Breeding method for improving mutation frequency of silkworms
A technology of mutation frequency and silkworm, which is applied in animal husbandry and other fields, to achieve the effect of increasing the mutagenesis base, increasing the variety of mutations, and shortening the processing time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
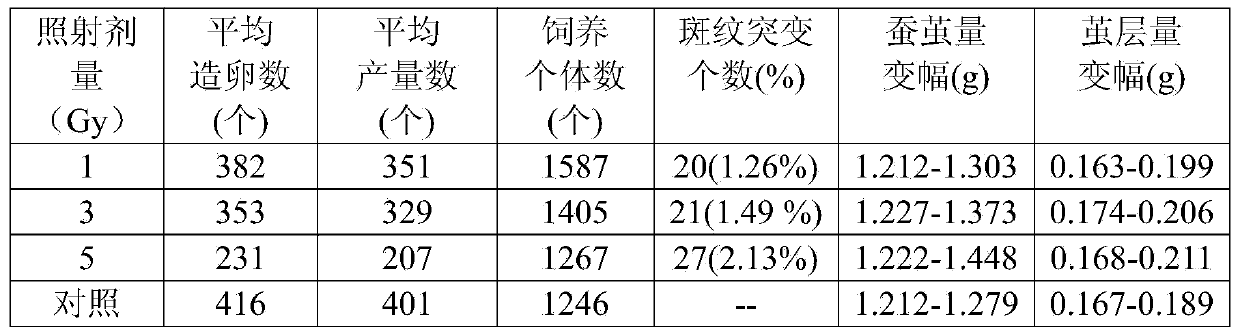
[0030] Example 1: 12 C 5+ Ion ray irradiated the 4th instar and 3rd day larval gonad of silkworm to produce mutants:
[0031] (1) Preparation for experimenting with silkworms
[0032] The hatched larvae of the silkworm variety (pnd) were reared with mulberry leaves, and the larvae on the 3rd day of the 4th instar were taken for irradiation (ie, as larvae to be treated).
[0033] (2) Local irradiation method
[0034] First, on a 2.0mm thick acrylic resin plate, make an 8×4mm hole (square hole) that matches the shape and size of the genital nest of the 4th instar 3rd day larvae (located on the back of the 5th abdominal segment); Align the existing part of the reproductive nest with the hole, and use scotch tape to fix the larva part on the experimental bench for irradiation, and use 18.3MeV / u carbon ion ( 12 C 5+ ) ray for irradiation, the underwater range of the carbon ion ray is about 1.1 mm, and the thickness of the resin plate is 2.0 mm, therefore, the carbon ion ray ca...
Embodiment 2
[0047] Example 2: 12 C 5+ Mutants Produced by Ion Ray Irradiation in the 4th Instar and 3rd Day Larva Gonad of Bombyx mori
[0048] (1) Preparation for experimenting with silkworms
[0049] The hatched larvae of the silkworm variety (pnd) were reared with mulberry leaves, and the larvae on the 3rd day of the 4th instar were taken for irradiation (ie, as larvae to be treated).
[0050] (2) Local irradiation method
[0051] First, on a 2.0mm thick acrylic resin plate, make an 8×4mm hole that matches the shape and size of the genital nest of the 4th instar 3rd day larvae (existing on the back of the 5th abdominal segment); Align the hole, and use scotch tape to fix the larva part on the experimental table for irradiation, and use 18.3MeV / u carbon ion ( 12 C 5+ ) ray for irradiation, the underwater range of the carbon ion ray is about 1.1 mm, and the thickness of the resin plate is 2.0 mm, therefore, the carbon ion ray cannot pass through the acrylic resin plate. The irradiati...
Embodiment 3
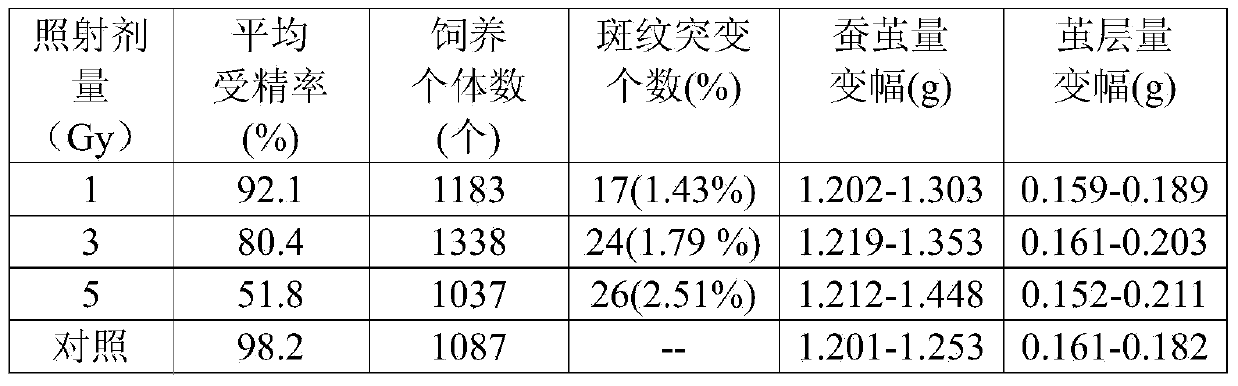
[0064] Example 3: 12 C 5+ Ion Irradiation of Mature Silkworm (Female) Gonads Produces Mutants
[0065] (1) Preparation for experimenting with silkworms
[0066] Larvae hatched from silkworm species (pnd) were reared on mulberry leaves, and mature female silkworms were taken for irradiation (i.e., as untreated silkworm larvae).
[0067] Remarks: When silkworms develop to the first day of the 5th instar, males and females can be identified, and then the males and females are reared separately. Ripe silkworm is a technical term for silkworms when they are mature, which means that the silkworm body is transparent and begins to spin silk. Female cooked silkworm refers to a cooked silkworm whose sex is female.
[0068] (2) Local irradiation method
[0069] First, on a 2.0mm thick acrylic resin plate, make a 12×6mm hole that matches the shape and size of the mature silkworm reproductive nest (existing on the back of the fifth abdominal segment); align the reproductive nest with ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com