Synchronous monitoring device for femtosecond laser micromachining
A femtosecond laser and monitoring device technology, applied in the field of femtosecond laser optical path, can solve the problems of indetermination, cumbersome experiments, increased errors and complexity, etc., to improve processing accuracy and repeatability, uniform laser energy distribution, The effect of simplifying the processing steps
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
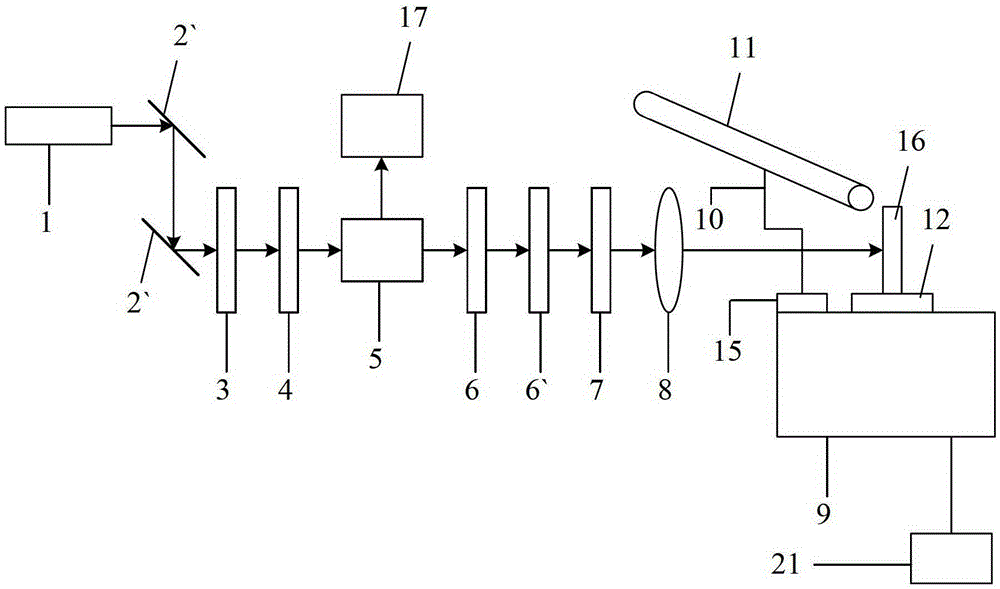
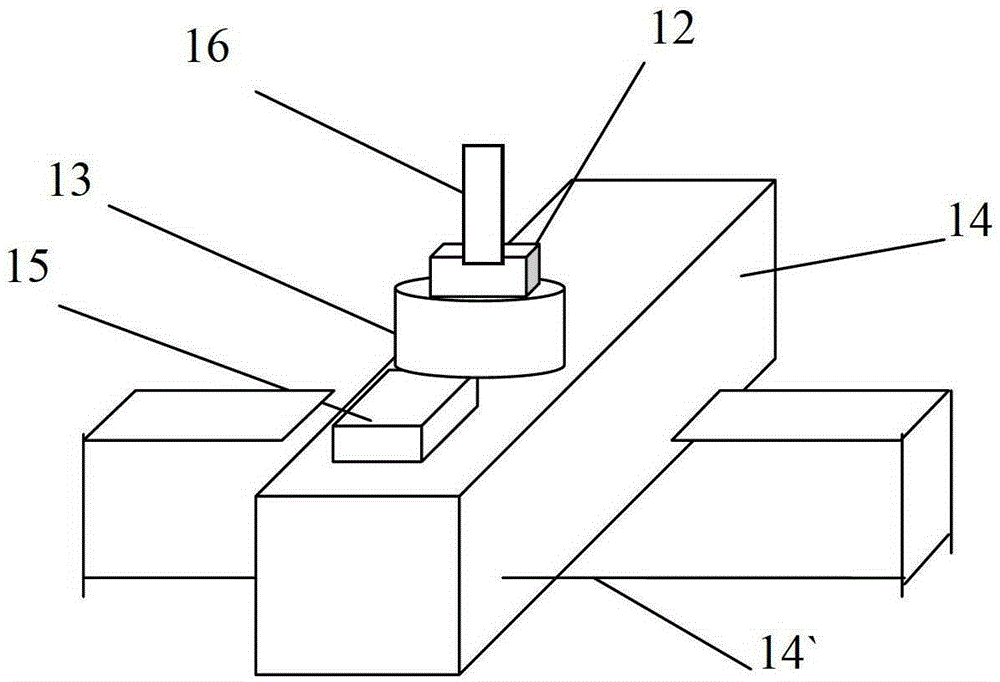
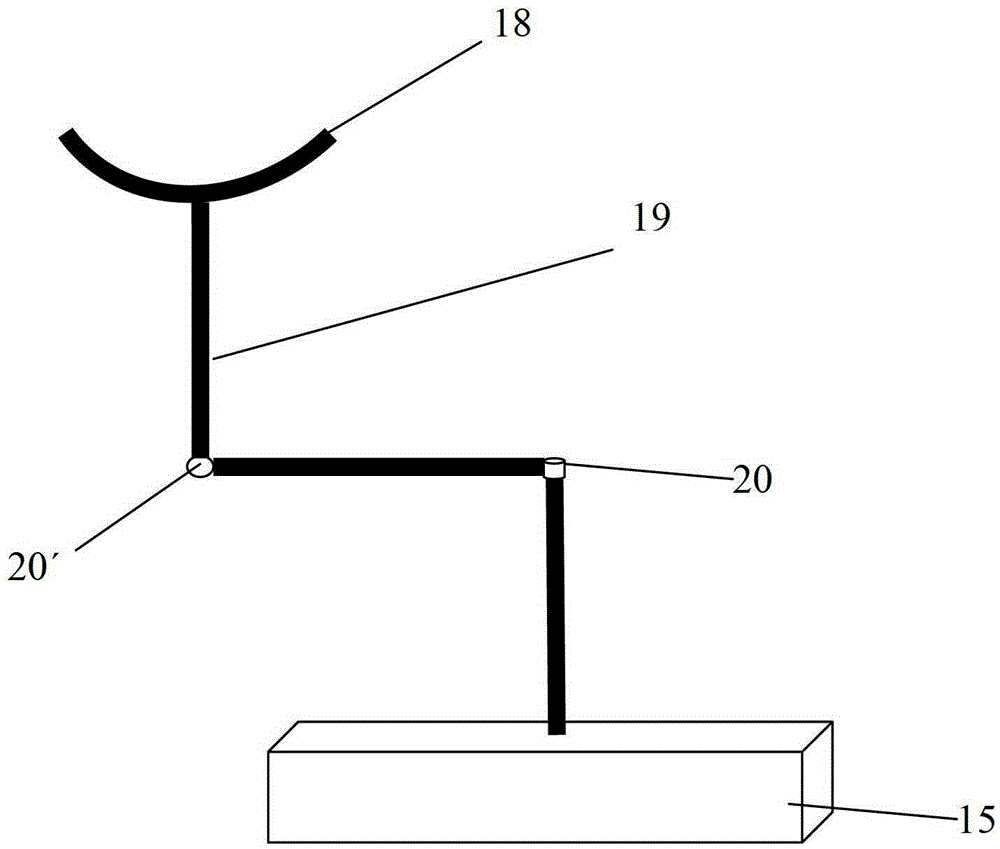
[0020] see figure 1 The synchronous monitoring device for femtosecond laser micromachining of the present invention includes: a femtosecond laser 1, and the device composition also includes: along the femtosecond laser optical path output by the femtosecond laser 1, two parallel total reflection mirrors 2, 2 are sequentially arranged ', attenuation film 3, polarizer 4, beam splitting prism 5, two diaphragms 6, 6', shutter 7, focusing lens 8 and processing object 16. The beam splitting prism 5 divides the femtosecond laser into two beams of identical energy, one beam is output along the femtosecond laser optical path of the femtosecond laser 1 for processing, while the other beam enters the power meter 17 along another optical path, As the energy specimen, the energy of the femtosecond laser is measured, which simplifies the processing steps and reduces the error caused by the energy measurement due to multiple interruptions of processing. In the present invention, the two ape...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com