Cell culture system
一种细胞培养、细胞的技术,应用在组织细胞/病毒的培养装置、胃肠细胞、动物细胞等方向,能够解决活微生物不能生长、未重现活肠等问题
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
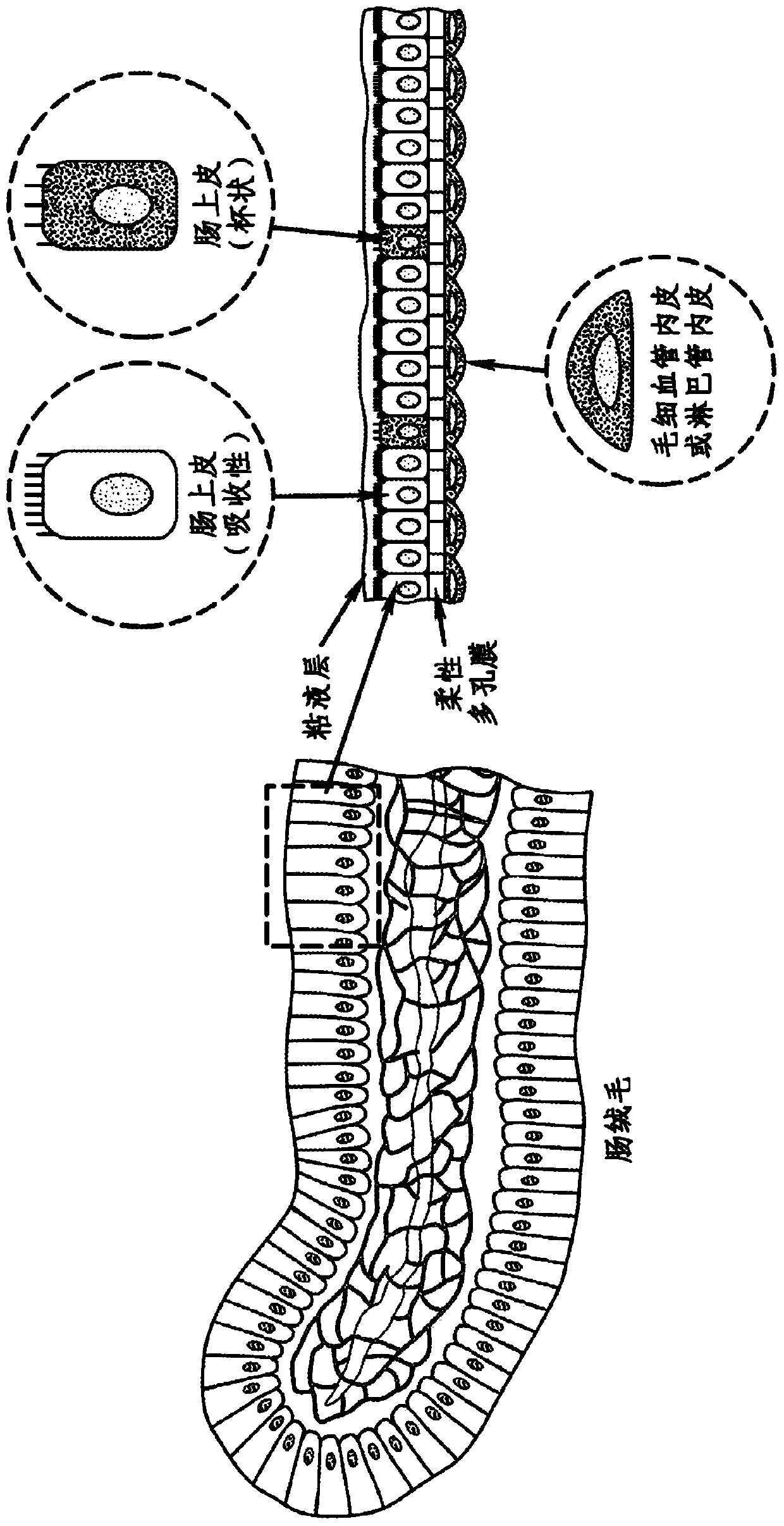
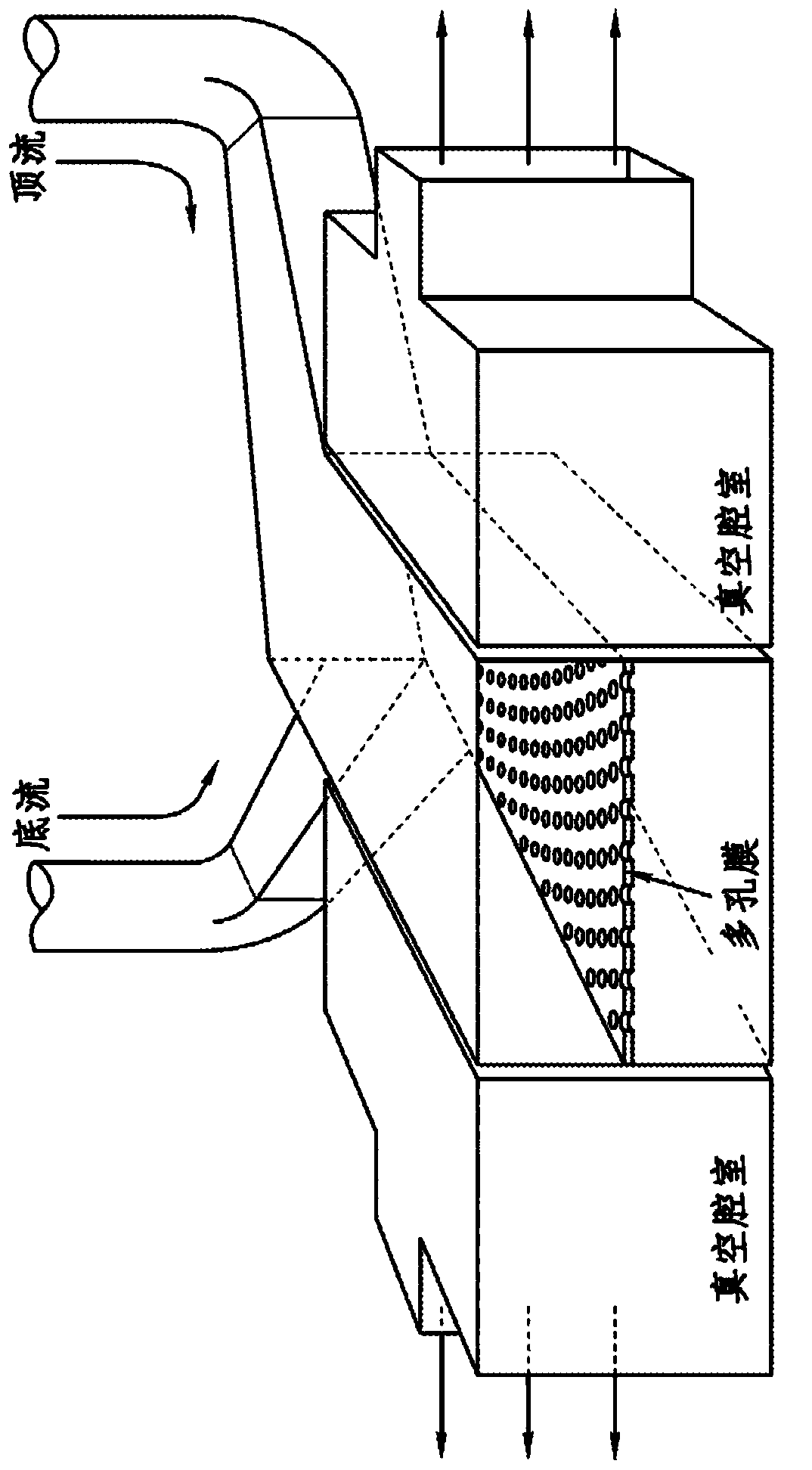
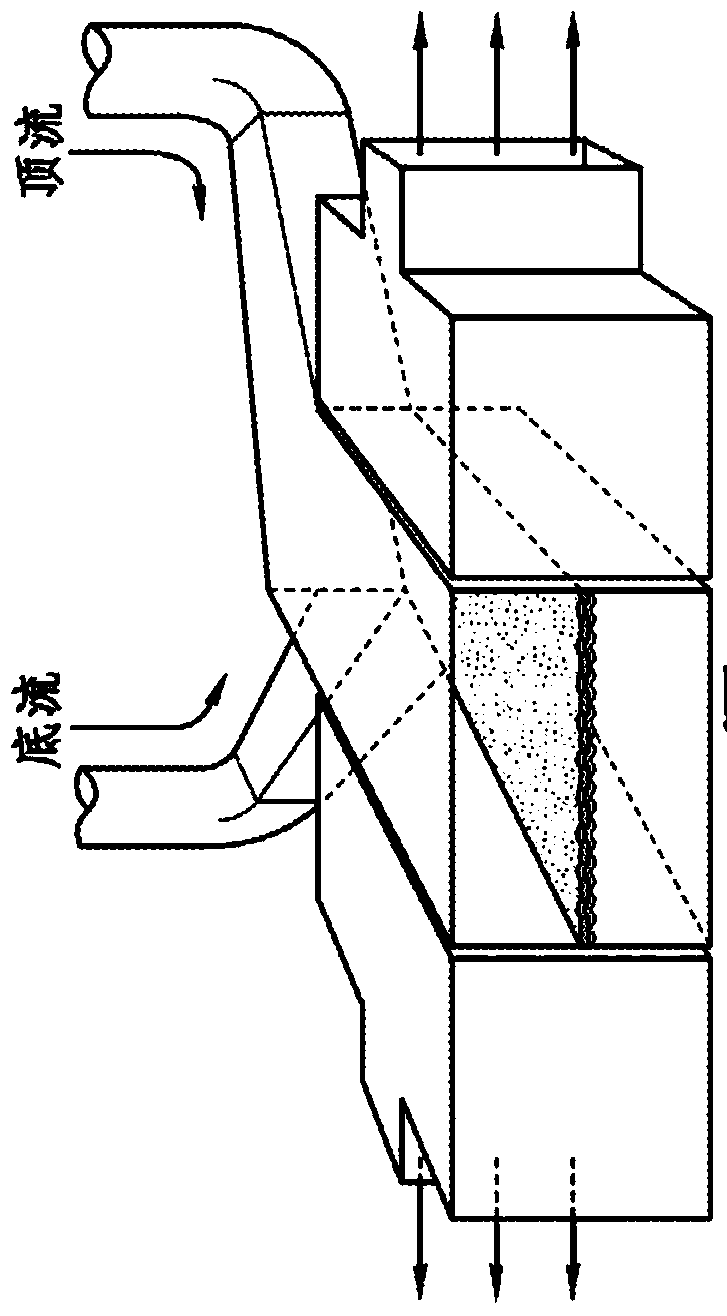
[0203] The "gut-on-a-chip" can be a microfluidic system containing a monolayer of cultured human intestinal epithelial cells and a monolayer of human endothelial cells from capillaries and / or lymphatic lacteal ducts coated with an extracellular matrix (ECM ) separated by a flexible porous membrane (which can undergo rhythmic mechanical twisting similar to intestinal motility (e.g., peristalsis and segmental movement)), which was designed to reproduce the tissue-tissue interface and microstructure of the human intestine ( figure 1 ). The goal of the "Gut on a Chip" project is to provide a robust, reproducible and predictable in vitro platform for human responses to orally delivered compounds, therapeutics, nutraceuticals, functional foods, pathogens and toxins. The gut-on-a-chip should be useful in a wide range of applications in the following fields: pharmacology, toxicology, drug development, drug delivery, drug metabolism, drug-drug interactions, drug bioavailability, drug ...
Embodiment 2
[0226] The development of living cell-based in vitro intestinal models (mimicking the mechanisms, structure, absorption, transport, and pathophysiological properties of the human intestine and its important microbial symbionts) could expedite drug development and potentially replace animal experiments. This paper describes one embodiment of a biomimetic "human intestine-on-a-chip" microdevice consisting of two microfluidic channels composed of porous flexible membranes coated with extracellular matrix (ECM). The membrane separates and is lined with human intestinal epithelial (Caco-2) cells to mimic the complex structure and physiology of the living intestine. Reconstruct the intestinal microenvironment through the following steps: make low shear stress (0.02dyne / cm 2 ) fluid at a low flow rate (30 μL / hr) flowed through the microchannel, and a periodic strain (10%; 0.15 Hz) imitating physiological peristaltic motion was applied. Under these conditions, the columnar epithelium...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com