Foundation coefficient K30 test method of railroad subgrade built by coarse-grained soil
A technology of foundation coefficient and railway subgrade, which is applied in the direction of applying stable tension/pressure to test the strength of materials, which can solve the problem that it is extremely difficult to determine whether the 1% deformation stability control requirement is met, and it is difficult to strictly implement this requirement. The use of the table is harsh and other problems, to achieve the effect of reducing the waiting time for downtime, easy implementation, and reducing records and calculations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
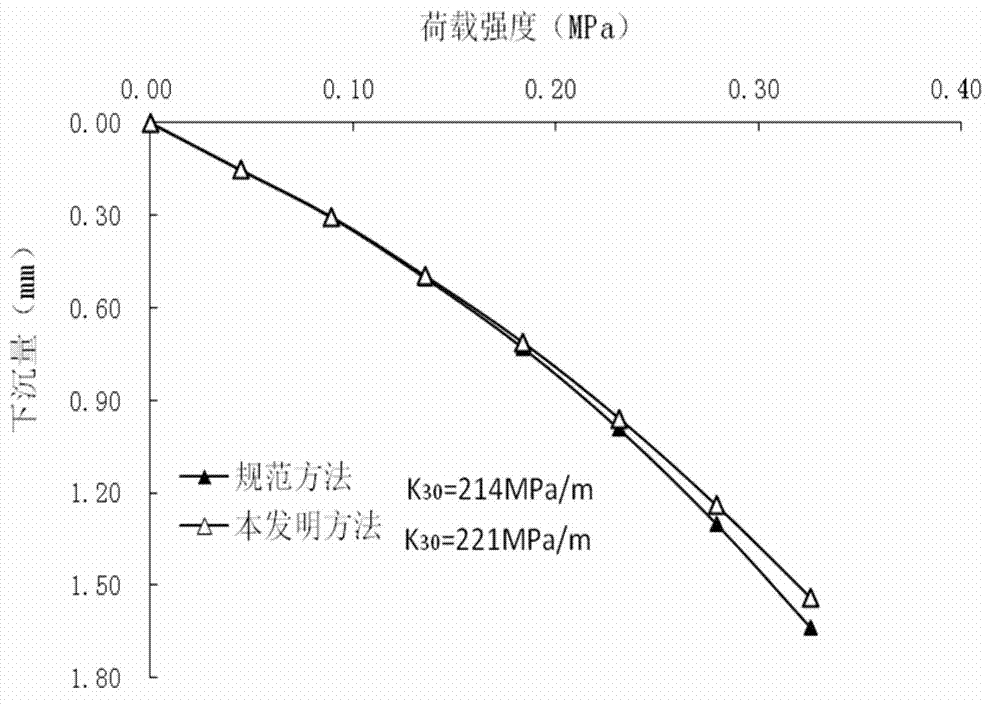
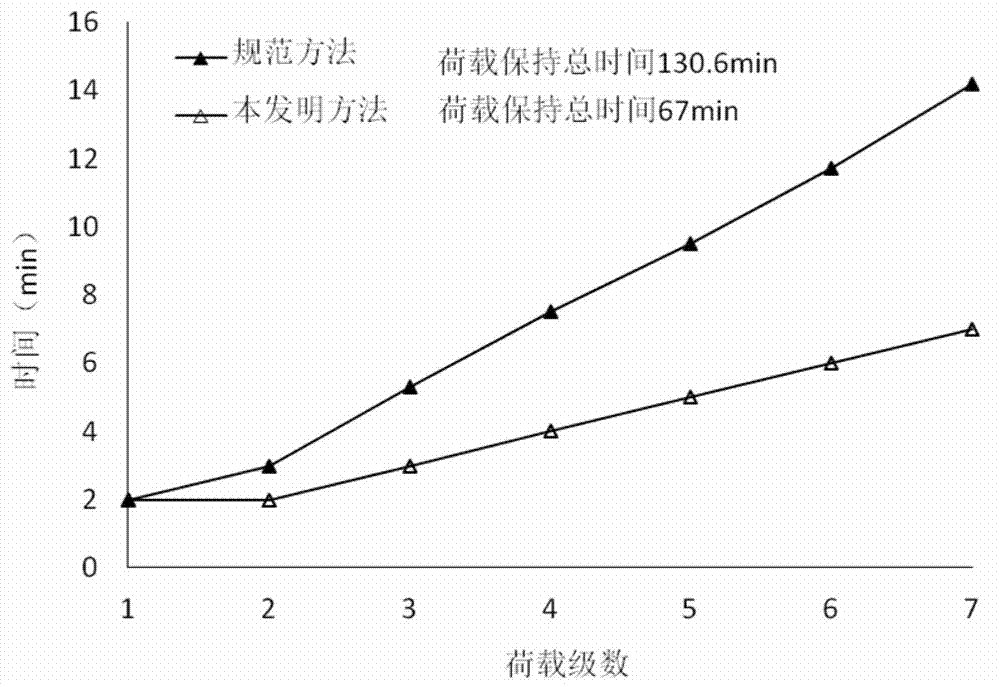
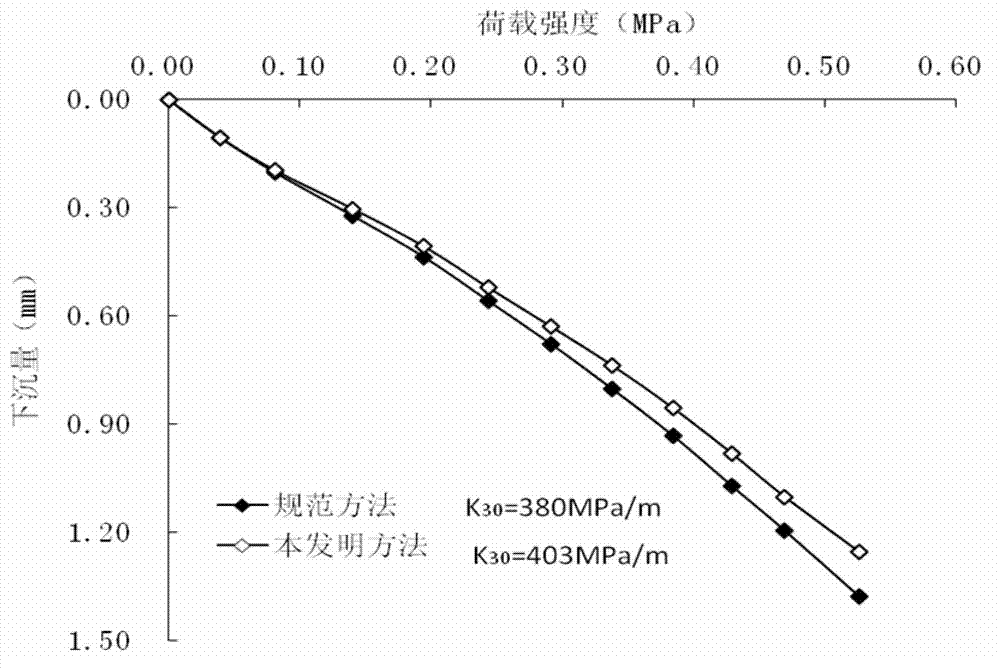
[0019] A specific embodiment of the present invention is that a foundation coefficient K 30 The test method includes the steps of leveling the test surface of the site, installing the foundation coefficient tester, preloading and stepwise loading in the loading test. The preload load is 0.04MPa, and the specific method of step-by-step loading in the loading test is: load step by step with the increment of each level of load being 0.04MPa, and the load retention time after the first level of load (0.04MPa) is applied is 2 minutes, starting from the second level of load (total load 0.08MPa), the number of minutes of the load retention time after each level of load is loaded is equal to the number of loading levels, and the level is recorded when the load retention time of each level of loading meets the requirements Loaded subsidence until the foundation coefficient K is reached 30 When the test termination condition of the test (the total amount of subsidence reaches 1.25mm an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com