High-speed railway based aerodynamic aerotrain with simulated wings on chassis of aerotrain body
An aerodynamic levitation, high-speed railway technology, applied in the direction of railway car body, railway car body parts, air resistance reduction technology, etc., can solve the problems of waste of resources, inability of trains to change tracks, serious safety accidents of maglev trains, etc., to reduce pressure , the effect of stable train running and simple structure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0049] See Figure 4 and Figure 5 , the wing-like structure is mainly composed of a fixed base 4 of cuboid structure and a horizontal wing 1 fixed thereon; wherein, one side of the fixed base is connected with the horizontal wing, and the other side is installed on the side of the locomotive or carriage, fixed The horizontal length of the base is 1 meter, the width is 30 cm, the thickness of the fixed base is 65 mm, and the horizontal wing and the fixed base form a 90-degree right angle.
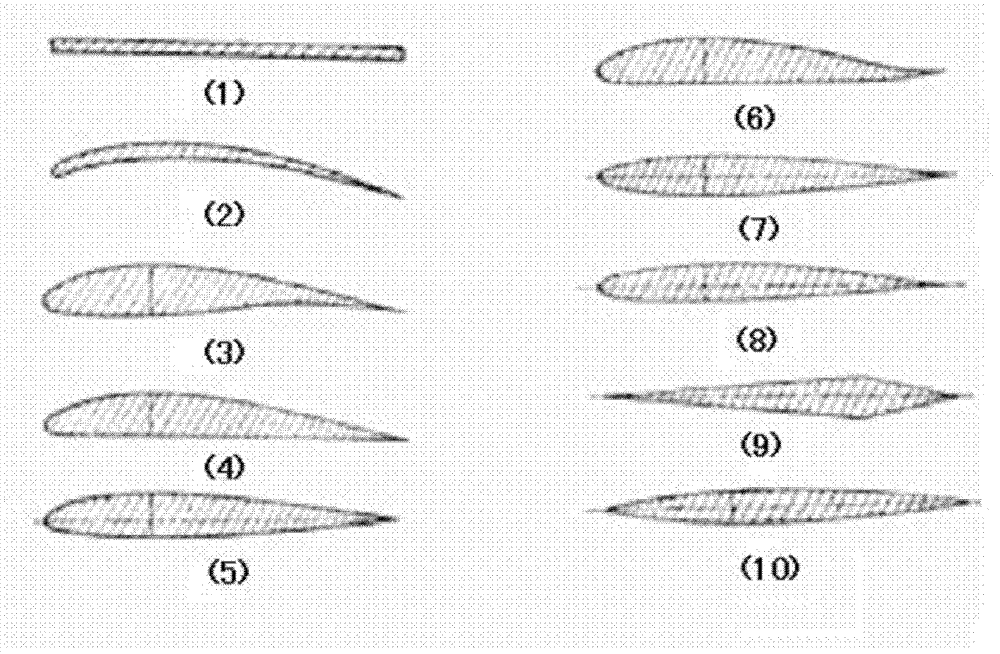
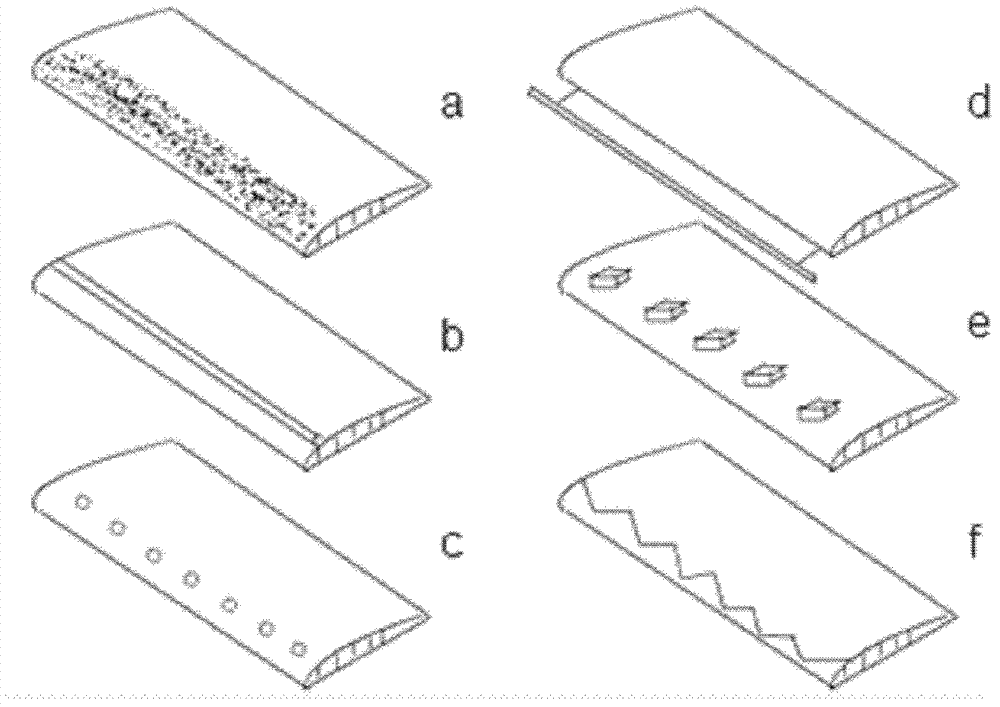
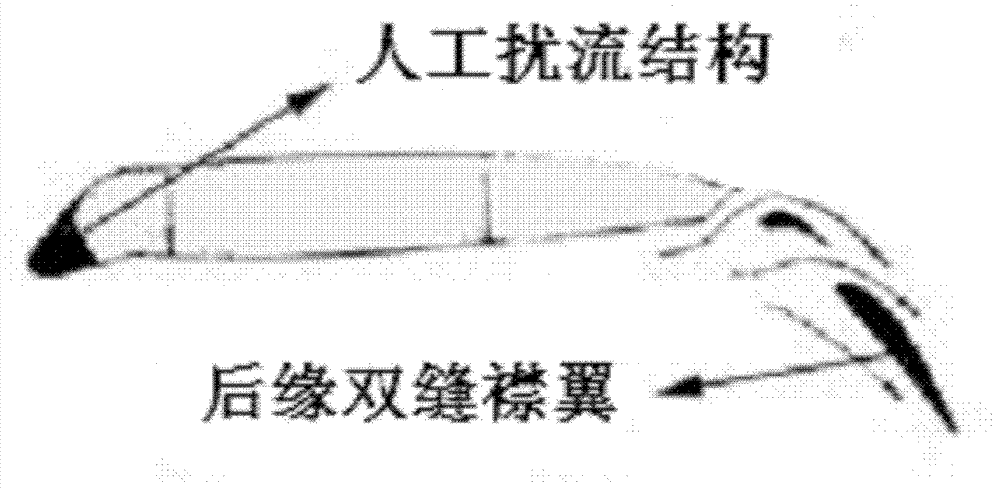
[0050] Described horizontal wing adopts flat wing, and the section of its flat wing is as follows figure 1 As shown in (1), it is streamlined as a whole, with an angle of attack, a leading edge sweep angle and a trailing edge sweep angle; the artificial spoiler structure 2 added near the leading edge part of the upper surface of the horizontal wing is A raised spoiler bar (such as figure 2 Shown in b); The trailing edge of the horizontal wing is equipped with a trailing edge double-sli...
Embodiment 2
[0063] See Figure 4 and Figure 5 , the wing-like structure is mainly composed of a fixed base 4 of cuboid structure and a horizontal wing 1 fixed thereon; wherein, one side of the fixed base is connected with the horizontal wing, and the other side is installed on the side of the locomotive or carriage, fixed The horizontal length of the base is 1 meter, the width is 30 cm, the thickness of the fixed base is 60 mm, and the horizontal wing and the fixed base form a 90-degree right angle.
[0064] Described horizontal wing adopts flat wing, and the section of its flat wing is as follows figure 1 Shown in (1), the artificial spoiler structure added near the leading edge part of the upper surface of the horizontal wing is a zigzag protruding spoiler (such as figure 2 shown in f).
[0065] The area of described horizontal wing is 2.25 square meters, and this moment root tip ratio is 1, and the length of horizontal wing is 225 centimetres, and leading edge sweep angle is 0 ...
Embodiment 3
[0077] See Figure 4 and Figure 5 , the wing-like structure is mainly composed of a fixed base 4 of cuboid structure and a horizontal wing 1 fixed thereon; wherein, one side of the fixed base is connected with the horizontal wing, and the other side is installed on the side of the locomotive or carriage, fixed The horizontal length of the base is 1 meter, the width is 30 cm, the thickness of the fixed base is 60 mm, and the horizontal wing and the fixed base form a 90-degree right angle.
[0078] Described horizontal wing adopts flat wing, and the section of its flat wing is as follows figure 1 Shown in (1), the artificial flow disturbance structure added near the leading edge part of the upper surface of the horizontal wing is to add an elastic flow-around band (such as figure 2 shown in d).
[0079] The area of described horizontal wing is 1.125 square meters, and this moment root tip ratio is 0.3, and the length of horizontal wing is 150 centimetres, and leading edg...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com