Permanent-magnet brushless self-adaptive variable-speed drive motor
A variable-speed drive, permanent magnet brushless technology, applied in the direction of magnetic circuit rotating parts, electrical components, electromechanical devices, etc., can solve the problems of high manufacturing and use cost, large number of parts, complex mechanism, etc. The process is simple and the effect of increasing the volume of the motor
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
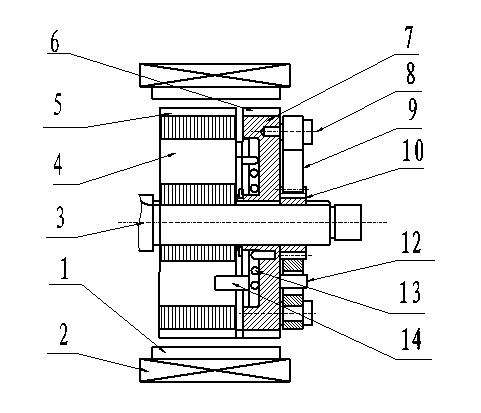
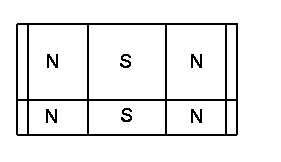
[0026] Example 1 see figure 1 and figure 2 , the main structure of the present invention is as follows: iron core 1 and winding 2 form the same stator part as the common brushless motor, the rotor shaft 3 is arranged in the center of the stator, the main rotor 4 is connected on the rotor shaft 3, and the permanent magnet 5 is arranged on its upper circumference, so that The polarity is periodically distributed according to N and S. The main rotor 4 needs to occupy most of the air gap of the stator, undertake the main function of energy conversion, and be fixedly connected with the rotor shaft 3, and output mechanical torque through the rotor shaft 3; on the rotor shaft 3 1. One end of the main rotor is the magnetic modulation rotor 7, and the magnetic modulation rotor 7 is provided with permanent magnets 6 in the circumferential direction, and the polarities are periodically distributed according to N and S. It can rotate a certain angle around the axis, change the magnetic ...
Embodiment 2
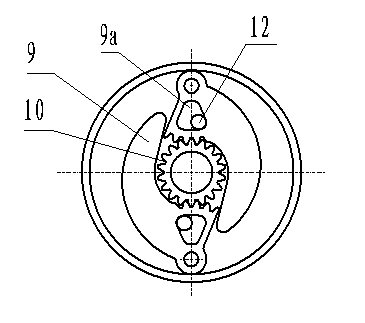
[0049] Embodiment 2 structure sees Figure 8 , In this example, the pin chute mechanism is used to replace the gear mechanism in Example 1, and the motion law is equivalent to the guide rod mechanism in mechanical design. The mechanism is described below, and the remaining motor parts are the same as in Embodiment 1. The centrifugal shoe 9 is connected to the magnetic adjustment rotor 7 through the shoe shaft 8. The centrifugal shoe 9 has a limit hole 11 and an elongated hole 14, and the pin 15 on the turntable 10 is embedded in the elongated hole to form a pin chute mechanism. The turntable 10 is fixed on the rotor shaft, the limit pin 12 is placed in the limit hole 11 and fixed on the end face of the speed-regulating rotor 7, so the magnetic-regulating rotor 7 can rotate along the turntable 10 in a certain range, and the other side of the speed-regulating rotor 7 A spring 13 is arranged on one side, and one end of its elastic force acts on the magnetizing rotor 7, and the o...
Embodiment 3
[0051] Embodiment 3 structure sees Figure 11 , which is characterized in that two magnetically adjustable rotors can also be used, which are symmetrically arranged at both ends of the main rotor, and jointly occupy the remaining part of the air gap. They have the same structure, but the rotational adjustment direction is symmetrical and opposite. This symmetrical design increases the cost. , but the adjustment process only changes the magnitude of the magnetic flux, does not change the phase of the magnetic flux, the magnetic flux waveform is better, and the control is simpler.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com