Optical beam splitter performing separation based on coupled mode
A technology of coupling mode and optical beam splitter, which is applied in the direction of light guide, optics, instrument, etc., can solve the problems of limited variation range of beam splitting ratio and large insertion loss, and achieve large process tolerance, low insertion loss and wide wavelength range Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
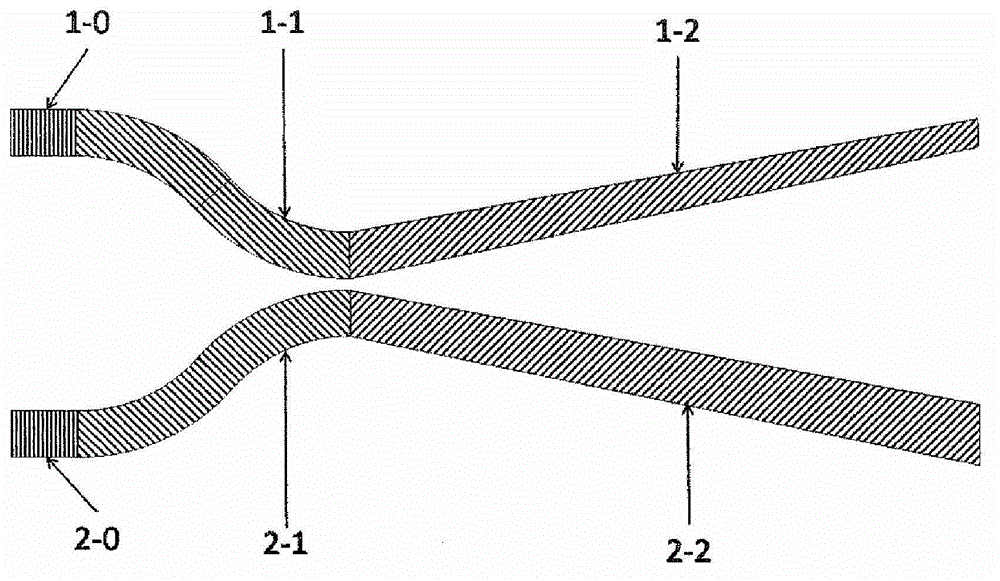
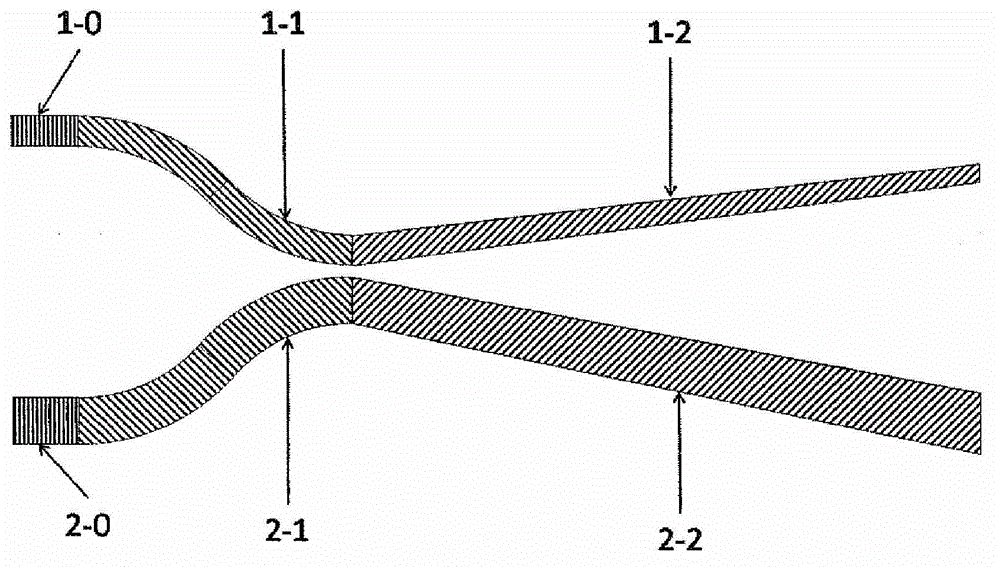
[0038] This embodiment is an optical beam splitter with a beam splitting ratio of 0.5 / 0.5 designed according to the structure shown in FIG. . Both the input end 1-0 of the first waveguide 1 and the input end 2-0 of the second waveguide 2 have a ridge width of 500nm. In the coupling mode excitation region 1-1 or 2-1, the distance between the two waveguides decreases in an arc-shaped manner. Small, to about 100nm or less, and the ridge width remains unchanged; in the coupling mode separation region 1-2 or 2-2, the distance between the two waveguides increases linearly, and the maximum distance is greater than 700nm, while the coupling mode separation region 1 of the first waveguide 1 The -2 ridge width decreases linearly to less than 450nm, while the coupled mode separation region 2-2 ridge width of the second waveguide 2 linearly increases to greater than 550nm.
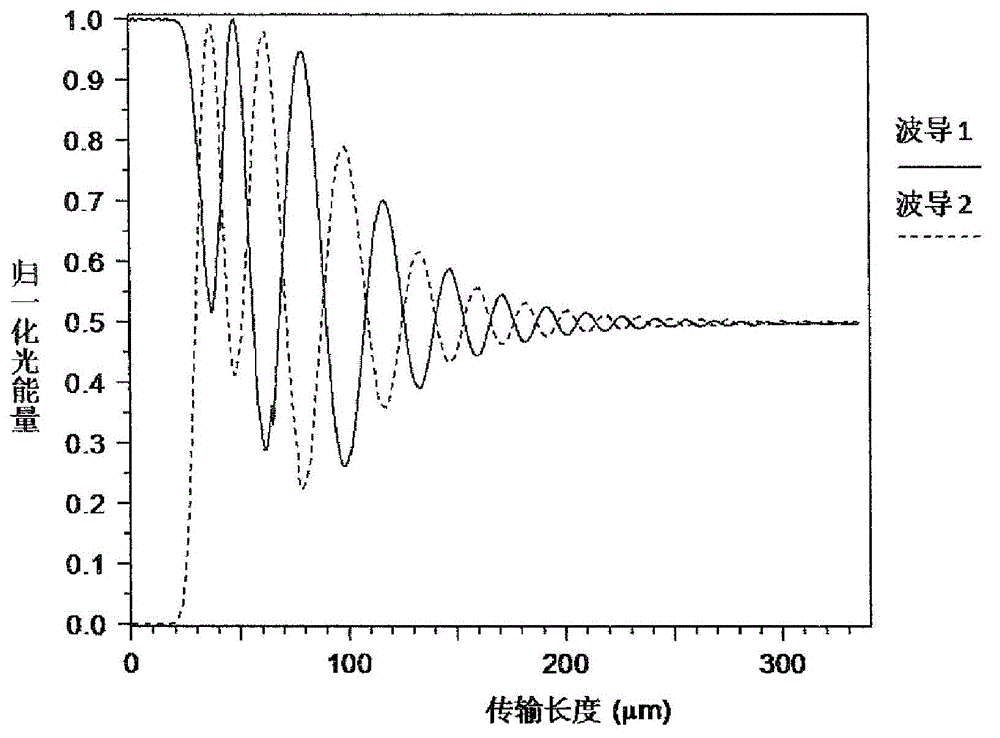
[0039] Figure 2(a) is the simulation result of the beam propagation method of the above embodiment, the wavelength...
Embodiment 2
[0041] The present embodiment is an optical beam splitter whose beam splitting ratio is 0.9 / 0.1 according to the structural design shown in Fig. The ridge width of the input terminal 2-0 is 532nm, and other parameters are the same as those in Embodiment 1.
[0042] Fig. 2(b) is the simulation result of the beam propagation method of the above embodiment. It can also be seen that as the transmission distance increases, the beam splitting ratio tends to be stable around 0.9 / 0.1, and there is no obvious insertion loss.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com