Wireless sensor network-based energy-efficient collaborative scheduling method
A wireless sensor, energy-efficient technology, applied in wireless communication, energy consumption reduction, advanced technology, etc., can solve the problems of not considering energy consumption and tracking accuracy, not considering the network energy balance distribution, not considering the coordinated scheduling of neighbor nodes, etc. Achieve the effect of improving tracking accuracy and network reliability, balancing energy distribution and computing resources, and saving communication energy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
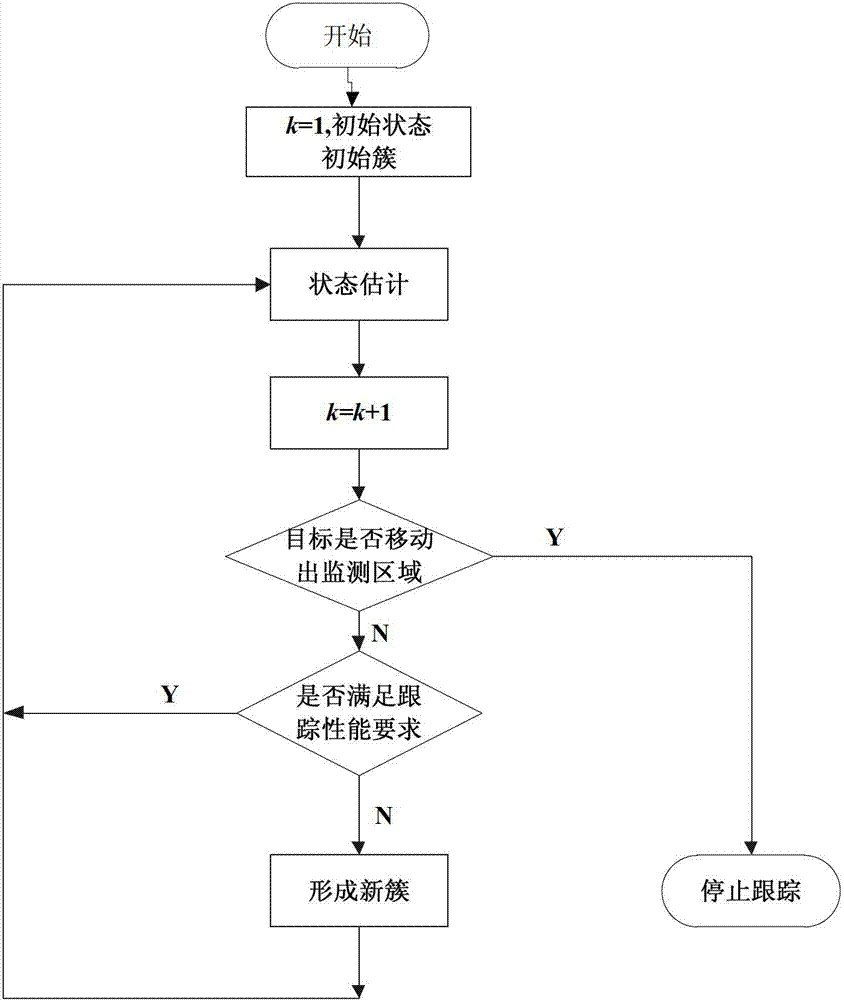
[0036] In combination with the above drawings, the present invention is based on an energy-effective collaborative scheduling method for wireless sensor networks, combined with a Gaussian particle filter method for target tracking, mainly including the following steps:
[0037] Step 1: Target initialization
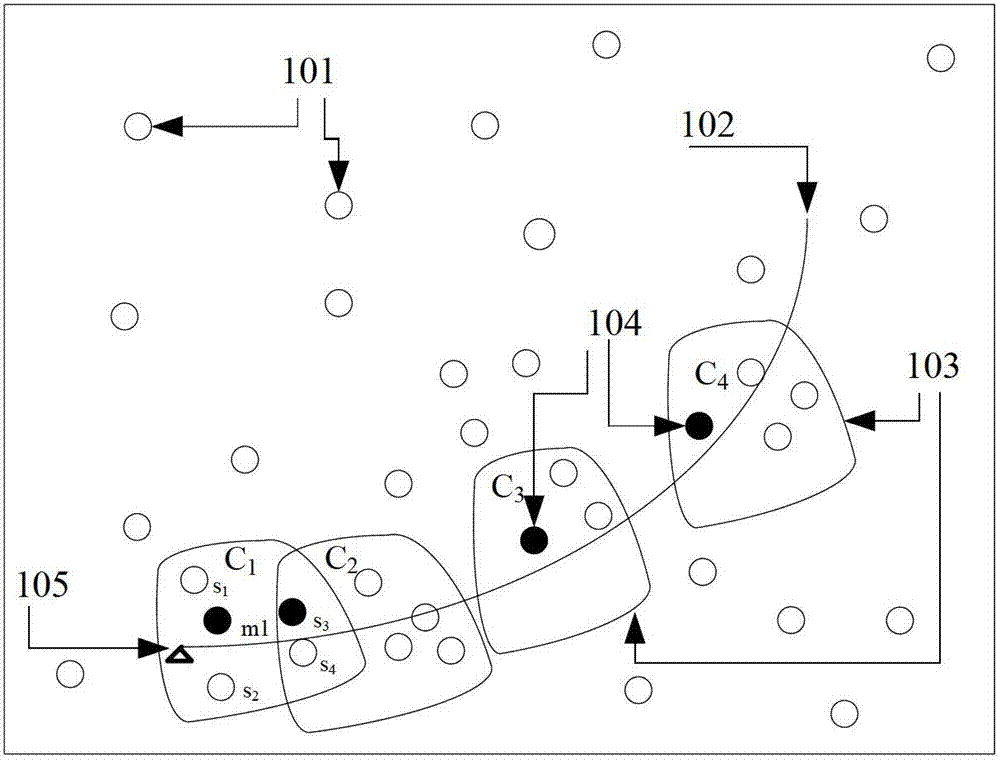
[0038] The target enters the monitoring area of the wireless sensor network at the initial time k=1, and the initial cluster S close to the target is awakened by prior information c1 ={m 1 ,s 1 ,...,s c1}, m 1 is the initial cluster head, which is the sensor node closest to the target, s 1 ,...,s c1 is the sensor node in the cluster. In order to adapt to the state estimation of the nonlinear non-Gaussian motion model, the present invention adopts the particle filter method, the cluster head m 1 get a set of particles from an initial prior distribution
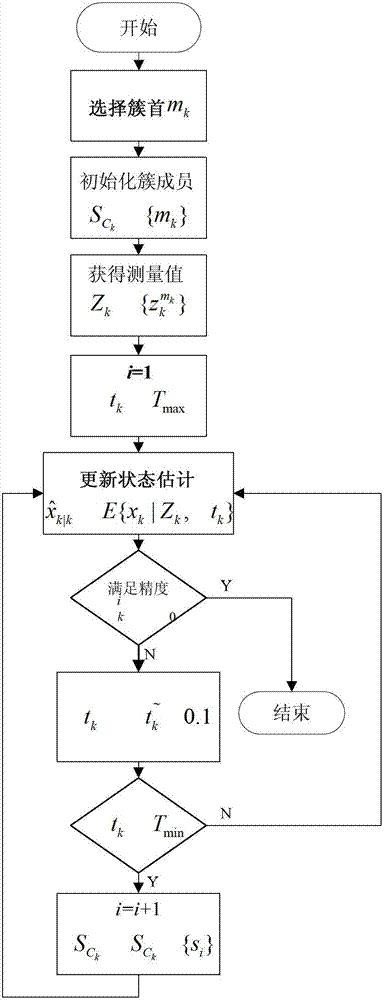
[0039] Step 2: State Estimation
[0040] cluster head m k Wake up the c in the cluster k sensor nodes joi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com