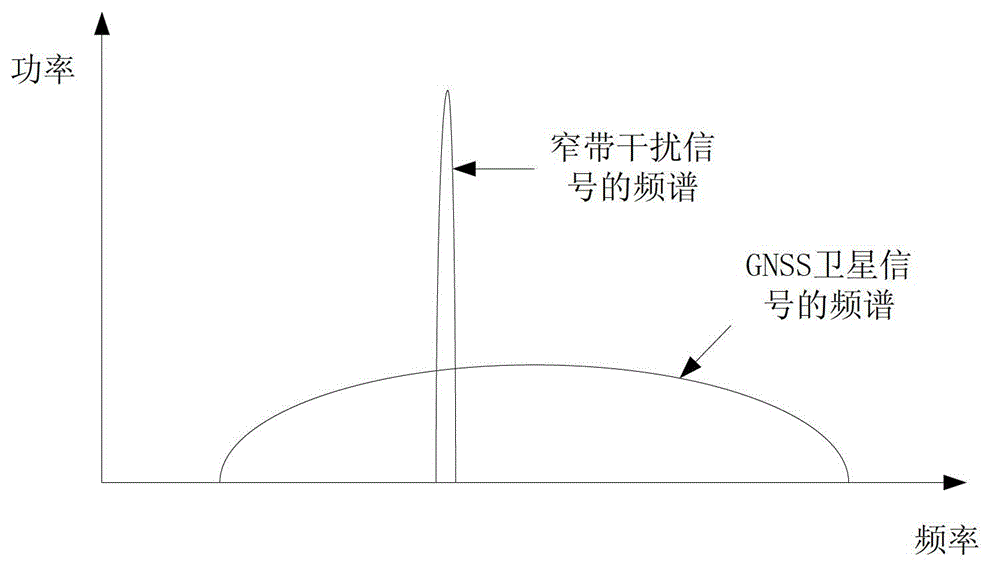
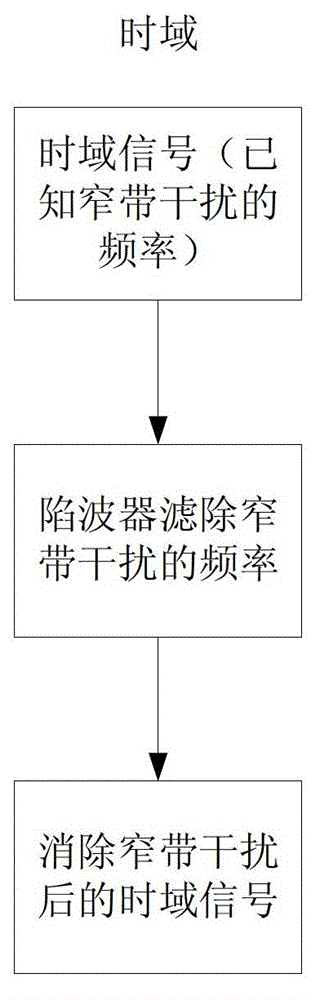
[0035] Secondly, according to the characteristics of the frequency bandwidth and low power spectral density of GNSS satellite signals, and the narrow frequency band and high power spectral density of narrowband interference signals, the receiver finds the frequency point where the power spectral density in the frequency domain signal becomes significantly larger, which is the narrowband The frequency point of the interfering signal. The receiver sets these bands or frequency points as the blocking frequencies of one or more notch filters.
[0036] Finally, the receiver passes the received time-domain signal through the one or more notch filters to filter out narrow-band interference signals. During filtering, the energy of the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com