Rotational inertia on-line identification method for alternating current (AC) permanent magnet synchronous motor servo system
A permanent magnet synchronous motor, rotational inertia technology, applied in control systems, control generators, vector control systems, etc., can solve the problem of high requirements for digital processing chip storage space and operation speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
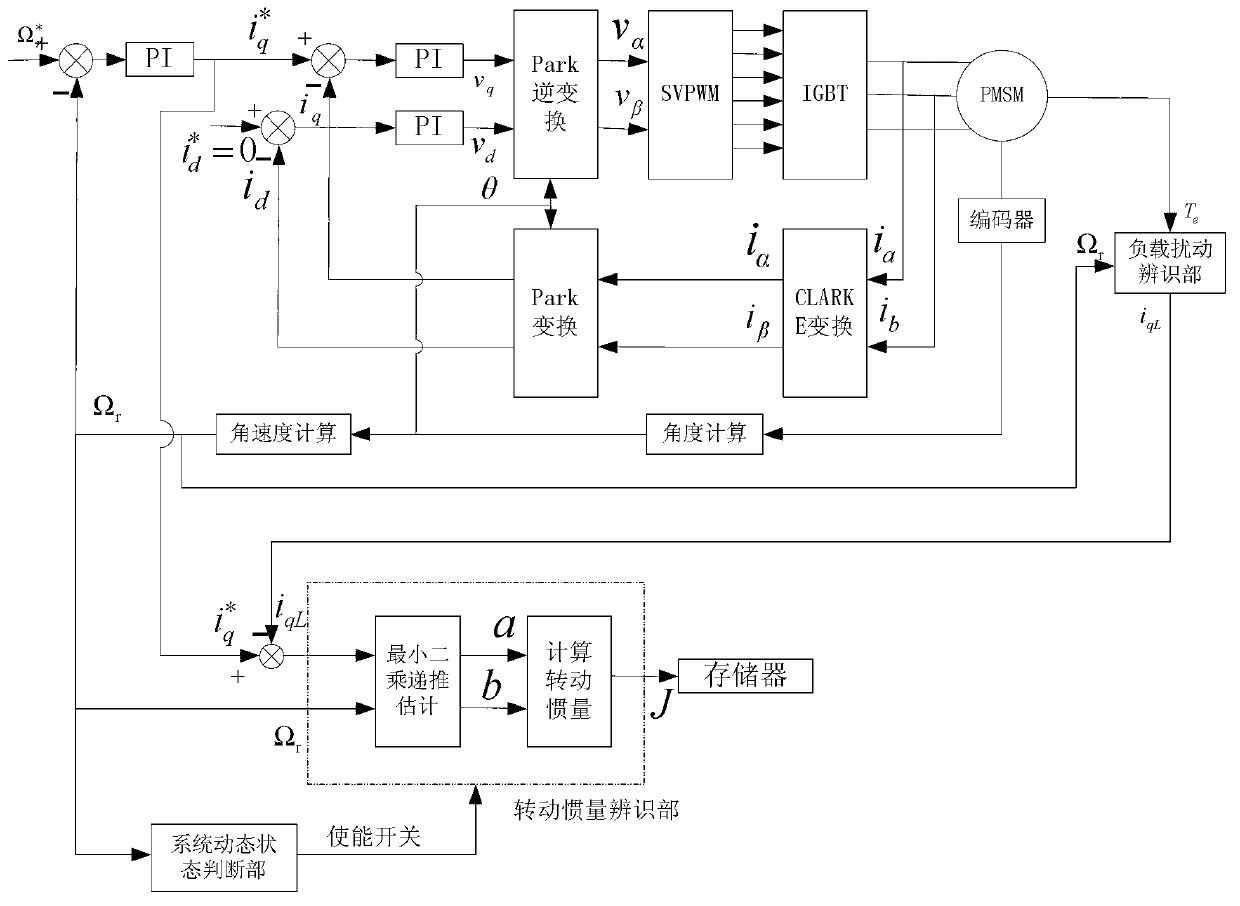
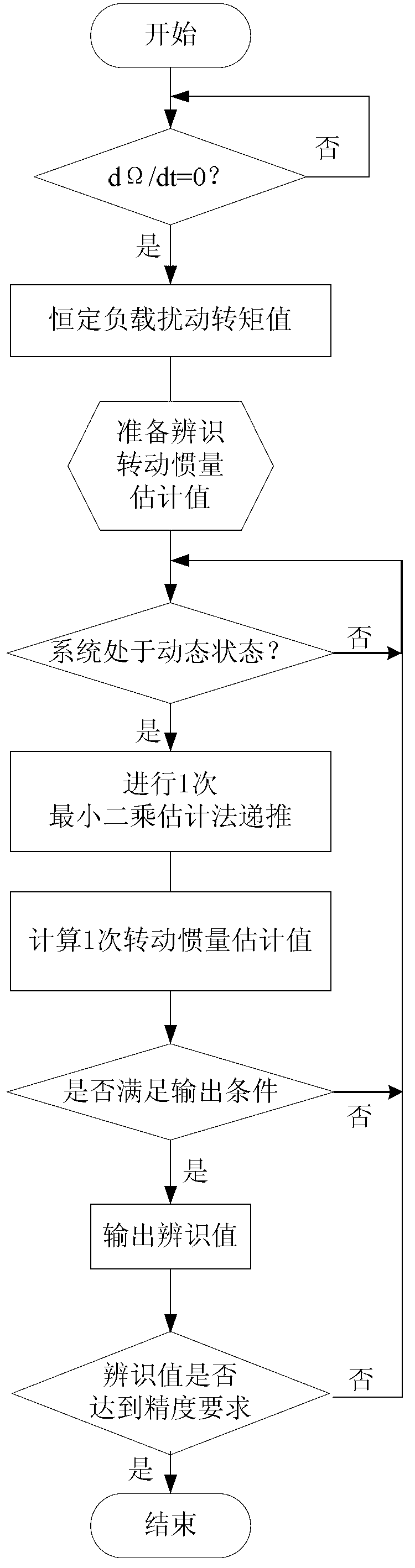
[0050] Specific implementation mode one: the following combination figure 1 with figure 2 Describe the present embodiment, the online identification method of the moment of inertia of the AC permanent magnet synchronous motor servo system described in the present embodiment, the online identification method is used in the dynamic operation process of the motor, and it is characterized in that it includes the following steps:
[0051] Step 1: Use the load torque identification unit to identify the constant load disturbance torque value T L ;
[0052] Step 2: Use the system dynamic state judgment part to judge whether the motor speed is in a dynamic change stage. When the motor speed is in a dynamic change stage, and the change rate of the motor speed is higher than the critical change rate of the motor moment of inertia identification, use the recursive based The estimated value of the moment of inertia is obtained by calculating the least square estimation method;
[0053]...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0058] Specific Embodiment 2: This embodiment further explains Embodiment 1. In Step 1 of this embodiment, the load torque identification unit is used to identify the constant load disturbance torque value T L The specific method is:
[0059] According to constant load disturbance torque T L The mechanical equation of motion:
[0060] J dΩ r dt + BΩ r + T L = T e ,
[0061] In the formula, J is the estimated value of the moment of inertia to be identified, Ω r is the mechanical angular velocity of the motor rotor, t is time, B is the viscous friction coefficient, T e is the electromagnetic torque of the motor;
[0062] when when T e = BΩ r +T L , ignore BΩ at this time r , with T e ≈T L , thus identifying the constant load disturbance torque ...
specific Embodiment approach 3
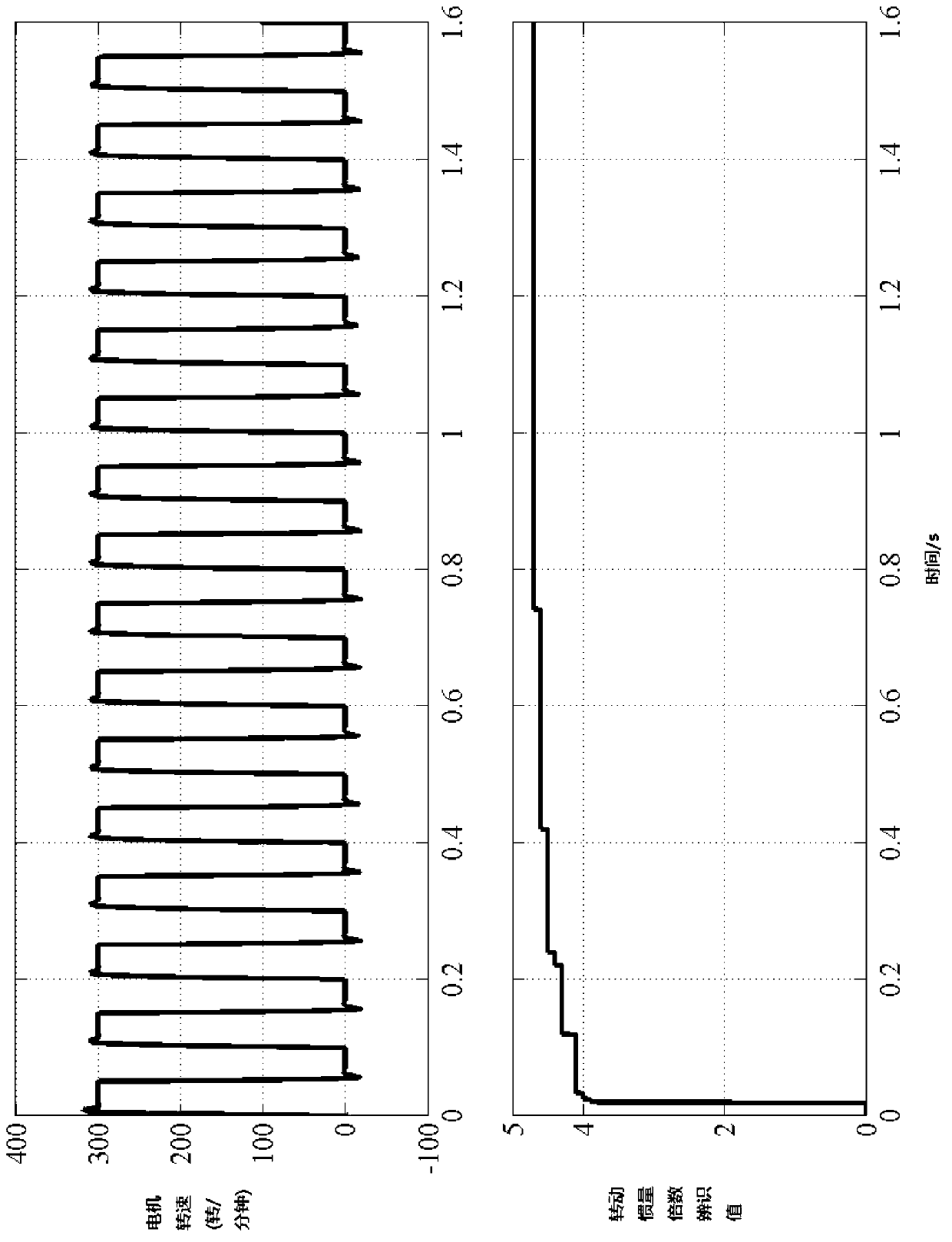
[0067] Specific implementation mode three: the following combination Figure 1 to Figure 6 Describe this embodiment, this embodiment will further explain Embodiment 2, the specific method for calculating and obtaining the estimated value of moment of inertia J by using the least squares estimation method based on recursion described in this embodiment is:
[0068] With a given q-axis component i of the stator current q To overcome the constant load disturbance torque T L The stator current q-axis component i qL The difference is used as input, and the mechanical angular velocity of the motor rotor Ω r As output, the transfer function H(s) of the motor dynamics in Laplace form is obtained:
[0069] H ( s ) = Ω r ( s ) ΔI q ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com