PTC ceramic sintering method
A sintering method and ceramic technology, which is applied in the field of electronic ceramic preparation, can solve problems such as high sensitivity, high reliability, impact resistance, high safety, weakened PTC effect, and increased room temperature resistivity.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
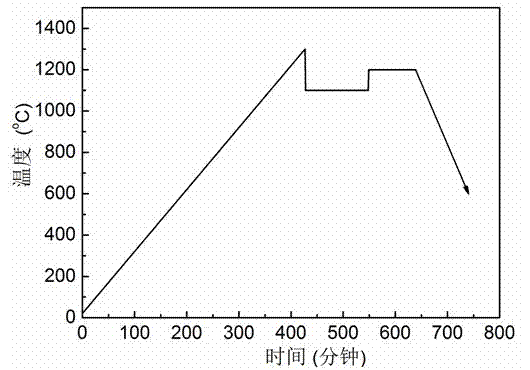
[0018] (1) Put the positive temperature coefficient (PTC) ceramic blank after debinding into the crucible, raise the furnace temperature to 1300°C at a rate of 3°C / min, keep it warm for 0 minutes, and the density of the ceramic will reach 76% of the theoretical density .
[0019] (2) After the step (1) is completed, the furnace temperature is lowered to 1100°C at a cooling rate of 200°C / min, and kept for 120 minutes, and the density of the ceramic reaches 98% of the theoretical density.
[0020] (3) After step (2) is completed, the furnace temperature is raised to 1200°C at a heating rate of 80°C / min, and held for 90 minutes. The density of the ceramic reaches the theoretical density, and then cools with the furnace, and finally obtains a dense structure and uniform grain size. , Ceramics with low room temperature resistivity and high PTC effect.
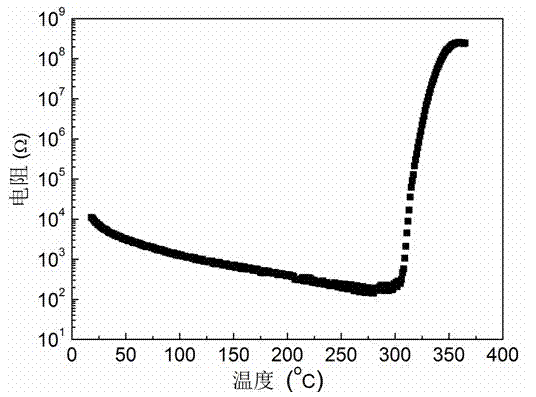
[0021] figure 1 A schematic diagram of the sintering method is given. After testing, the room temperature resistance reaches 72...
Embodiment 2
[0023] (1) Put the positive temperature coefficient (PTC) ceramic green body after debinding into the crucible, raise the furnace temperature to 1350°C at a heating rate of 5°C / min, keep it warm for 5 minutes, and the density of the ceramic will reach 79% of the theoretical density .
[0024] (2) After step (1) is completed, the furnace temperature is lowered to 1150°C at a cooling rate of 150°C / min and kept for 180 minutes, and the density of the ceramic reaches 98% of the theoretical density.
[0025] (3) After step (2) is completed, the furnace temperature is raised to 1250°C at a heating rate of 100°C / min, and the temperature is kept for 140 minutes. The density of the ceramic reaches the theoretical density, and then cools with the furnace, and finally obtains a compact structure and uniform grain size. , Ceramics with low room temperature resistivity and high PTC effect.
[0026] image 3 A schematic diagram of the sintering method is given. After testing, the room te...
Embodiment 3
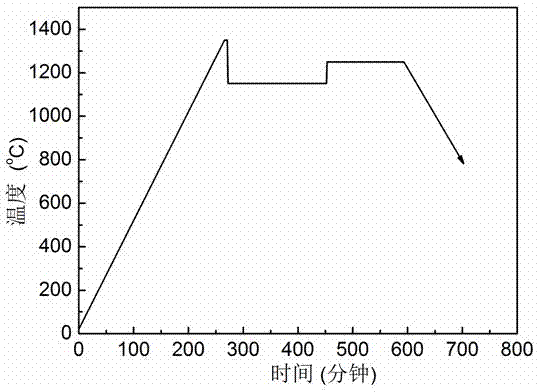
[0028] (1) Put the positive temperature coefficient (PTC) ceramic green body after debinding into the crucible, raise the furnace temperature to 1380°C at a heating rate of 7°C / min, keep it warm for 10 minutes, and the density of the ceramic will reach 83% of the theoretical density .
[0029] (2) After step (1) is completed, the furnace temperature is lowered to 1190°C at a cooling rate of 100°C / min, and kept for 240 minutes, and the density of the ceramic reaches 99% of the theoretical density.
[0030] (3) After step (2) is completed, the furnace temperature is raised to 1280°C at a heating rate of 150°C / min, and held for 180 minutes. The density of the ceramic reaches the theoretical density, and then cools with the furnace, and finally obtains a compact structure and uniform grain size. , Ceramics with low room temperature resistivity and high PTC effect.
[0031] Figure 5 A schematic diagram of the sintering method is given. After testing, the room temperature resist...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Room temperature resistance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Room temperature resistance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Room temperature resistance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com