Tunable small wavelength interval equal power dual wavelength fiber laser
A fiber laser and wavelength spacing technology, applied in the field of lasers, can solve the problems of unseen small wavelength spacing lasers, unsatisfactory effect, and difficulty in implementation, and achieve the effect of compact structure, stable and reliable performance, and no insertion loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
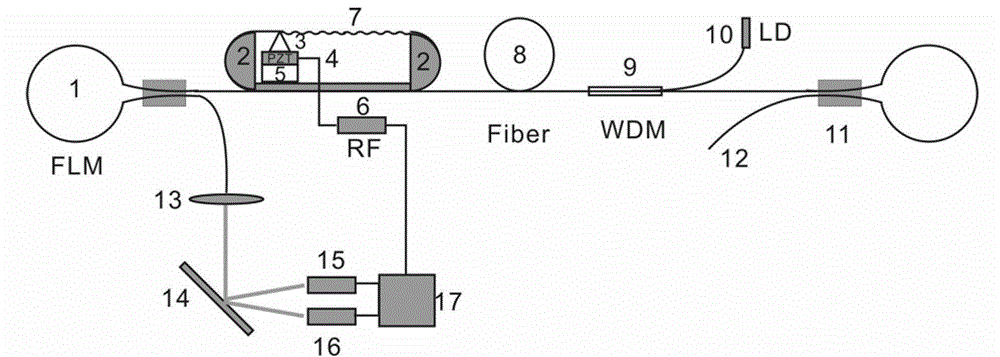
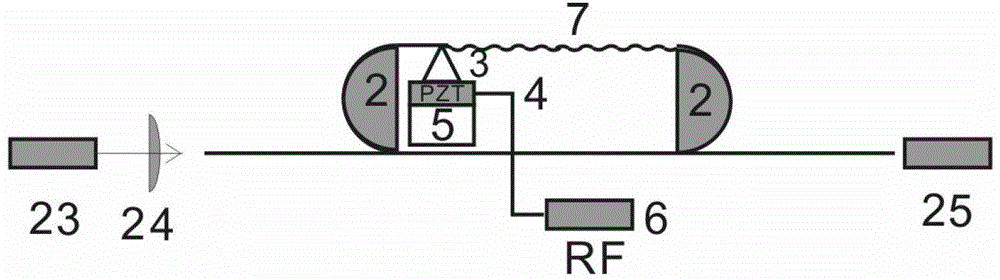
[0052] Such as figure 1 As shown, following the above-mentioned technical solution of the present invention, the tunable small-wavelength interval equal-power dual-wavelength fiber laser of this embodiment includes a fiber laser main body, a tunable filter, and an equal-power controller.
[0053] In this embodiment, taking the dual-wavelength output around 1080 nm as an example, the wavelength interval can be continuously adjusted from 8 nm to 24 nm. (In this embodiment, the neodymium-doped fiber is selected as the doped fiber, which has three gain ranges, namely 1080nm, 940nm and 1320nm, wherein the transition probability at 1080nm is the largest, the gain spectrum is also the strongest, and the gain spectrum is also relatively wide, from 1040nm —1160nm has a strong gain, the maximum gain is at 1080nm, and its front and rear edges are not symmetrical. To achieve dual-wavelength equal power output, the same net gain must be obtained first. This is achieved by two methods, one ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com