High temperature semitransparent material spectrum direction apparent emissivity inversion measuring device and method
A technology of translucent material and apparent emissivity, which is used in measurement devices, analysis materials, material analysis by optical means, etc., can solve the problems of low temperature upper limit, low measurement accuracy, and measurement dead angle.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
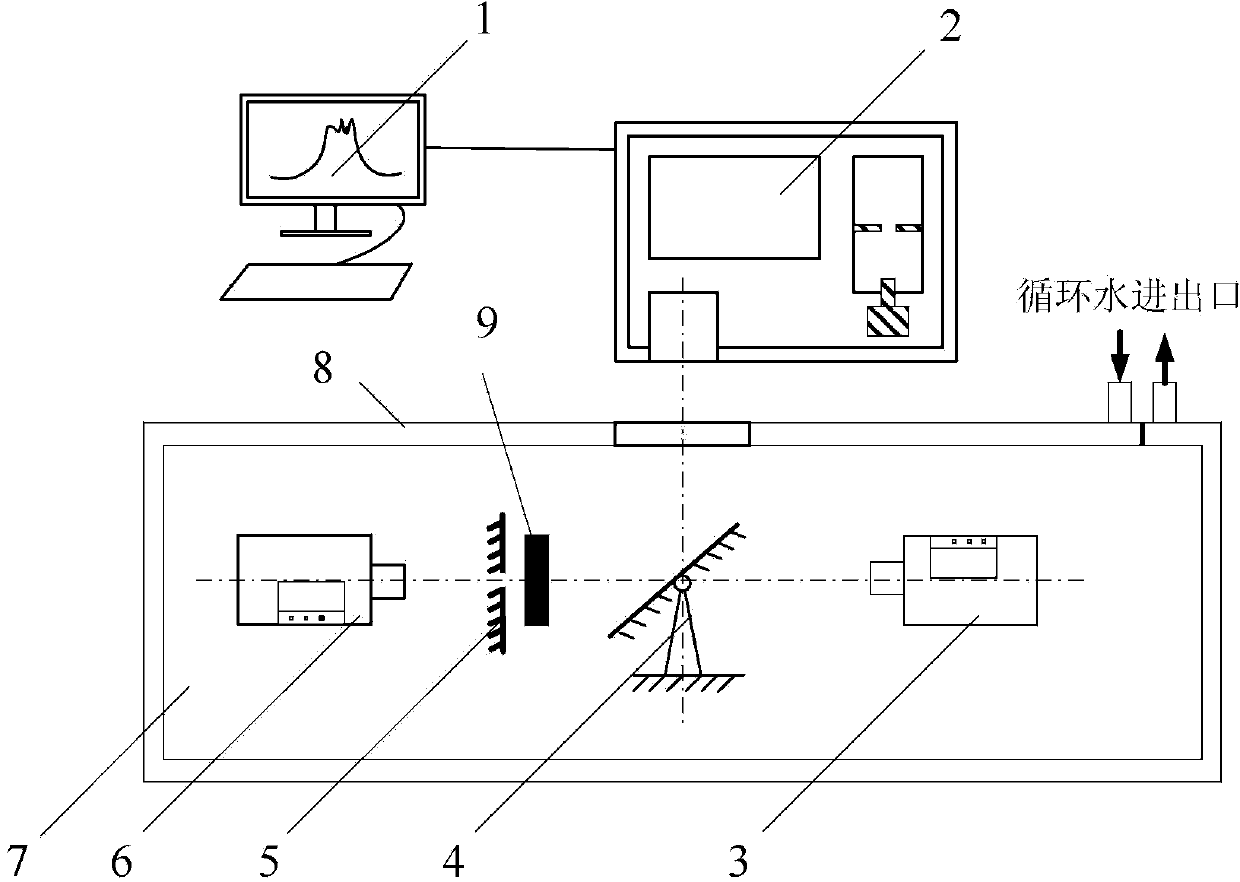
[0114] Specific implementation mode 1. Combination figure 1 Describe the specific implementation mode, a high-temperature translucent material spectral direction apparent emissivity inverse measurement device, which includes a data processing system 1, a Fourier transform infrared spectrometer 2, a vacuum tank 7, and a blackbody light source placed in the vacuum tank 7 A6, rotatable reflector 4, blackbody radiation heater 5 and blackbody light source B3; Blackbody radiation heater 5 and rotatable reflector 4 are positioned between blackbody light source A6 and blackbody light source B3, and blackbody radiation heater 5 is positioned at blackbody light source A6 and Between the rotatable reflectors 4; the blackbody radiation heater 5 is used for radiative heating of the translucent test piece 9 to be tested to keep both surfaces of the translucent test piece 9 being translucent boundary conditions, and to make the translucent test piece 9 The radiation energy projected onto the...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0115] Specific embodiment two, combine figure 1 To illustrate the specific implementation, the outer wall of the vacuum tank 7 is provided with a circulating water thermostat sleeve (8). Other compositions and connections are the same as in the first embodiment.
[0116] Place the test piece 9 and its heating device in the vacuum tank 7 to avoid the influence of natural convection on the temperature field of the test piece; use radiation heating to keep both surfaces of the test piece are translucent boundary conditions, while the radiation heater 5 In order to approximate a black body, all the radiant energy projected on the heater through the translucent test piece can be absorbed; the outside of the vacuum tank 7 is cooled by circulating water to maintain a constant temperature in the tank, avoiding the influence of background stray radiation on the measurement.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0117] Specific embodiment 3. Based on the specific embodiment 1, the method for inversely measuring the apparent emissivity of the spectral direction of the high-temperature translucent material is realized by the following steps:
[0118] Step 1. Turn on the incident blackbody light source (blackbody light source A6), and use the Fourier transform infrared spectrometer to collect the spectral radiation signal data of the blackbody light source and record it as S 1 ;
[0119] Step 2. Place the sample in the test piece rack, turn on the radiation heater, heat the sample to the predetermined test temperature, keep the temperature stable, use the Fourier transform infrared spectrometer to collect data and record it as S 2 , the obtained data S 2 Including: ①The remaining signal S after the spectral radiation signal of the black body light source passes through the translucent specimen 1 ′; ②The spectral radiation signal S of the translucent specimen itself s ; ③ The remaining...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com