Irrigation method for improving water use efficiency of peanuts in dry land
A technology for peanut and watering, applied in the direction of botany equipment and methods, applications, watering devices, etc., can solve the problems of peanut water management technology lack of norms, standards, adverse effects on soil physical properties, low water use efficiency, etc., to improve Water use efficiency, technical conditions are easy to control, and the effect of water use efficiency improvement
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] 1 Materials and methods
[0025] 1.1 Materials
[0026] The peanut varieties were Huayu 22 and Huayu 25.
[0027] 1.2 Method
[0028] 1.2.1 Mulching and sowing
[0029] The summer direct-seeding peanut varieties Huayu No. 22 and Huayu No. 25, which are drought-resistant and barren-resistant, are suitable for arid and semi-arid areas, and are sown when the ground temperature of the 0-10cm soil layer reaches 15°C. Watering is manually controlled, and the amount of water at the bottom before sowing is 1200m 3 / hm, and the soil moisture content was determined by the drying method. Apply ternary compound fertilizer (15-15-15) 600kg / hm before sowing 2 , the management measures are the same as the high-yield field.
[0030] 1.2.2 Experimental grouping and irrigation methods
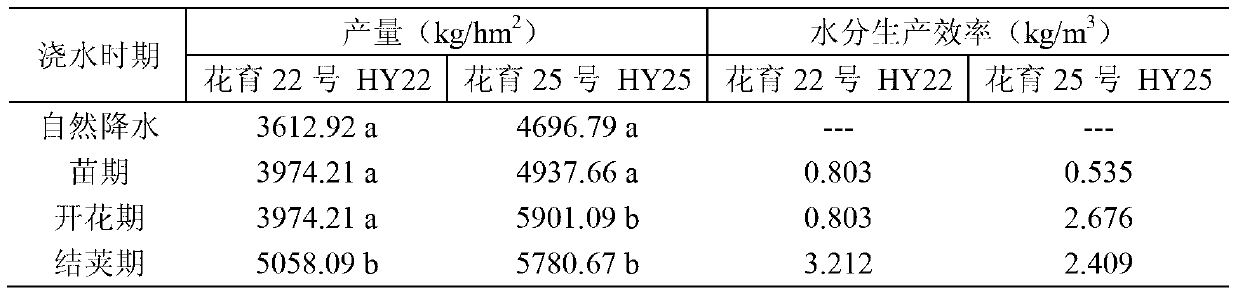
[0031] The experiment set up four water treatments: no watering during the whole growth period (that is, using natural precipitation), watering at the seedling stage, watering at the flower needle ...
Embodiment 2
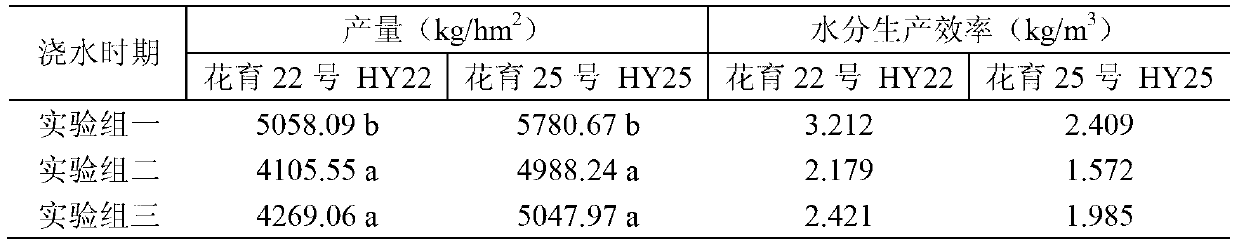
[0044]The materials used in the experiment were the same as in Example 1, and three experimental groups were established. Experimental group one, the irrigation method is the same as the pod-forming stage watering group of embodiment 1; Experimental group two, the irrigation method is basically the same as the pod-forming stage watering group of embodiment 1, the difference is: monitor the soil moisture content in the pod-forming stage When the soil water content in the 0-20cm soil layer drops below 27% of the field water holding capacity for 5 consecutive days, or when the soil water content of the sandy loam texture drops below 6.5% for 5 consecutive days, the irrigation will be carried out; experimental group 3, irrigation method Basically the same as the watering group at the pod stage of Example 1, the difference is: when the soil moisture content is monitored during the pod stage, when the soil moisture content in the 0-20cm soil layer drops to about 33% of the field wate...
Embodiment 3
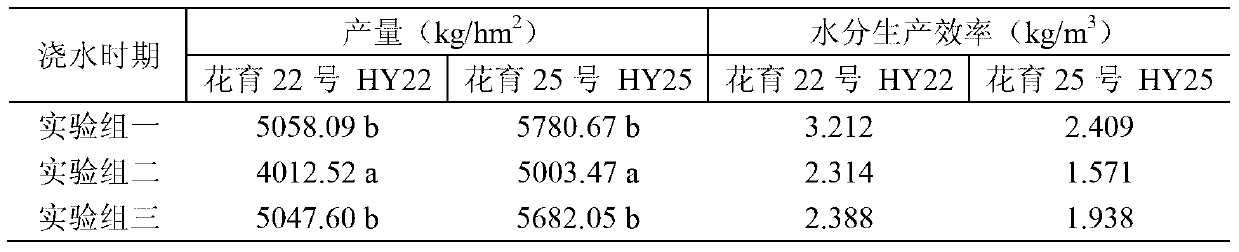
[0048] The materials used in the experiment were the same as in Example 1, and three experimental groups were established. Experimental group one, the irrigation method is the same as the watering group at the pod-forming period of Example 1; Experimental group two, the irrigation method is basically the same as the watering group at the pod-forming period of Example 1, the difference is that the amount of water to be controlled is 140m 3 / hm 2 ; Experimental group three, the control irrigation volume is 160m 3 / hm 2 . The experimental results are shown in Table 3.
[0049] Table 3 shows that the irrigation volume is controlled at 150, 160m 3 / hm 2 The two levels have no effect on the peanut yield, but the irrigation amount is 140m 3 / hm 2 Resulting in a decrease in peanut production; the irrigation volume is 140, 160m 3 / hm 2 The water use efficiency of the two levels of experimental groups is lower than that of the irrigation volume of 150m 3 / hm 2 experimental gr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com