Method for detecting Sybil attack in underwater wireless sensor networks
An underwater sensor and intrusion detection technology, applied in network topology, wireless communication, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of high energy consumption, large storage resources and energy overhead, and inability to use energy to supplement energy, etc., to ensure safety and good performance. Expansion effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0066] specific implementation
[0067] In order to further explain the technical means and effects of the present invention to achieve the intended purpose of the invention, the specific implementation, structure, features and effects of the present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and preferred embodiments. back.
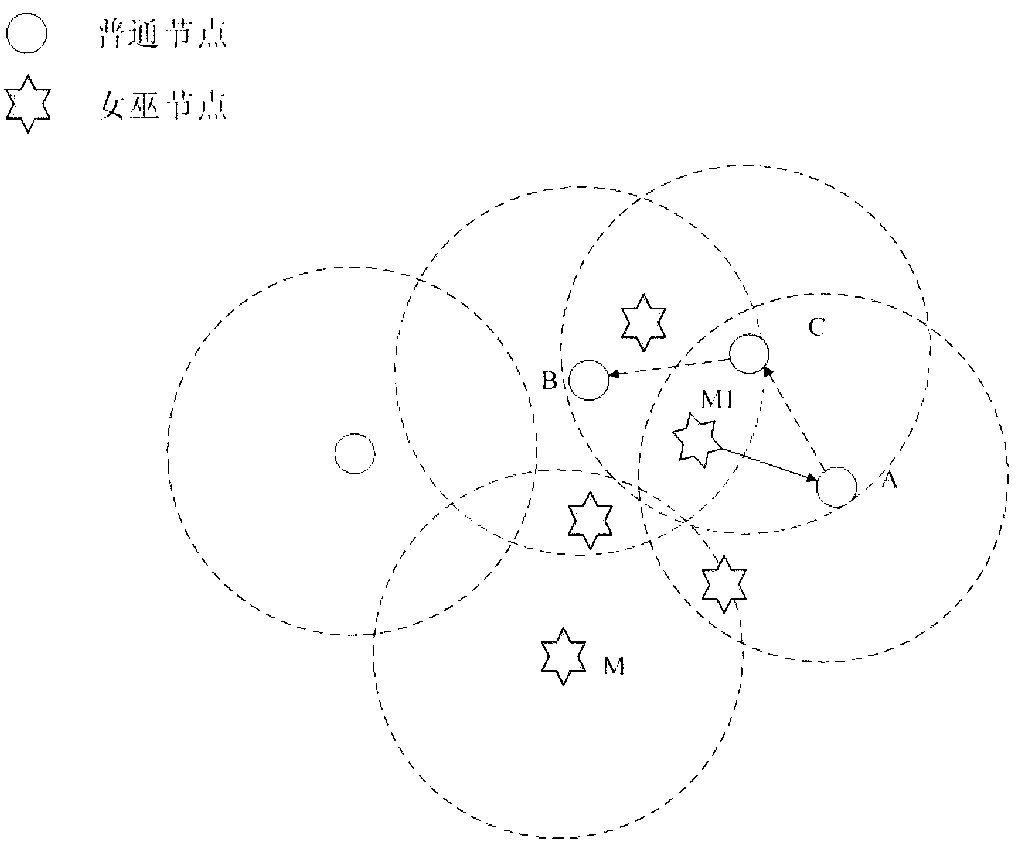
[0068] The essence of sybil attack is that sybil nodes act as legitimate nodes by forging false identities or stealing the identities of legitimate nodes, and put these nodes into the network, receive information from source nodes or intermediate nodes, and tamper with information such as coordinates, hops, and routes at will Or discard the data, so that the information cannot be safely and correctly transmitted to the destination node, which seriously affects the security positioning, geographic location routing, multi-path and topology structure of the underwater sensor network.
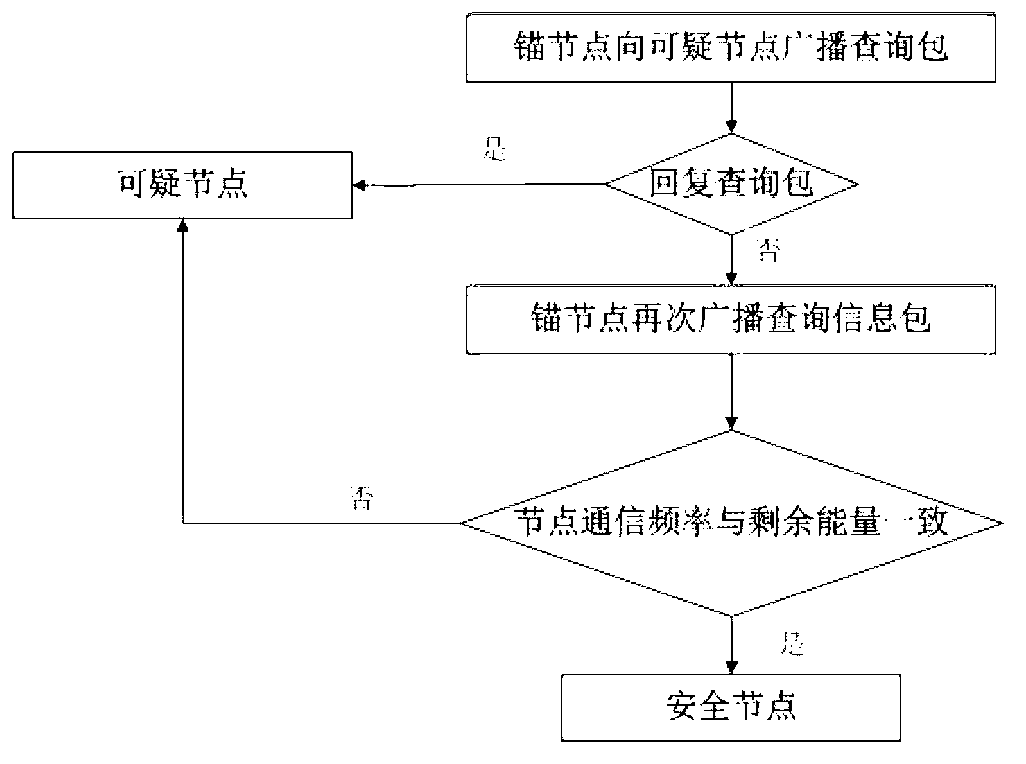
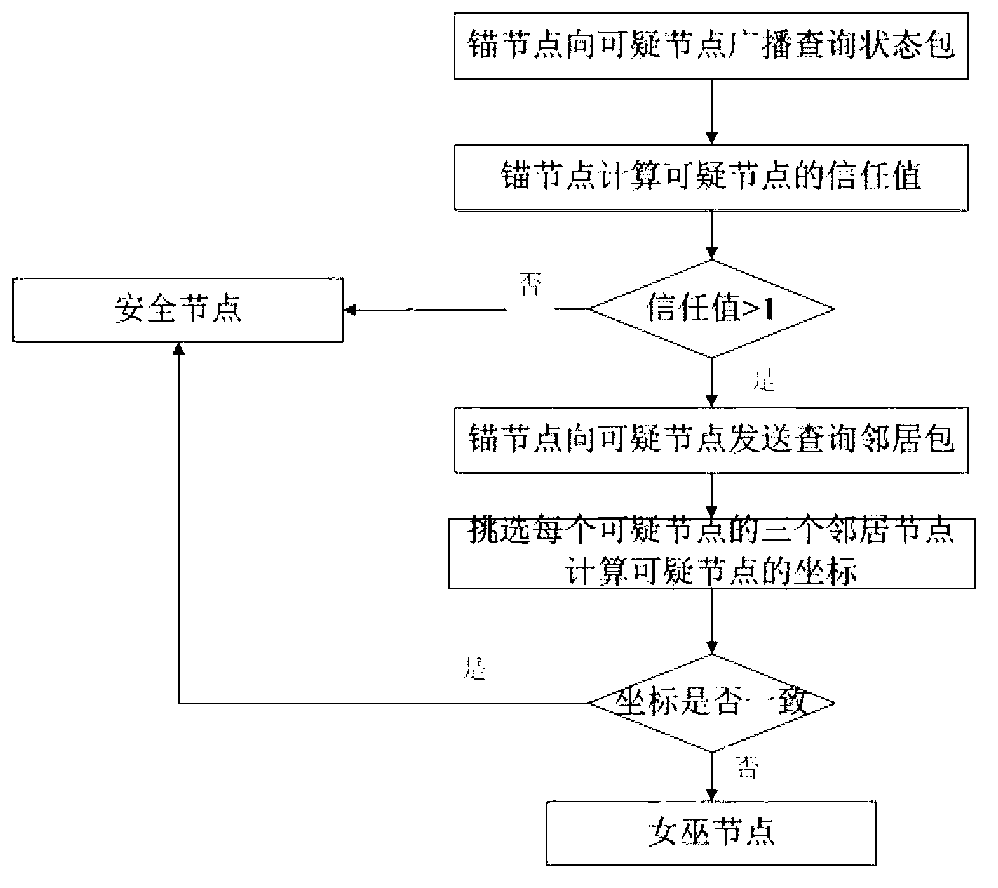
[0069] According to the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com