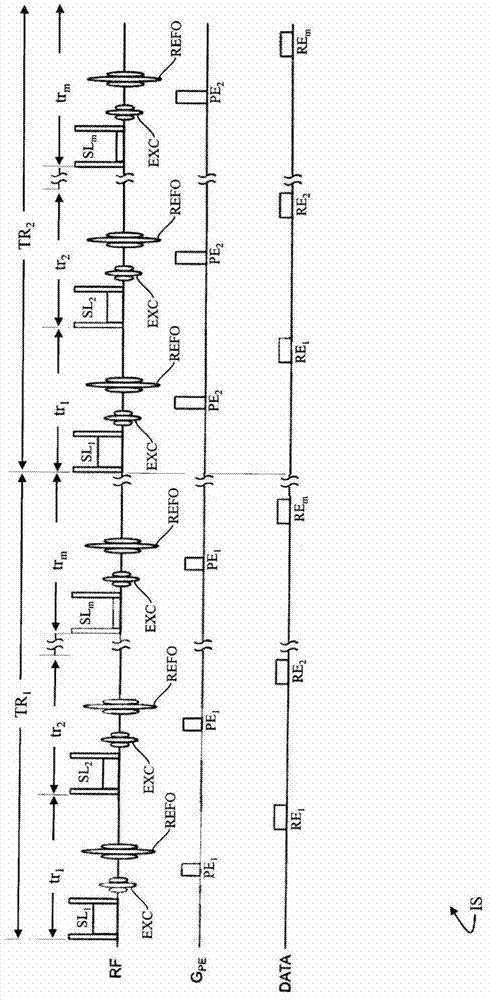
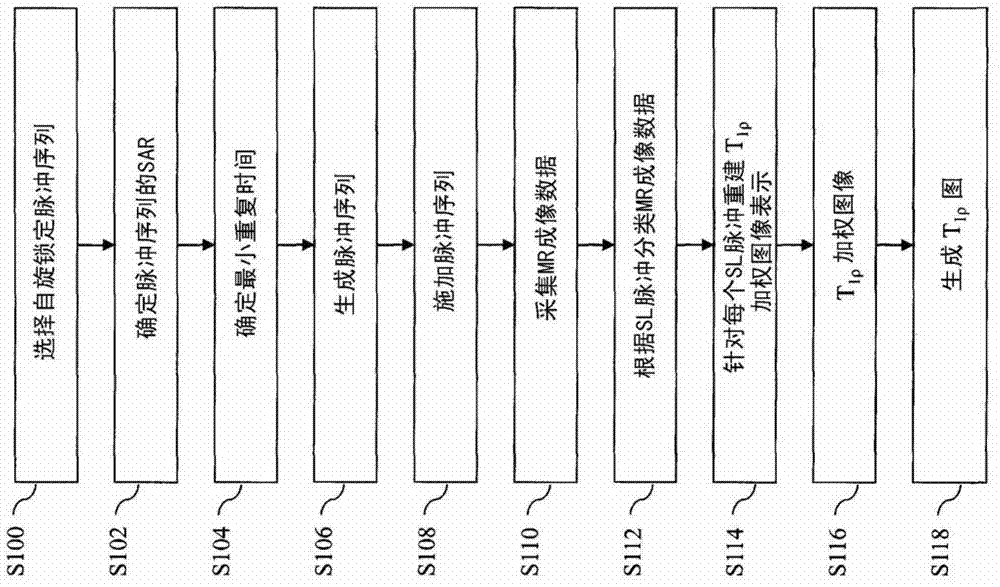
Interleaved spin-locking imaging
A lock-on-pulse, image-representation technique for use in the field of spin-lattice relaxation pulse sequences, which can solve the problems of patient discomfort during scan times, increase motion artifacts, sacrifice scan resolution or anatomical coverage, and achieve short repetition times , the effect of reducing the scan time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
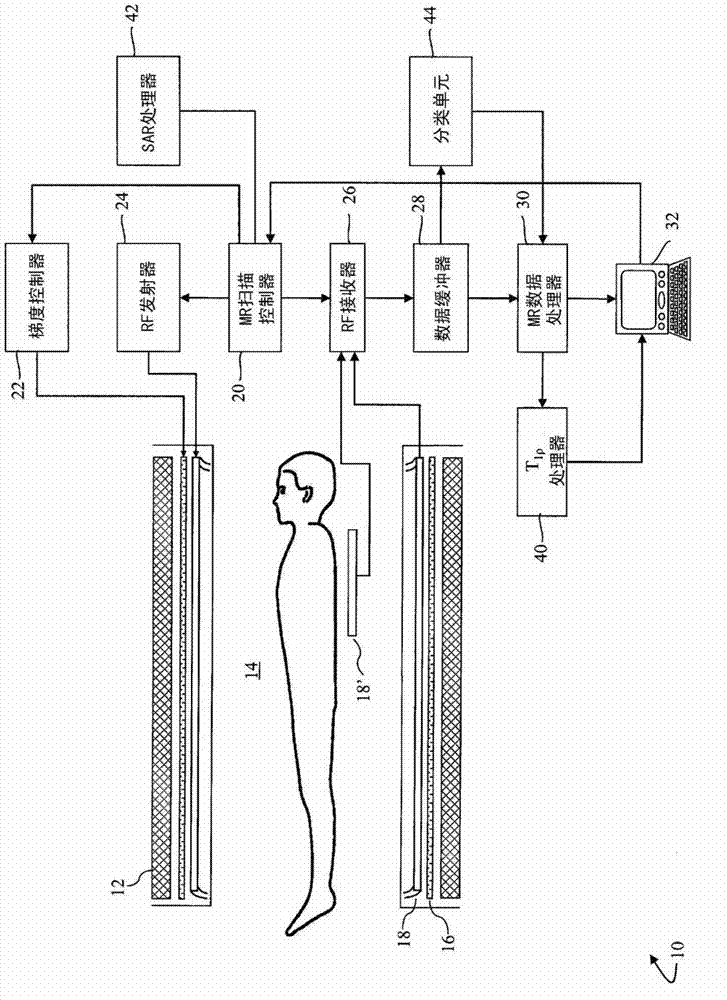
[0018] refer to figure 1 , the magnetic resonance imaging system 10 includes a main magnet 12 that generates a temporally uniform B across the examination region 14 0 field. The main magnet can be a ring or bore magnet, a C-shaped open magnet, open magnets of other designs, and the like. The gradient magnetic field coil 16 disposed adjacent to the main magnet acts to move along with respect to B 0 Selected axis of the magnetic field to generate a magnetic field gradient. A radio frequency coil, such as a whole body radio frequency coil 18, is positioned adjacent to the examination region. Optionally, in addition to or instead of the whole body RF coil 18, a local or surface RF coil 18' is provided.
[0019] A scan controller 20 controls a gradient controller 22 which causes the gradient coils to apply selected phase-encoding gradients across the imaging region, as may be appropriate for a selected magnetic resonance imaging or spectroscopy sequence. The scan controller 20...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com