Porous screw blade rotor in heat exchange tube
A technology of helical blades and heat exchange tubes, applied in the field of porous helical blade rotors, can solve the problems of insignificant effect of field synergy to strengthen heat transfer, damage to the inner wall of heat exchange tubes, and short service life of bearings, saving materials and enhancing the effect of mixed flow. , the effect of reducing the operating speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
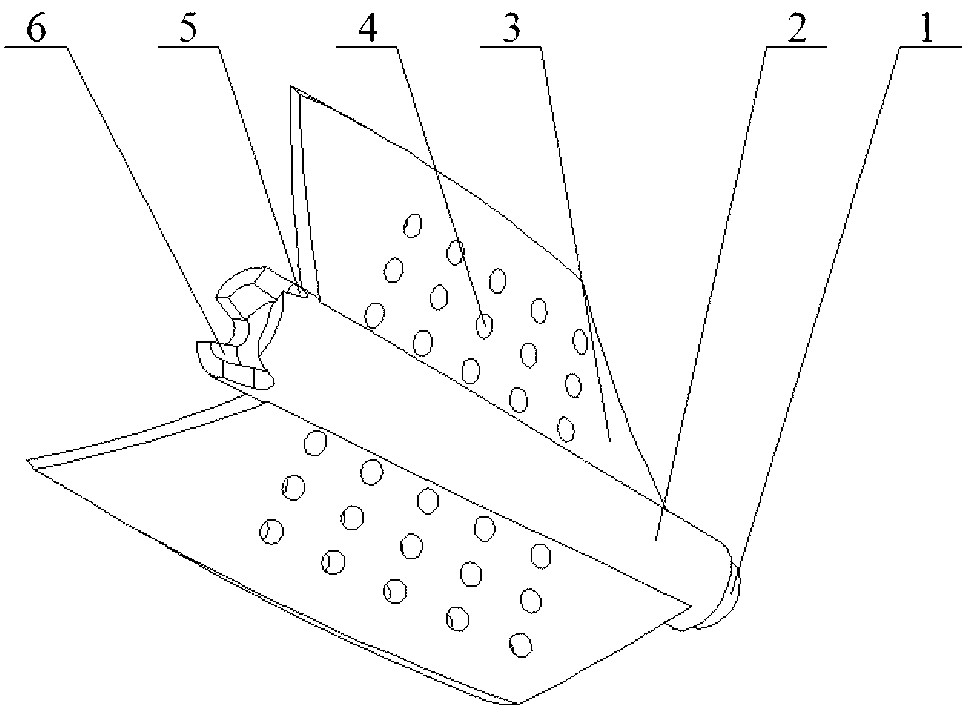
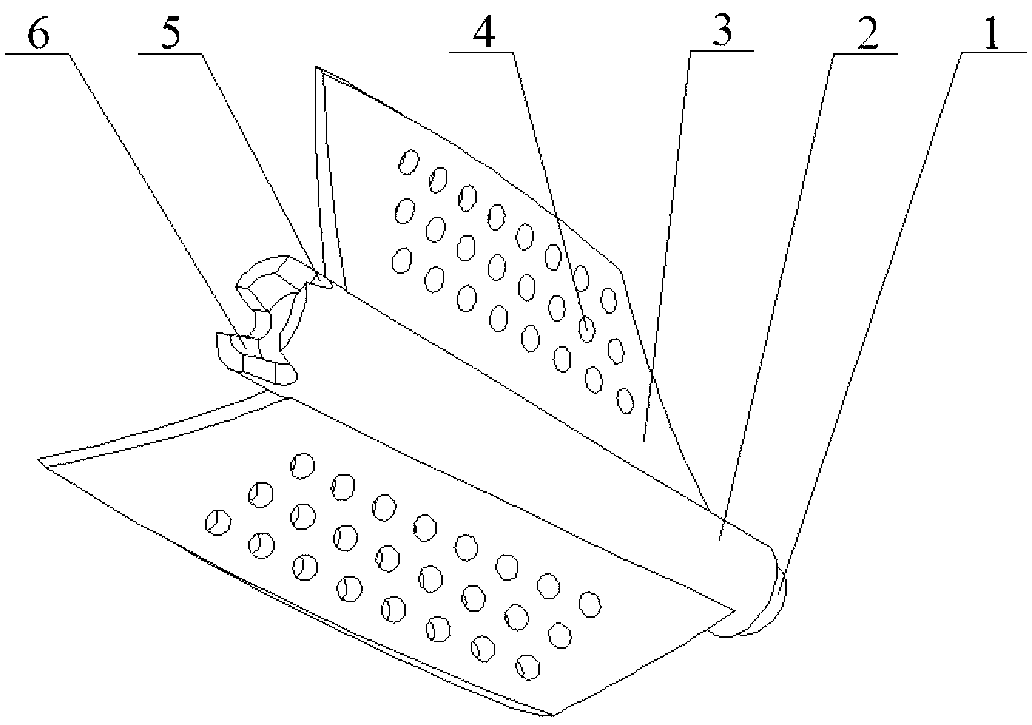
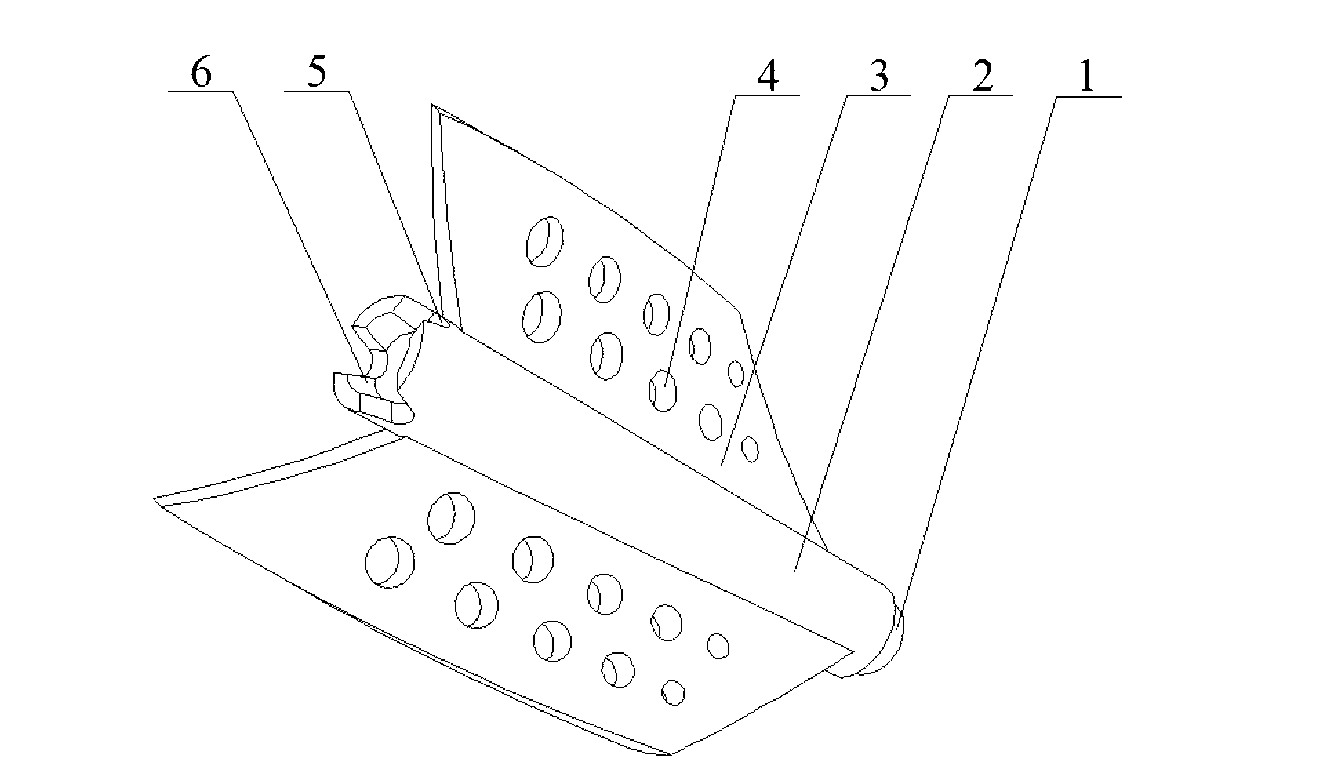
[0019] Such as Figure 5 As shown, the present invention is a porous helical blade rotor in a heat exchange tube. The enhanced heat transfer device includes a rotor, a rotating shaft 7, a heat exchange tube 8 and a hanging piece 9. Several rotors are connected in series through the rotating shaft 7. The hanging piece 9 is fixed on the heat exchange tube. The two ends of the tube 8 and the two ends of the rotating shaft 7 are respectively fixed on the pendant 9. The rotor of the present invention is composed of a certain number of porous spiral blades 3 fixed on the surface of the hollow shaft 2, and the hollow shaft 2 is also provided with a ball-and-socket protrusion Table 1, a hole 5 communicating with the inner hole of the hollow shaft and a ball-and-socket concave table 6. Among the two adjacent rotors, the ball-socket boss 1 at the head of the hollow shaft 2 of one rotor is combined with the ball-socket recess 6 at the tail of the other rotor to connect and adjust them to...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com