Nickel zinc ferrite soft magnetic material and preparation method thereof
A technology of nickel-zinc ferrite and soft magnetic materials, applied in the field of magnetic materials, can solve the problems of inability to meet NFC and FRID, etc., and achieve high magnetic permeability, improve magnetic properties, and improve magnetic properties.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0018] The present invention also provides a preparation method of the nickel-zinc ferrite soft magnetic material, comprising the following steps:
[0019] S1. Weigh and mix the raw materials corresponding to the main phase in proportion, sieve after ball milling and drying, and obtain the main phase calcined material after pre-calcination;
[0020] S2. Add the raw materials corresponding to the auxiliary phase in proportion to the main phase calcined material obtained in S1, and sieve after ball milling and drying;
[0021] S3. Molding the mixed system obtained in S2, and transferring it to a furnace for sintering to obtain the nickel-zinc ferrite soft magnetic material.
[0022] In the present invention, when preparing the main phase, the raw materials corresponding to the main phase are mixed first, and then ball milled. The steps and technical parameters of the ball milling are well known to those skilled in the art, and there is no special requirement in the present inve...
Embodiment 1-10
[0029](1) Weigh the raw materials of the main phase according to the main phase formula shown in Table 1, mix them, and then perform ball milling until the average particle size of the system is 160 μm, sieve after drying, and transfer to an air furnace at 850±10°C Calcined for 2 hours to obtain the main phase calcined material.
[0030] (2) Add auxiliary phase raw materials to the main phase pre-fired material according to the auxiliary phase formula shown in Table 1, mix evenly and perform ball milling until the average particle size of the system is 160 μm, sieve after drying, and then add binder PVA to press molding Obtain a green body; transfer the green body into an air furnace, sinter at 950±10°C for 2 hours, and obtain nickel-zinc ferrite soft magnetic materials after cooling, respectively denoted as S1-S10.
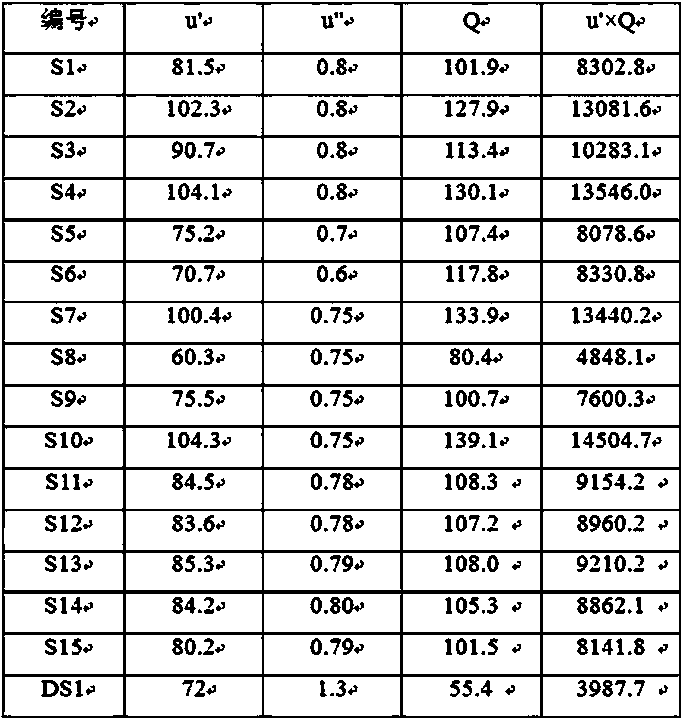
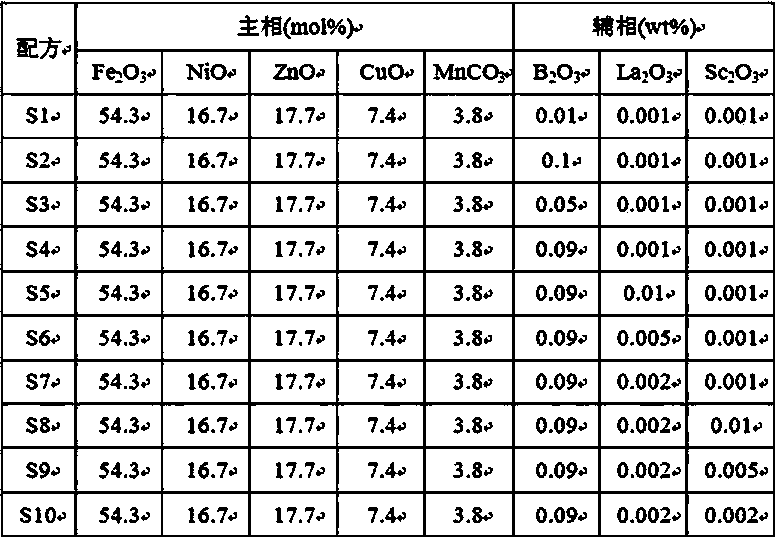
[0031] Table 1
[0032]
[0033] Note: The content (mol%) of each component in the main phase formula in Table 1 is calculated based on the total molar conte...
Embodiment 11-15
[0035] The same steps as in Example 1 were used to prepare the main phase calcined material, and then the auxiliary phase raw materials were added according to the auxiliary phase formula shown in Table 2, and ball milling was carried out after mixing evenly until the average particle size of the system was 160 μm. After drying, sieve, Then add binder PVA and press to form a green body; transfer the green body into an air furnace, sinter at 950±10°C for 2 hours, and obtain nickel-zinc ferrite soft magnetic materials after cooling, which are respectively marked as S11-S15.
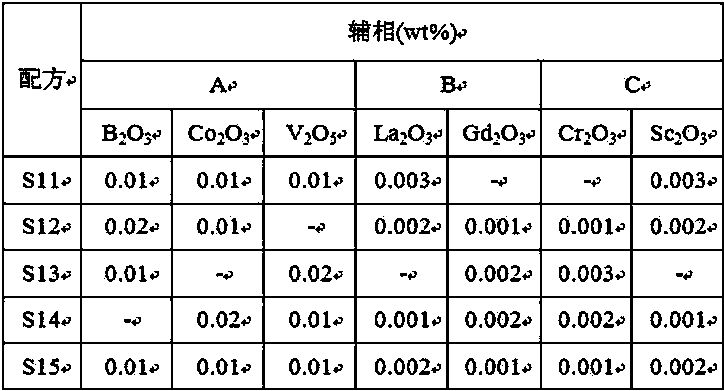
[0036] Table 2
[0037]
[0038] Note: The content (wt%) of each component in the auxiliary phase formula in Table 2 is based on the total mass content of the nickel-zinc ferrite soft magnetic material; the main phase composition in Table 2 is: Fe 2 o 3 54.3mol%, NiO16.7mol%, ZnO17.7mol%, CuO7.4mol% and MnCO 3 3.8mol%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com