Optical scanning head drive control system based on hollow encoder and phase difference
A technology of drive control and optical scanning, which is applied in the field of optical scanning, can solve the problems of high precision and stability, and achieve the effect of improving errors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
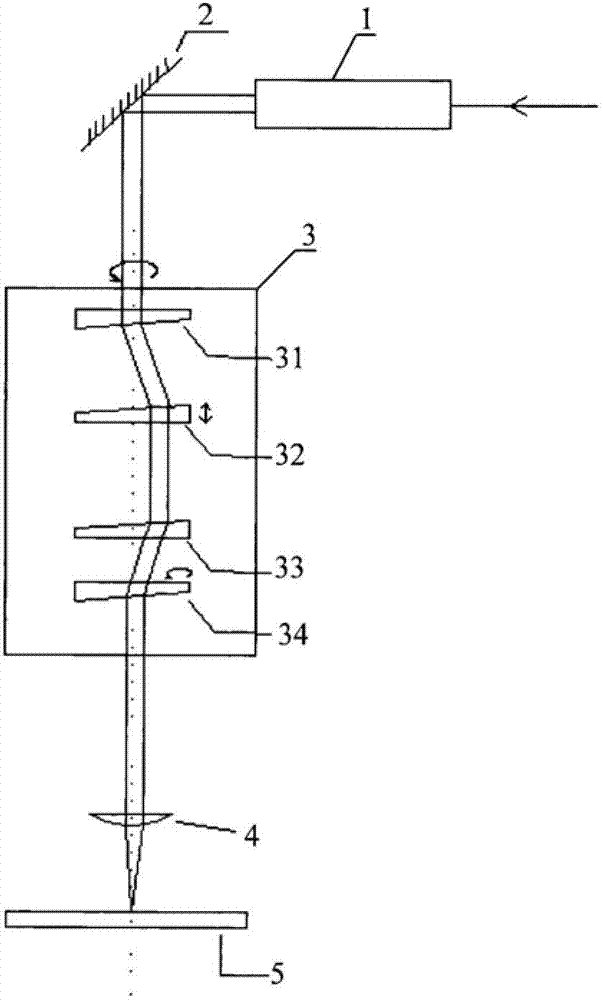
[0025] like figure 2 As shown, in order to directly collect the relative rotation angle of a pair of optical wedges 33 and 34, a hollow encoder is installed on the outer ring of the optical wedge to directly feed back the angle of the optical wedge.
[0026] The system includes a host computer interface, an upper following mirror drive module, a reference mirror driver, a lower following mirror drive module, etc. The upper computer interface part is mainly responsible for exchanging information with the upper computer and processing the IO control signals from the outside, so as to coordinate the work of each lens driving part. When driving, the upper following mirror driving module drives the optical wedge 33 to rotate, the lower following mirror driving module drives the optical wedge 34 to rotate, and the reference mirror driver simultaneously drives the optical wedges 31 and 32 to rotate.
[0027] like figure 2 As shown in , the host computer interface receives the com...
Embodiment 2
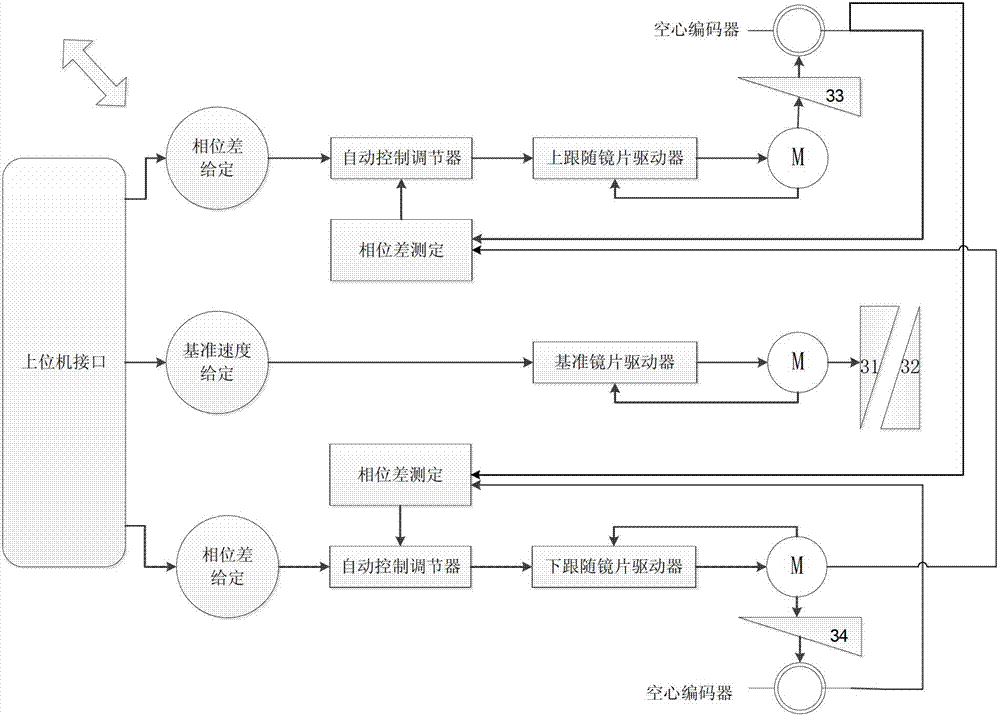
[0035] like image 3 As shown, compared with the first embodiment, in the second embodiment, the position feedback signal of the optical wedge 31 driven by the reference motor M is added. Since the reference motor operates at a constant speed, the position signal of the optical wedge 31 driven by it is fed back to the upper follower drive module and the lower follower drive module, and the precision of the deviation phase of its position is higher.
[0036] The position signal of the optical wedge 31 directly adopts the position signal fed back by the position sensor of the motor M.
[0037] like image 3 As shown, the outer rings of the optical wedges 33 and 34 are equipped with hollow encoders for feeding back the angle signals of each optical wedge. The phase difference signal between the optical wedges 31 and 33 is fed back to the automatic control regulator of the upper follower lens drive module, and the automatic control regulator compares the given phase difference s...
Embodiment 3
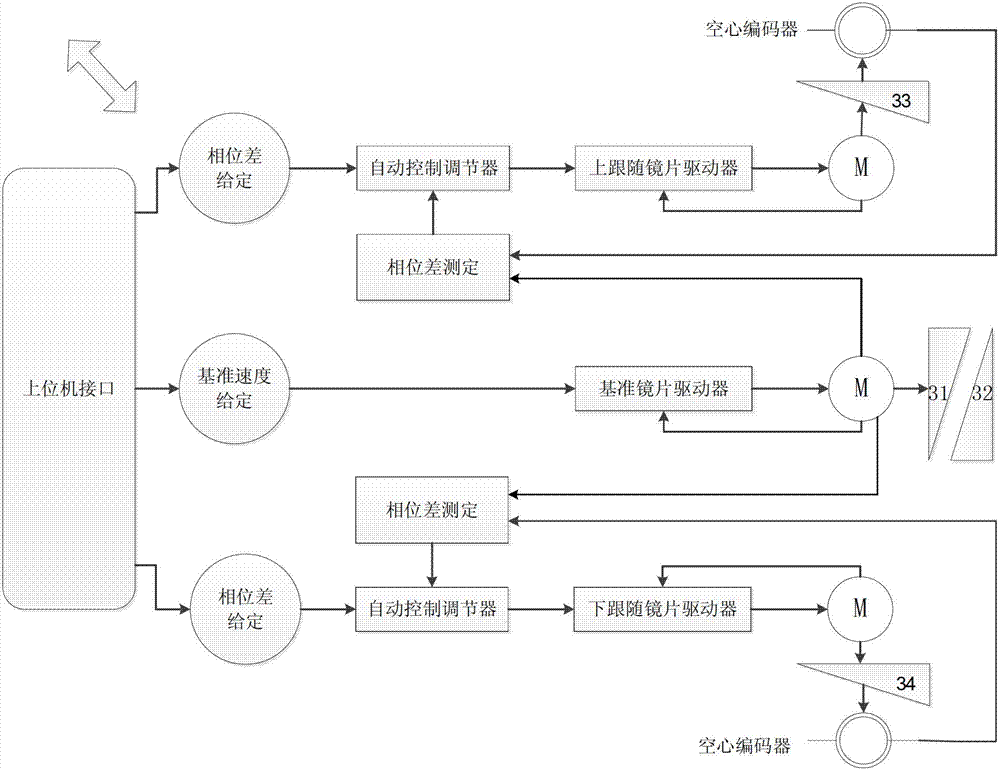
[0040] like Figure 4As shown, the third embodiment is compared with the second embodiment, a hollow encoder is installed on the outer ring of the optical wedge 31, and the position signal of the optical wedge 31 directly fed back by the hollow encoder is used as a reference signal.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com