Method of rapidly eliminating antibiotic-resistant plasmids in E. coli
A technology of Escherichia coli and antibiotics, applied in the field of microbial genetics, to achieve good results, high plasmid elimination rate, and promote breakdown
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
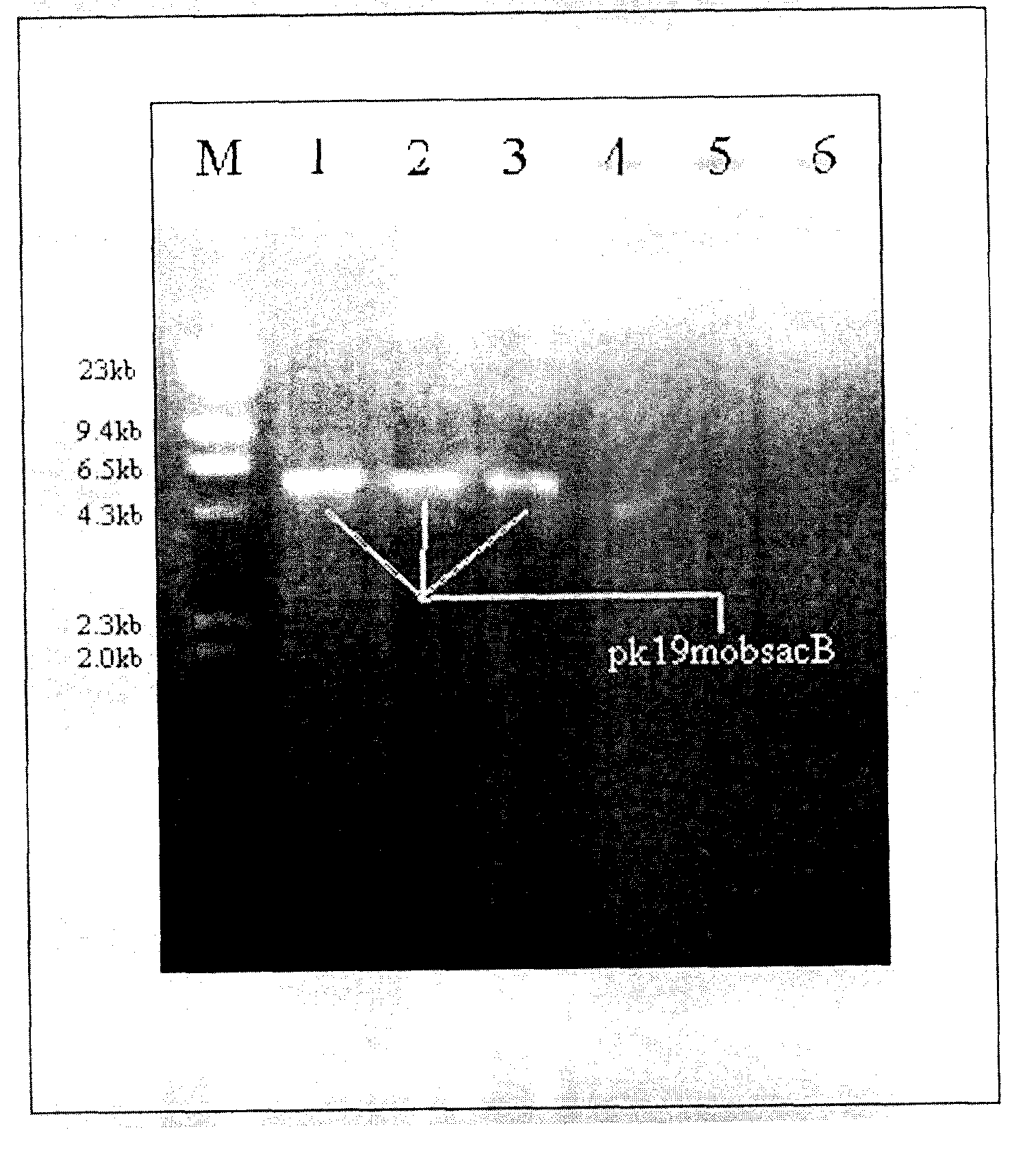
[0047] Escherichia coli SCS110, JM109, and DH5α contain the antibiotic resistance plasmid pK19mobsacB, which belongs to Gram-negative bacteria. Because there is a kanamycin resistance gene on the pK19mobsacB plasmid, Escherichia coli SCS110, JM109, and DH5α containing the pK19mobsacB plasmid can all be used in the Grow on kanamycin-resistant plates.
[0048] A method for obtaining Escherichia coli that eliminates antibiotic resistance plasmids after electric shocking human enterobacteria, the steps are as follows:
[0049] A. Preparation of competent cells:
[0050] (1) Pick the antibiotic-resistant plasmid pk19mobsacB from the LB plate (Schafer A, Tauch A, Jager W, et al. Small mobilizable multi-purpose cloning vectors derived from the Escherichia coli plasmids pK18 and pK19: selection of defined deletions in The chromosome of Corynebacterium glutamicum.Gene, 1994, 145 (1): 69-73) Escherichia coli single bacterium colony, such as Escherichia coli SCS110 strain single bacteri...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com